200 Alphabetical Listing
zeros()
Catalog >
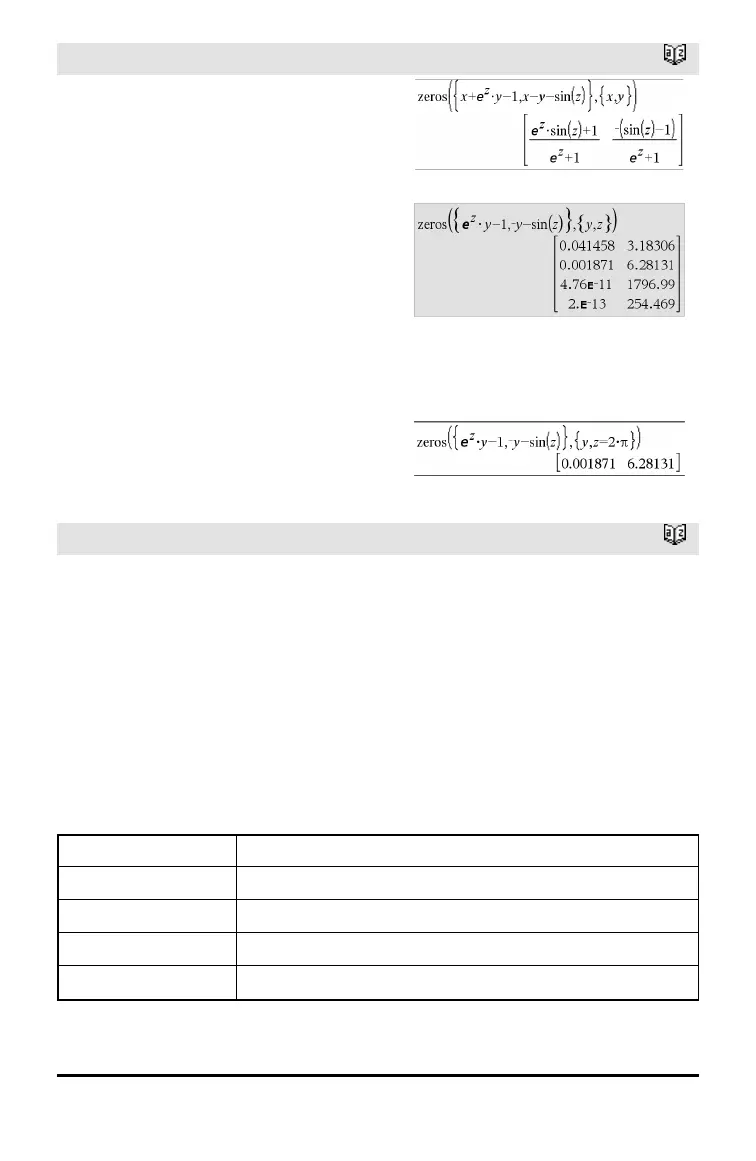
If you do not include any guesses and if any
expression is non-polynomial in any variable
but all expressions are linear in the
unknowns, zeros() uses Gaussian
elimination to attempt to determine all real
zeros.
If a system is neither polynomial in all of its
variables nor linear in its unknowns, zeros()
determines at most one zero using an
approximate iterative method. To do so, the
number of unknowns must equal the
number of expressions, and all other
variables in the expressions must simplify
to numbers.
Each unknown starts at its guessed value if
there is one; otherwise, it starts at 0.0.
Use guesses to seek additional zeros one by
one. For convergence, a guess may have to
be rather close to a zero.
zInterval
Catalog >
zInterval σ,List[,Freq[,CLevel]]
(Data list input)
zInterval σ,v,n [,CLevel]
(Summary stats input)
Computes a z confidence interval. A
summary of results is stored in the
stat.results variable. (See page 172.)
For information on the effect of empty
elements in a list, see “Empty (Void)
Elements,” page 232.
Output variable Description
stat.CLower, stat.CUpper Confidence interval for an unknown population mean
stat.x Sample mean of the data sequence from the normal random distribution
stat.ME Marginof error
stat.sx Sample standard deviation

 Loading...
Loading...