RAID Configuration
The introduction of RAID levels and types are as below:
RAID 0 breaks the data into blocks which are written to separate hard drives.
Spreading the hard drive I/O load across independent channels greatly
improves I/O performance.
RAID 1 provides data redundancy by mirroring data between the hard drives and
provides enhanced read performance.
RAID 5 provides data striping at the byte level and also stripe error correction
information. This results in excellent performance and good fault tolerance.
RAID 10 uses four hard drives to create a combination of RAID 0 and 1 by forming a
RAID 0 array from two RAID 1 arrays.
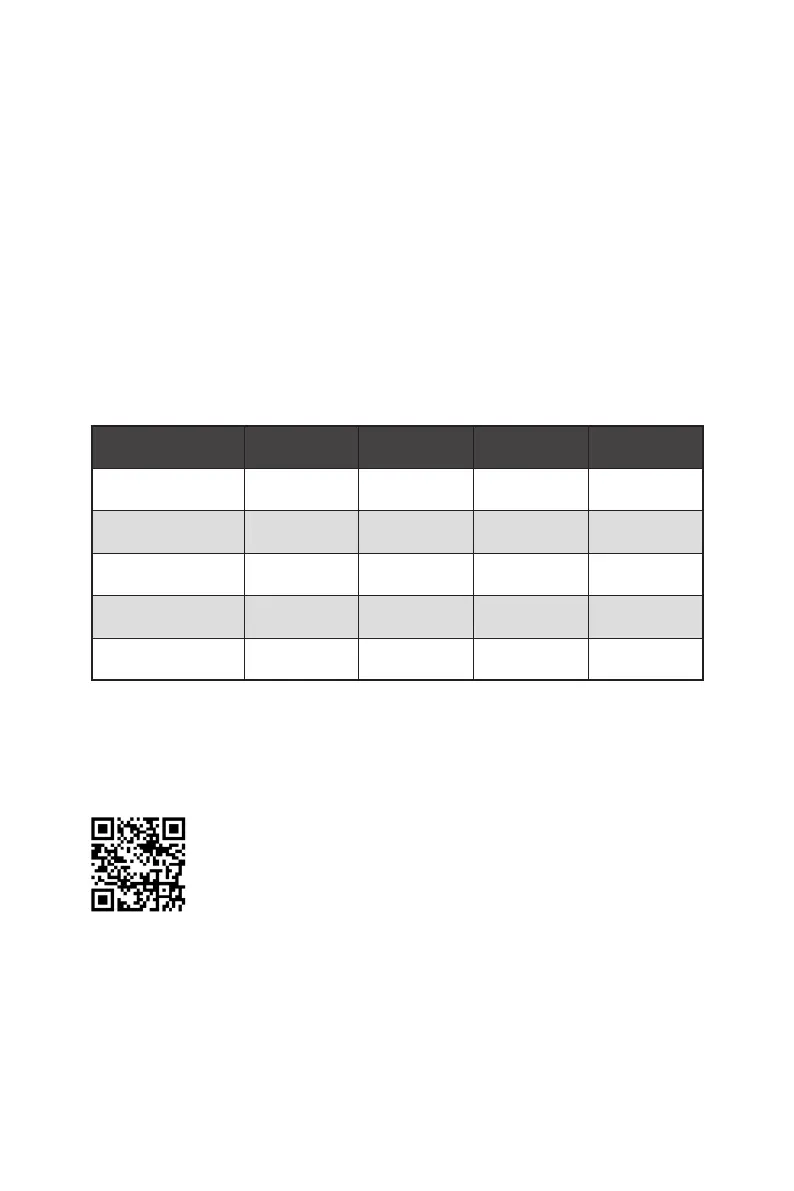
RAID level comparison
RAID 0 RAID 1 RAID 5 RAID 10
Minimum # drives 2 2 3 4
Data protection None Excellent Excellent Excellent
Read performance Excellent OK Good OK
Write performance Excellent Good OK Good
Capacity utilization 100% 50% 67%~(1-1/n) 50%
⚠
Important
All the information/ volumes/ pictures listed in your system might differ from the
illustrations in this appendix.
Intel RAID User Guide
If you’d like to know more instructions on how to set up Intel RAID,
please refer to
http://download.msi.com/manual/mb/IntelRAID600.pdf
or scan the QR code to access.
50
RAID Configuration

 Loading...
Loading...











