Edition Manual Chapter Page
2014-03-31 Workshop Manual, GGP Park 3 Steering 2
3.1 Description
3.1.1 Mechanical system
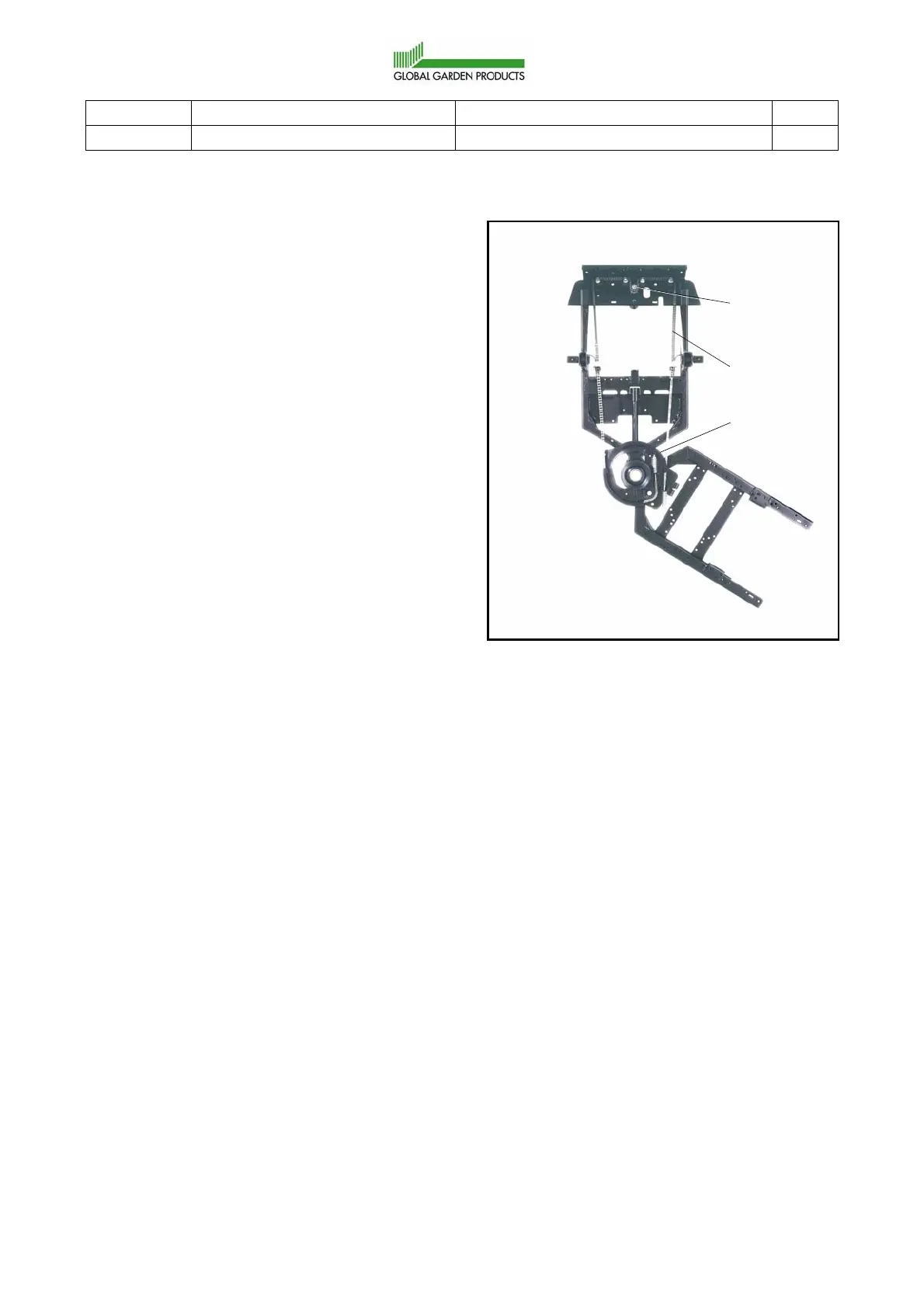
The sprocket (A) is directly coupled to the
stering wheel on the same shaft. A chain (and
wires) (B) is engaged with the sprocket and
connected to the steering disc (C) on the rear
frame. Thus, the rear frame is forced into actual
angles, related to the front frame when the
driver turns the steering wheel.
3.1.2 Hydraulic assisted system
Below is given a brief description about how the
steering torque converter works and its
connection to the valves. For a complete
description, see section 4 “Hydraulic system”.
Section 4 describes how the lifting cylinder
works together with the steering torque
converter. It also describes the pressure
division between the two systems and
adjustments.
The power assisted steering is a hydraulic
auxiliary system. The main components are the
torque converter and the oil pump in the
hydrogear.
As opposed to standard power steering (e.g. in
a car), this power assisted steering has a
limited capacity. This implies that in certain
circumstances it has what may be experienced
as negative characteristics.
At low engine speed, or in situations where
extra steering power is required, the steering
may be considered to be somewhat jerky.
The machine should always be in motion when
the steering is used. Avoid turning the steering
wheel when the machine is standing completely
still and the accessory is in lowered working
position.
The machine can be steered even when the
engine is switched off. Nevertheless, it may
require more force than normal to steer the
A
B
C

 Loading...
Loading...











