# 45466K003Page 4
Unconfined Space
An unconfined space is defined as “a space whose
volume is more than 50 cubic feet per 1000 BTU per hour
of the combined input rating of all appliances installed in
that space.” When a furnace is installed in an unconfined
space in a building, it can be assumed that the infiltration
will be sufficient to supply the required air. If the furnace is
installed in a ventilated attic or crawl space, it is assumed
that the infiltration is sufficient to supply the required air.
However, in a building of unusually tight construction,
additional outdoor air should be provided.
Confined Space
A confined space is defined as “a space whose volume is
less than 50 cubic feet per 1000 BTU per hour of the
combined input rating of all appliances installed in that
space.”
If the furnace is installed in a confined space within the
building and combustion air is taken from a heated space,
the combustion air and ventilating air must enter and leave
the space through two permanent openings of equal area.
One opening shall be located within 12" of the ceiling and
the other within 12" of the floor, each having a free area of
1 square inch per 1000 BTU/HR of total input rating of all
appliances within the space and not less than 100 square
inches each.
If the furnace is installed in a space within a building of tight
construction, makeup air must be supplied from outdoors. In
this case, one opening shall be within 12" of the ceiling and
one opening within 12" of the floor. If combustion ducts are
vertical, each opening shall have a free area of 1 square
inch per 4000 BTU/HR of the total input rating of all appli-
ances within the enclosure. If horizontal combustion ducts
are run, 1 square inch per 2000 BTU/HR is required.
Contaminated Combustion Air
Excessive exposure to contaminated combustion air will
result in safety and performance related problems. The
recommended source of combustion air is outdoor air.
However, the use of indoor air in most applications is
acceptable if the following guidelines are followed:
1. If the furnace is installed in a confined space, it is
recommended that the necessary combustion air come
from the outdoors by way of an attic, crawl space, air
duct, or direct opening.
2. If indoor combustion air is used, there must be no
exposure to the substances listed in item 5.
3. All provisions for indoor combustion air must meet the
requirements for combustion air indicated in the
National Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1/NFPA 54
(latest edition), and/or any applicable local codes. In
Adequate provisions for combustion air and ventilation of
furnace must be made. Refer to Section 5.3, “Air for
Combustion and Ventilation,” of the National Fuel Gas
Code, ANSI Z223.1/NFPA54 (latest edition), Sections 7.2,
7.3, or 7.4 of CSA B149.1 Natural Gas and Propane
Installation Codes (latest editions), or applicable provi-
sions of the local building codes.
Counterflow Models section on page 15 for more
information on using the special base assembly.)
When a counterflow unit is installed on a combustible
floor, 1" clearance must be provided between the supply
duct and the floor.
Combustion and Ventilation Air
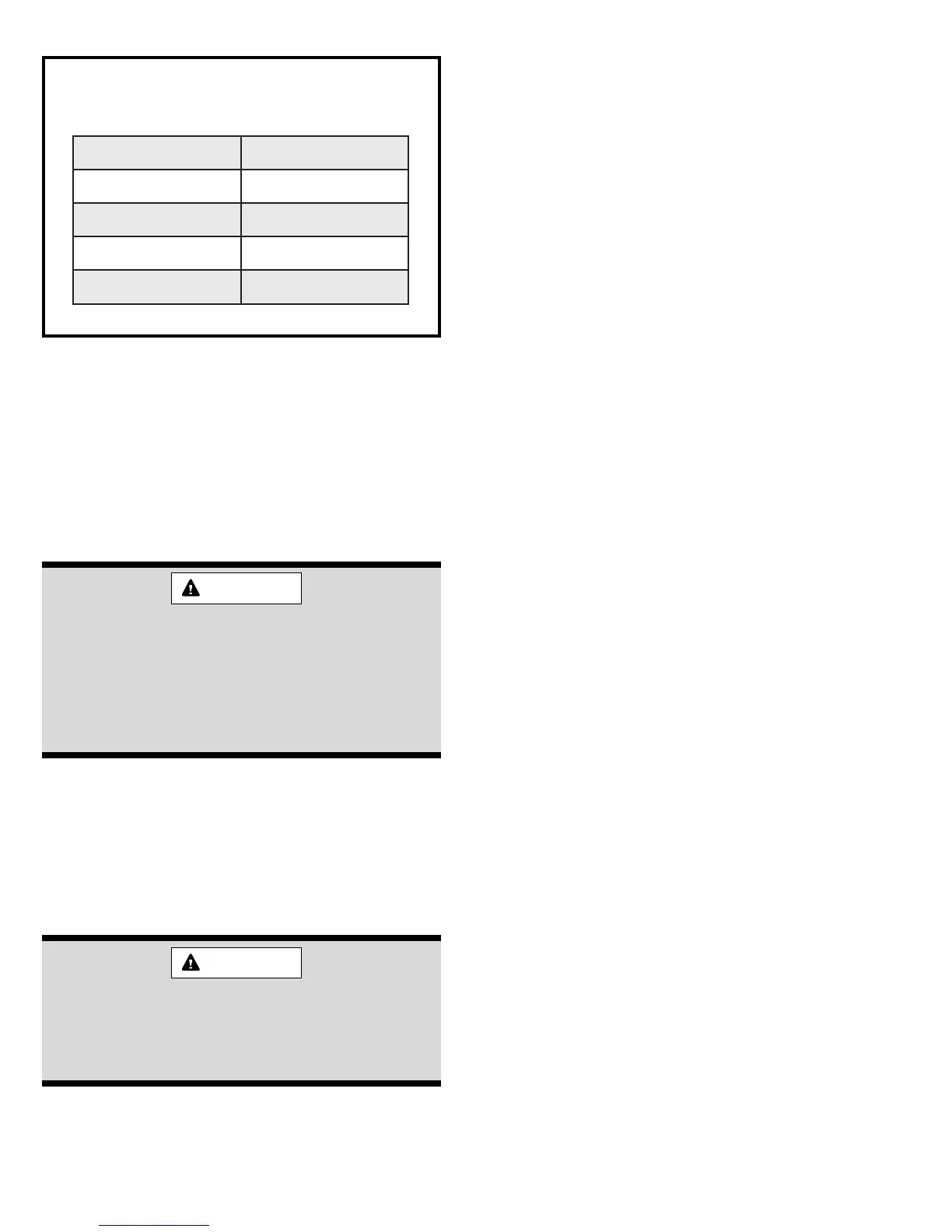
Table 1
Minimum Clearances to Combustibles
sediStinU "0
tinUforaeR"0
tinUfotnorF "2
epiPeulF"0
poTmunelP "1
Insufficient combustion air can cause head-
aches, nausea, dizziness, or asphyxiation.
When considering combustion air require-
ments, enough air must also be provided to
meet the needs of all fuel-burning appliances
and exhaust fans.
WARNING
Air openings in the front of the furnace must
be kept free of obstructions. Any obstruction
may cause improper operation that can result
in a fire hazard or carbon monoxide injury.
WARNING
 Loading...
Loading...