16
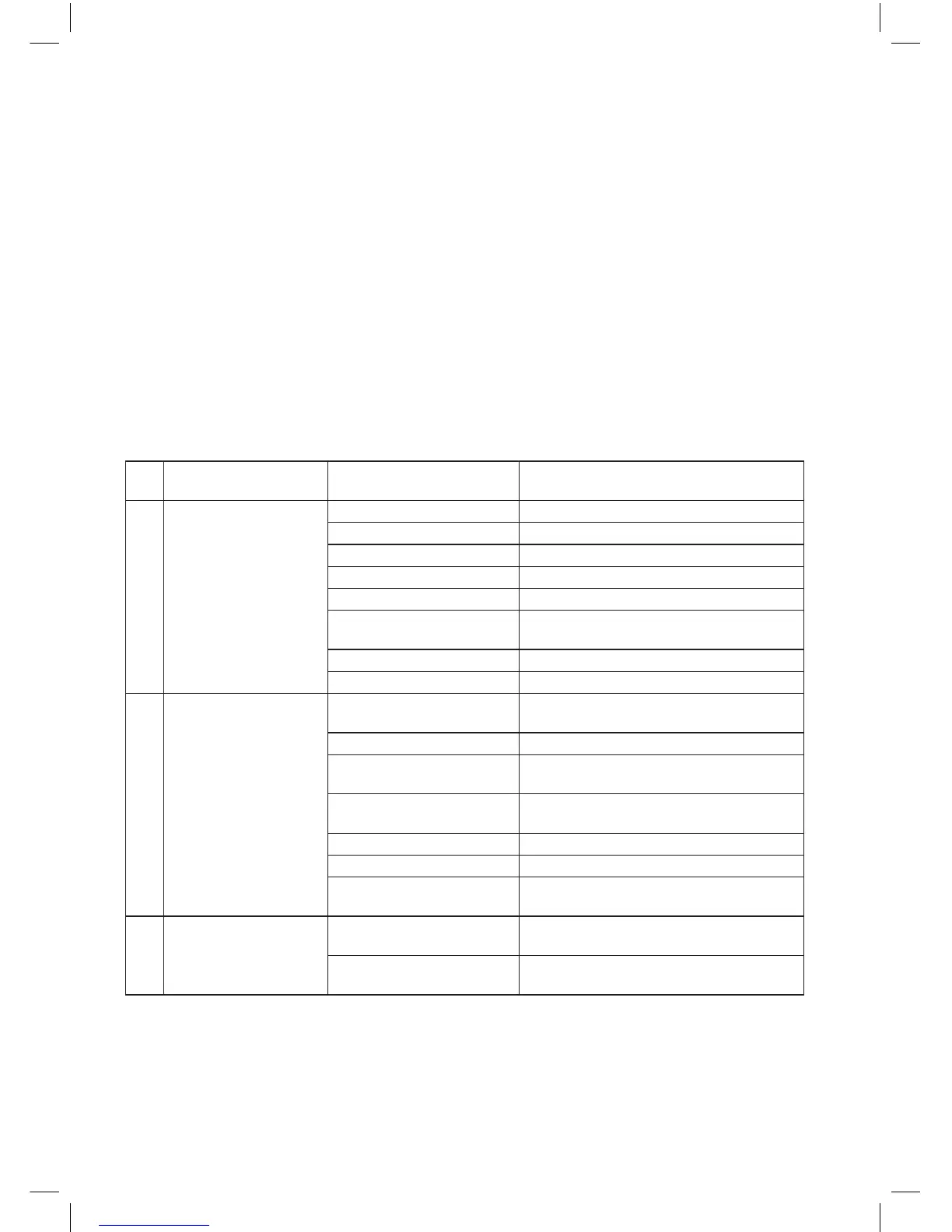
7. Motor Troubleshooting Chart
Sr.
No.
Trouble Cause Remedy
1 Hot bearings Excessive belt pull Decrease belt tension.
Pulley too far away Move pulley closer to bearing.
Pulley dia. too small Use larger pulley.
Misalignment Correct by realignment of drive.
Broken ball or rough races Replace bearings.
Excess lubricant Reduce quantity of grease
(Bearing should be lled only half).
Overloaded bearings Check alignment, side thrust & end thrust.
Bearing running dry Regrease the bearing.
2 Motor connected but
does not start
No supply voltage/ One
phase open/ Voltage too low
Check voltage on each phase.
Motor may be overloaded Reduce load or start at no load.
Control gear defective Examine each step of the control gear for
bad contacts or open circuit.
Starting torque too high If with autotransformer starting, change to
higher tap.
Rotor defective Look for broken rings.
Short circuit to earth Check with Megger.
Fault in starter or star/delta
switch
Check contacts & connections.
3 Motor runs & then stops
down
Power failure Check for loose connections to line, fuses &
control gear.
Over load Examine overload trips & see that they are
set at approx. 150% of full load current.
IS: 7816: Guide for testing insulation
resistance of rotating machines.
IS: 9628: Specication for Three phase
induction motors with type of protection
‘n’.
IS: 6381: Specication for construction and
testing of apparatus with type of protection
‘e’.
IS: 12065: Permissible limits of noise level
for rotating electrical machines.
IS: 12075: Mechanical vibration of rotating
electrical machines with shaft heights
56mm and higher – Measurement,
Evaluation and Limits of Vibration severity.
IS/IEC: 60034-1: Rotating electrical
machines – Part 1: Rating and
Performance.
IS/IEC: 60034-5: Degree of protection for
rotating electrical machines.
EN: 60204: Safety of machinery –Electrical
equipment of machines.
 Loading...
Loading...











