hp calculators
HP 33S Normal distribution applications
Practice solving problems involving the normal distribution
Example 1: Find Q(x) for a Z value of +1. Make sure the HP 33S is in RPN mode.
Solution: With the input value given as a Z-score, we're dealing with the standardized normal distribution having a
mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. Press ¹ä to enter RPN mode.
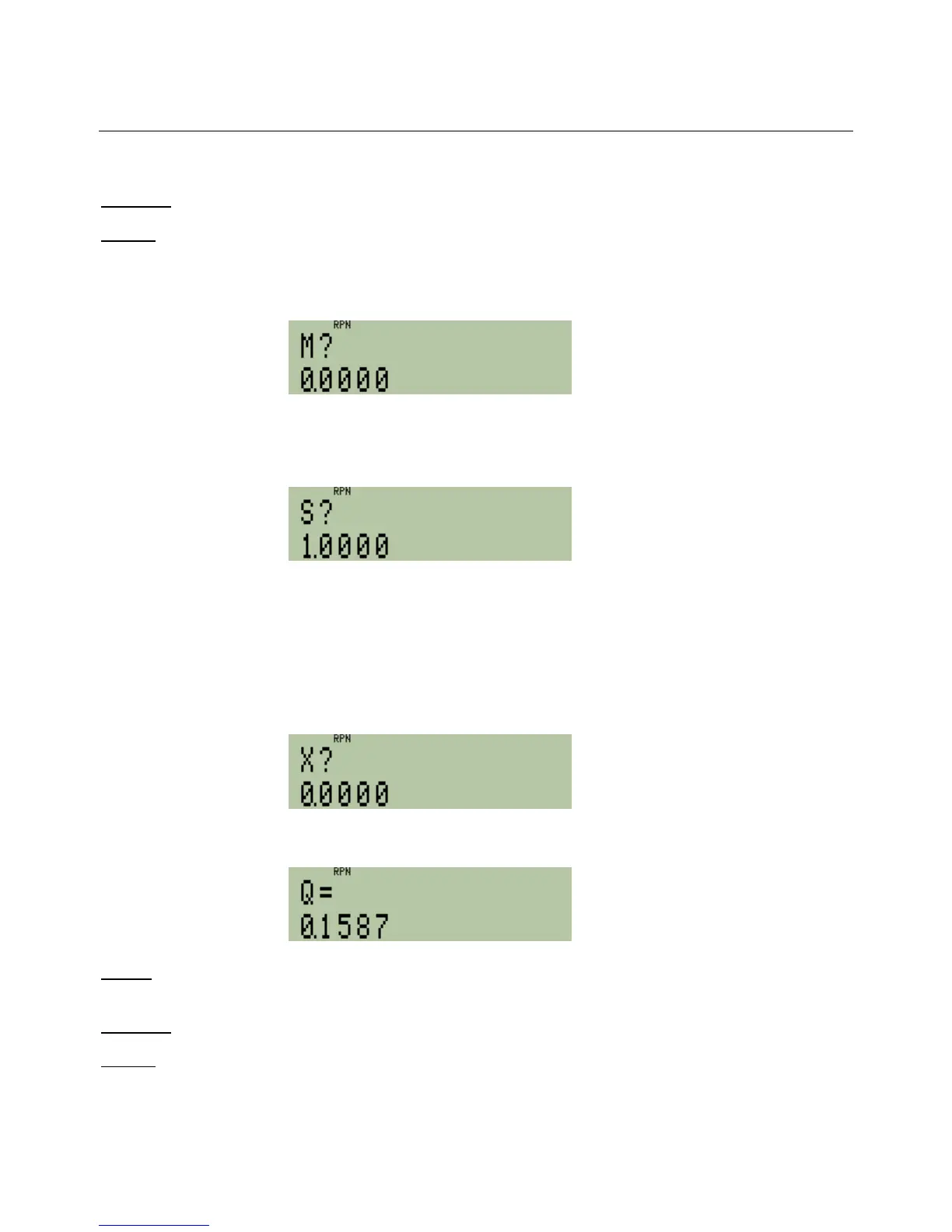
In RPN mode: tS
Figure 2
Since we are dealing with a standardized normal distribution, the mean should stay equal to 0.
In RPN mode: ¥
Figure 3
Since we are dealing with a standardized normal distribution, the standard deviation is equal to 1.
In RPN mode: ¥
Now, calculate Q(x) for an x value of 1 by pressing:
In RPN mode: tD
Figure 4
In RPN mode: 1¥
Figure 5
Answer: The upper tail probability for the standardized normal distribution with a value of x equal to +1 is 0.1587.
This means that only 15.87% of all values would be larger than a Z-score of +1.
Example 2: Find Q(x) for a Z value of -1. Make sure the HP 33S is in RPN mode.
Solution: With the input value given as a Z-score, we're dealing with the standardized normal distribution having a
mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1. Press ¹ä to enter RPN mode.
hp calculators - 3 - HP 33S Normal distribution applications - Version 1.0

 Loading...
Loading...





