Do you have a question about the metso automation neles NP726 and is the answer not in the manual?
| Output Signal | Pneumatic |
|---|---|
| Supply Pressure | 1.4 - 7 bar (20 - 100 psi) |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to +85°C (-40°F to +185°F) |
| Enclosure Rating | NEMA 4X, IP66 |
| Housing Material | Aluminum |
Basic information on the positioner.
Explains the force balance principle of operation.
Describes the ID plate and its information.
Lists key technical parameters like signal ranges and pressures.
Lists certifications like CENELEC, CSA, FM.
Guidelines for recycling and disposal.
Important safety warnings and cautions.
General notes on mounting positioners with actuators.
Steps for mounting S1 positioner on VDI/VDE 3845 actuators.
Steps for mounting S2 positioner on Series B actuators.
Instructions for combining positioner with limit switch.
Guidance on connecting air supply and signal lines.
Explains the function and setting of the changeover piece.
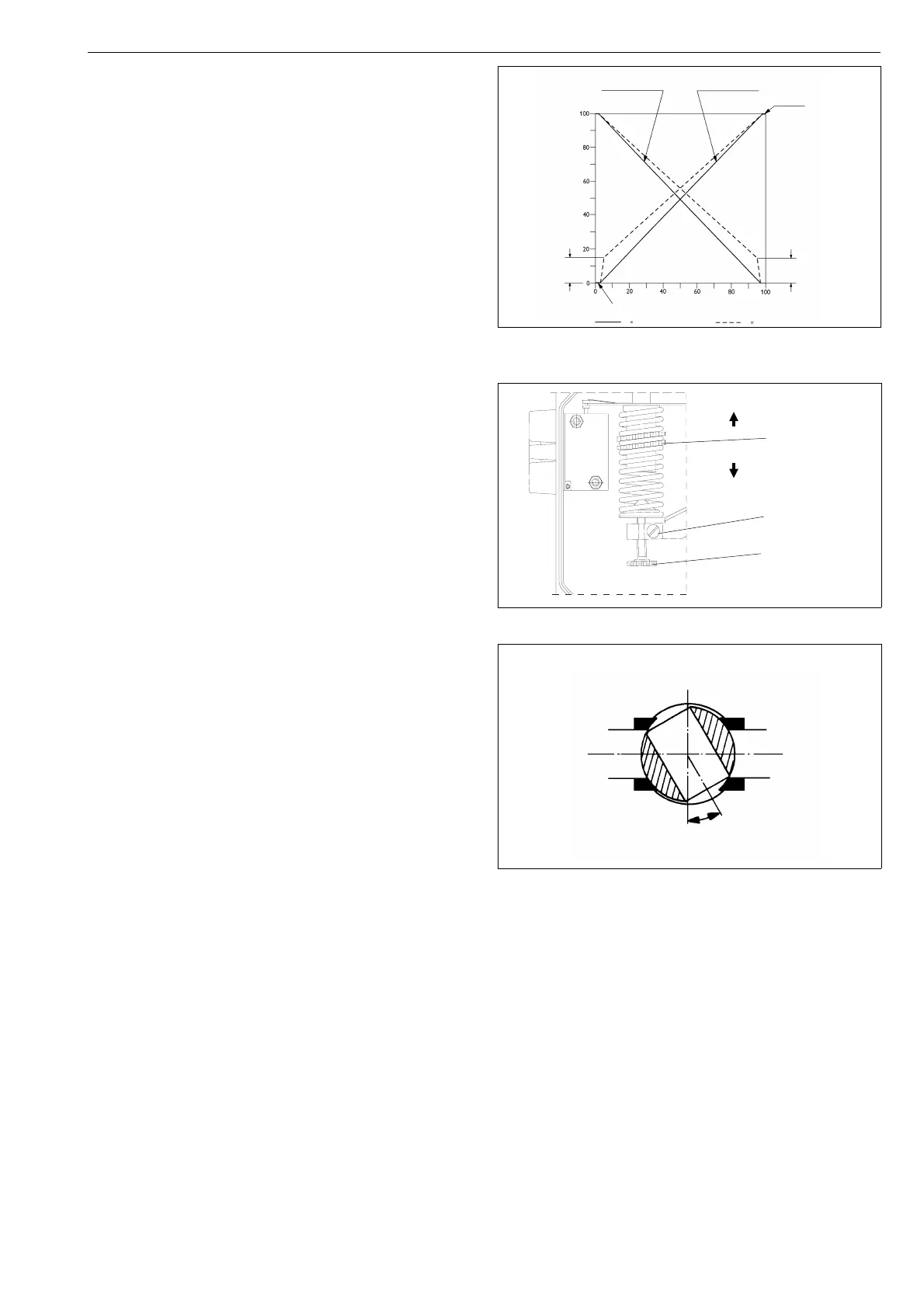
Describes the cam plate markings and signal ranges.
Steps for setting the changeover piece position.
Notes on the pilot valve, removal unnecessary for changeover.
Steps for setting the cam plate position.
Detailed steps for performing basic adjustment.
Explains adjustment for ball valves considering 'dead angle'.
Method for split range adjustments using cam plate.
Maintenance of the supply air filter.
Instructions for pilot valve removal and cleaning.
Steps for replacing the diaphragm.
Lists common problems and their potential causes.
Options for flameproof enclosure I/P converter.
Natural gas construction details.
Dust-proof construction details.
Option for positioners with pressure gauges.
Equipment needed for adjustments.
Information required for ordering spare parts.
Detailed exploded view and parts list.
Lists mounting parts for specific actuators.
Lists mounting parts for Quadra-Powr actuators.
Lists mounting parts for specific actuators.
Lists mounting parts for specific actuators.
Explains the product type code structure and options.