MX-7711-02
3. Key system differences
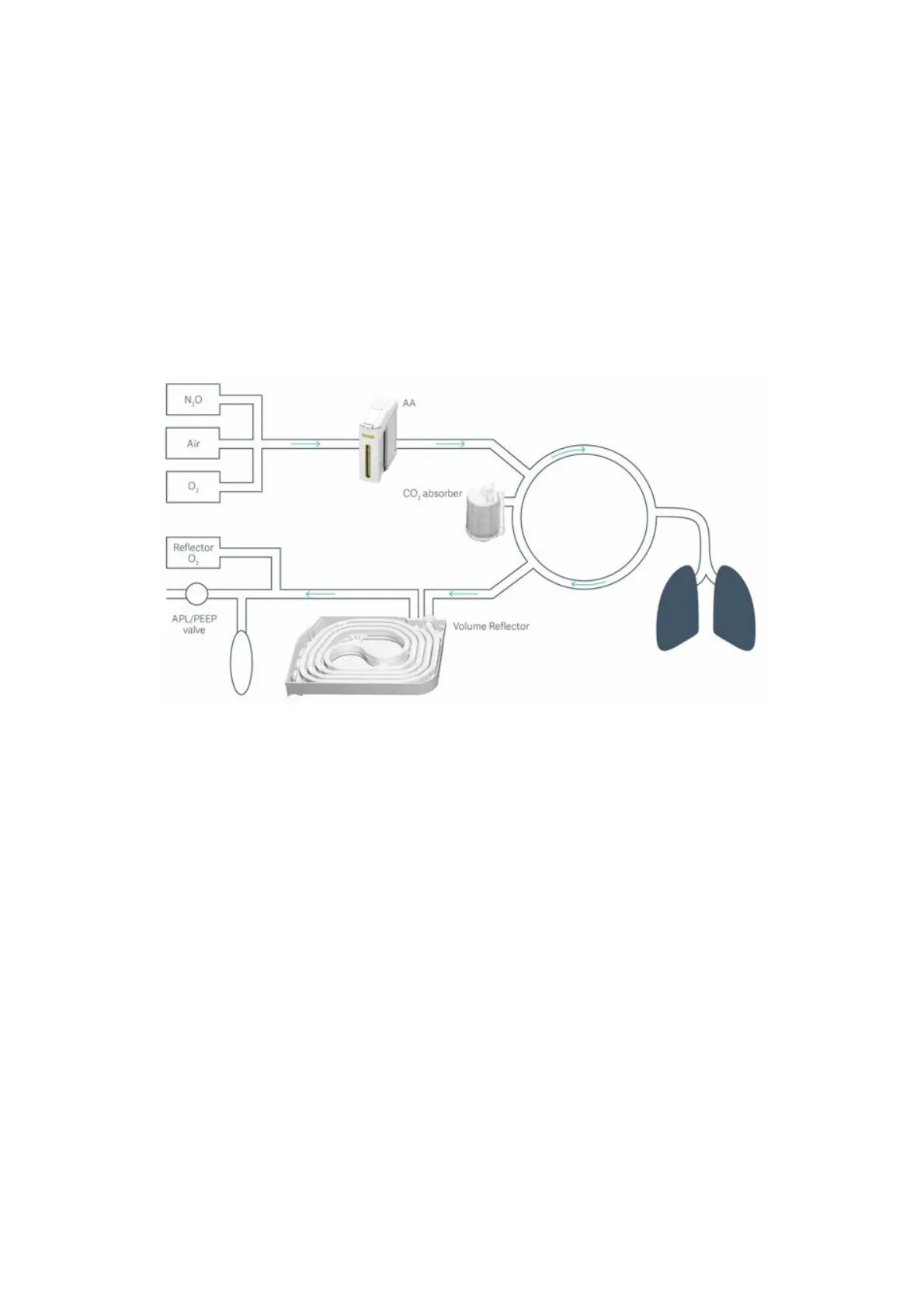
Rebreathing
The most significant difference between intensive care ventilators anesthesia devices is that
anesthesia ventilators are based on a rebreathing system and adjustable fresh gas flows. This
means that depending on the set fresh gas flow, expired gases will be rebreathed.
If non-rebreathing is desired, we recommend the user to set the fresh gas flow higher than the
patients expired minute volume. If the user to set the fresh gas flow to 20 l/min, the system is
designed to automatically adjust the fresh gas flow to just above the patient’s minute volume and
thus guarantee a non-rebreathing system.
If the fresh gas flow is set to less than expired minute volume, part of the expired gas will be
returned to the inspiratory limb.
In a circlular system, expiratory gas is purified in the CO
2
absorber before it is mixed with fresh gas
and delivered to the patient. This requires the use of a CO
2
absorber to prevent high CO
2
levels in
the circuit.
Please be aware that if high fresh gas flows are used, the CO
2
absorber will not be part of the
breathing circuit and thus not be consumed.
When the gas passes through the soda lime, CO
2
is absorbed and water and heat are produced. A
higher rebreathing fraction could thus humidify and warm inspiratory gases and may make active
humidification redundant.

 Loading...
Loading...