Instruction Manual Supplement
D104299X012
DVC6200 SIS
October 2018
19
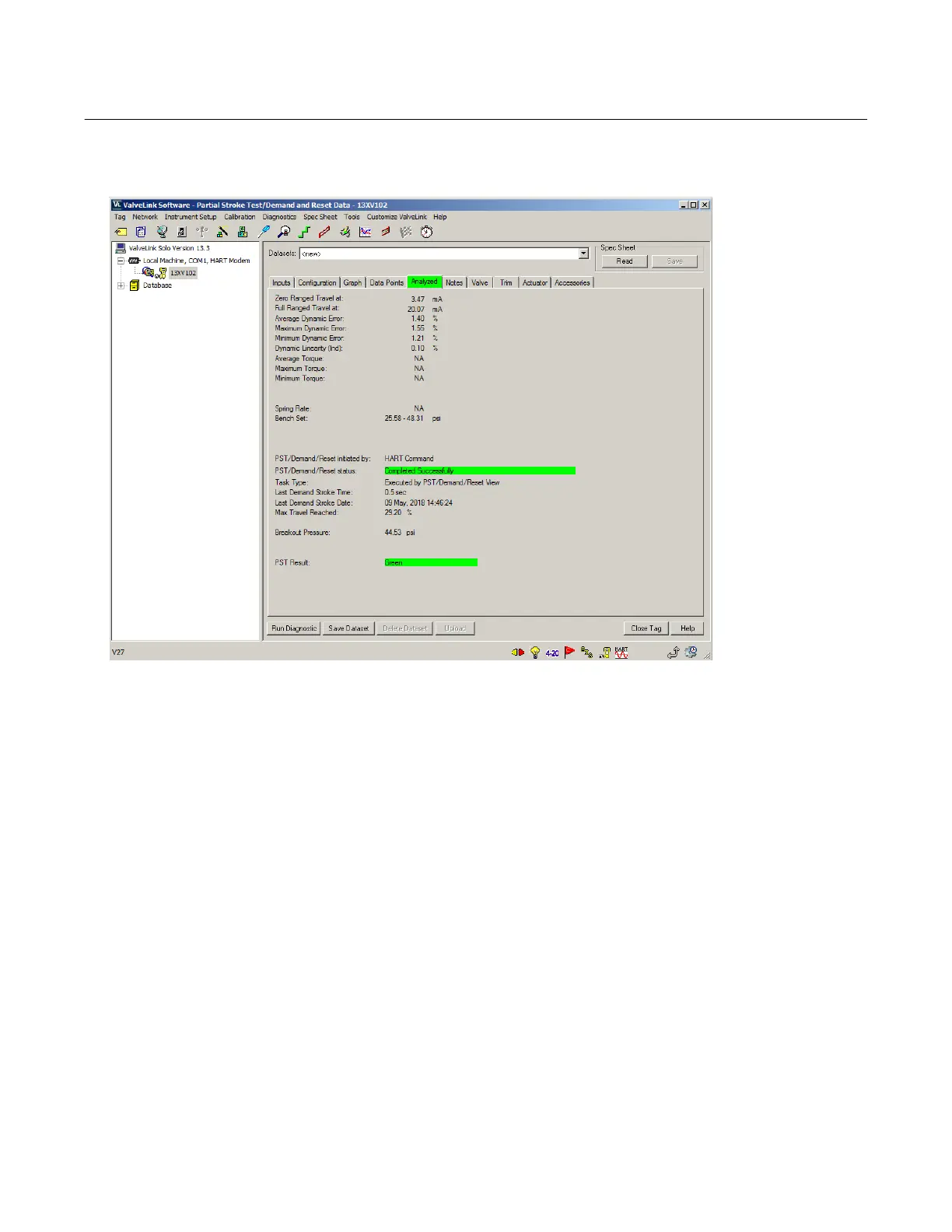
Figure 27. PST Analyzed Data with Short Duration PST Disabled
Select a PST style, either with or without Short Duration PST, and standardize on that style, as the data may be difficult
to compare between the two styles. If the desire is to minimize the amount of time the valve is away from the normal
end, then enabling Short Duration PST is recommended. If the amount of time away from the normal end is not a
concern, then disabling Short Duration PST will cause the set point to pause at the end of the outgoing stroke for the
travel to catchup to the set point. The results of the test with the Short Duration PST disabled will be similar to the PST
as offered in earlier versions of SIS instruments.
Partial Stroke Test Information
A valve stroke test is the process of taking the valve from the normal end to another target position at a preconfigured
ramp rate before returning to the normal end while gathering data. The data is analyzed to evaluate the condition of
the valve assembly against a set of user defined thresholds. A valve stroke test is only run if everything is normal in the
instrument. A safety demand signal will always take precedence over a valve stroke test.
Test Start Point defines the normal end of the valve. The valve needs to be at this end for a PST to be initiated. When a
PST is initiated the valve will be move from this end to the target travel and then back. See figure 28.
Travel Target Movement is the percentage of the calibrated travel span that the valve moves away from its normal
operating end of travel towards its tripped end of travel during the test. The default value is 10%. See figure 28.
Outgoing Ramp Rate is the rate at which the valve will move during the outgoing stroke of the Partial Stroke test. The
default value is 0.25%/second. The outgoing stroke is from the normal end to the PST target. See figure 29.

 Loading...
Loading...











