hp calculators
HP 12C Net Present Value
hp calculators - 2 - HP 12C Net Present Value - Version 1.0
Cash Flow and NPV calculations
Cash flow analysis is an extension of the basic TVM concepts applied to compound interest problems when payments
occur in regular periods and do not have the same value. Any financial investment can be represented as an initial
investment of money and a series of cash flows that occur in regular periods of time. Each flow of money can be positive
(received) or negative (paid out) and considered as a cash flow. Common cash flow problems usually involve the
calculation of the Internal Rate of Return (IRR) or the Net Present Value (NPV).
The NPV expresses the amount of money resulting from the summation of the initial investment (CF
0
) and the present
value of each anticipated cash flow (CF
j
) calculated to the time of the initial investment. The IRR is the discounted rate
applied to all future cash flows that cause NPV = 0.
The expression that calculates the Net Present Value is:
()() ()
j
j
2
2
1
1
0
111 i
CF
i
CF
i
CF
CFNPV
+
++
+
+
+
+= L
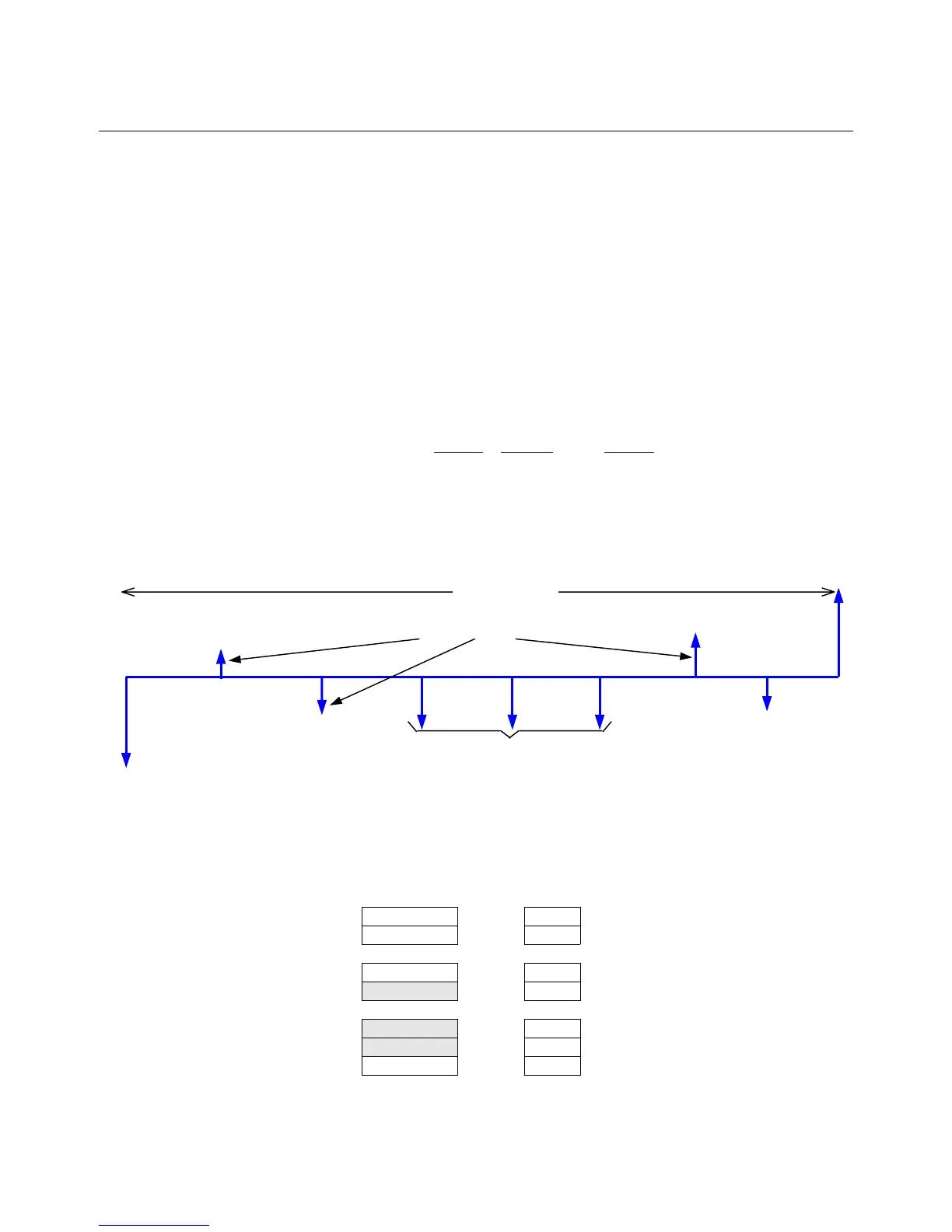
Figure 1
Cash flow diagrams
The cash flow diagram in Figure 1 illustrates one of the many possible situations that can be handled by the HP12C.
Figure 2
The HP12C cash flow approach
In the HP12C each cash flow amount is stored in its corresponding register in memory. For each cash flow amount there
is a related register to store the number of consecutive occurrences of this amount. This approach is shown below:
Registers Cash flow N
j
R
0
CF
0
N
0
R
1
CF
1
N
1
...
... ...
R
6
CF
6
N
6
R
7
CF
7
N
7
...
... ...
R
.8
CF
18
N
18
R
.9
CF
19
N
19
FV
CF
20
N
20
Figure 3
gJ Initial Cash Flow
gK Last Cash Flow
gK Intermediate Cash Flow
ga Number of consecutive occurrences of CFj
Composition Period

 Loading...
Loading...





