fx-CG500 Quick Start Guide 3
If an object, such as a ball, is dropped from a initial height, c, the height, h, in feet, as a
function of time, t, in seconds, can be modeled by h = -16t
2
+ c.
If the object is tossed upwards with an initial velocity, v, then the model becomes
h = -16t
2
+ vt + c. These models ignore air resistance.
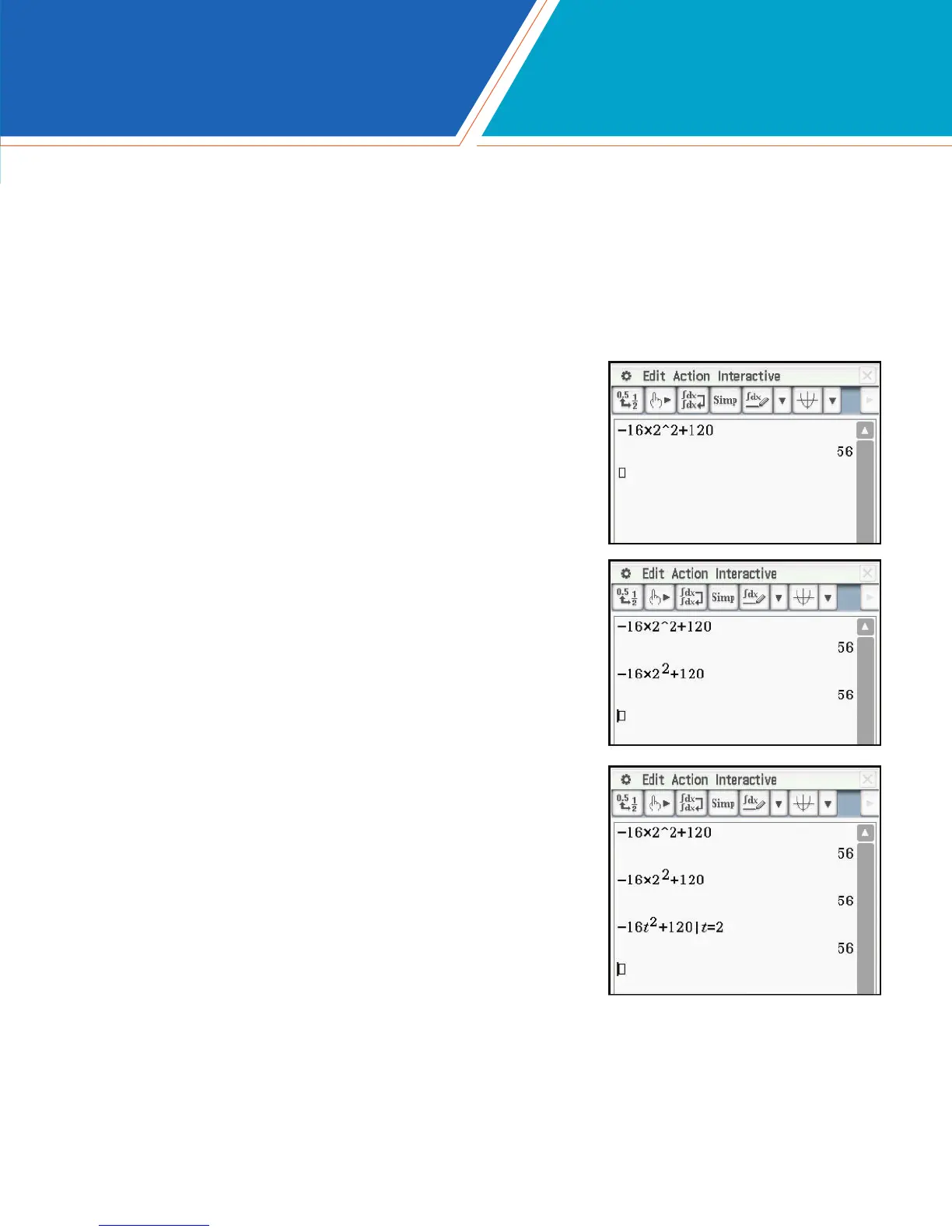
1. If a ball is dropped from a height of 120 feet,
compute the height after 2 seconds.
Tap M for the Main menu.
Press z16*2^2+120E.
For a more mathematical display, the raised exponent
template can be found on the Math1 Keyboard.
Press z16*2kO2:
+120E.
This expression can also be evaluated using a variable for
substitution. A command in the form expression | variable =
value means evaluate the expression with the given value(s)
substituted for the variable(s).
Press z16k_[)O2:
+120-U_[=2E.
MAIN MENU
 Loading...
Loading...











