
Do you have a question about the Xantrex SW Series and is the answer not in the manual?
| Input Voltage | 12V, 24V, or 48V DC |
|---|---|
| Output Voltage | 120V AC |
| Waveform | Pure Sine Wave |
| Output Frequency | 60 Hz |
| Operating Temperature | -20°C to +50°C |
| Battery Charger | Yes |
| Protections | Overload, Over-temperature, Short Circuit |
General safety guidelines and warnings for using the inverter.
Important notes regarding tools, wiring, and system configuration.
Specific safety measures for working with batteries and equipment.
Instructions for connecting DC power cables to the inverter and battery.
Procedure for connecting AC power input to the inverter.
Procedure for connecting AC power output to the loads.
Requirements and recommendations for AC wiring connections.
Details on connecting AC power to the terminal block.
Step-by-step guidelines for AC wiring installation.
Cautions and recommendations for DC wiring and battery cable sizing.
Guidelines for selecting appropriate battery cable size and length.
Requirements for battery overcurrent protection and disconnect switches.
Procedure for properly connecting battery cables to the inverter.
Instructions and requirements for grounding the inverter system.
Daily controls and settings for inverter and generator operation.
Controls for turning the inverter ON/OFF, Search, or Charger modes.
Controls for managing generator operation: OFF, AUTO, ON, EQ.
Assists in investigating error conditions indicated by the ERROR LED.
Configuration settings for various inverter operating modes.
Configures inverter operation modes like FLT, SELL, SLT, LBX.
Adjusts settings for the three-stage battery charging process.
Configures operating characteristics for utility and generator AC inputs.
Sets automatic generator start conditions and run times.
Configures generator start routines for different generator types.
Sets voltage points for automatic transfer to utility during low battery.
Controls selling power to the grid and sets sell current limits.
Manages when utility power is used for charging or selling.
Describes the various operational modes of the inverter/charger.
Detailed explanation of the inverter's operating modes: OFF, SRCH, ON, CHG.
Mechanisms to prevent battery over-discharge.
Settings for managing low battery cut-out and cut-in voltages.
Operation details for the inverter acting as a battery charger.
Guidelines for setting charger parameters based on battery type.
How the inverter transfers between modes and manages AC power.
Using the generator to assist the inverter with heavy loads.
Setting up automatic generator start and stop based on system conditions.
Troubleshooting generator errors indicated by the ERROR LED.
Operating the inverter for utility backup during outages.
Using the inverter to sell excess power to the utility grid.
Combining utility interactive sales with backup power.
Managing utility power usage for battery charging and load support.
Limiting peak AC load draw from the utility grid.
Automatically transferring loads based on low battery voltage.
Guidelines for determining the appropriate battery bank size.
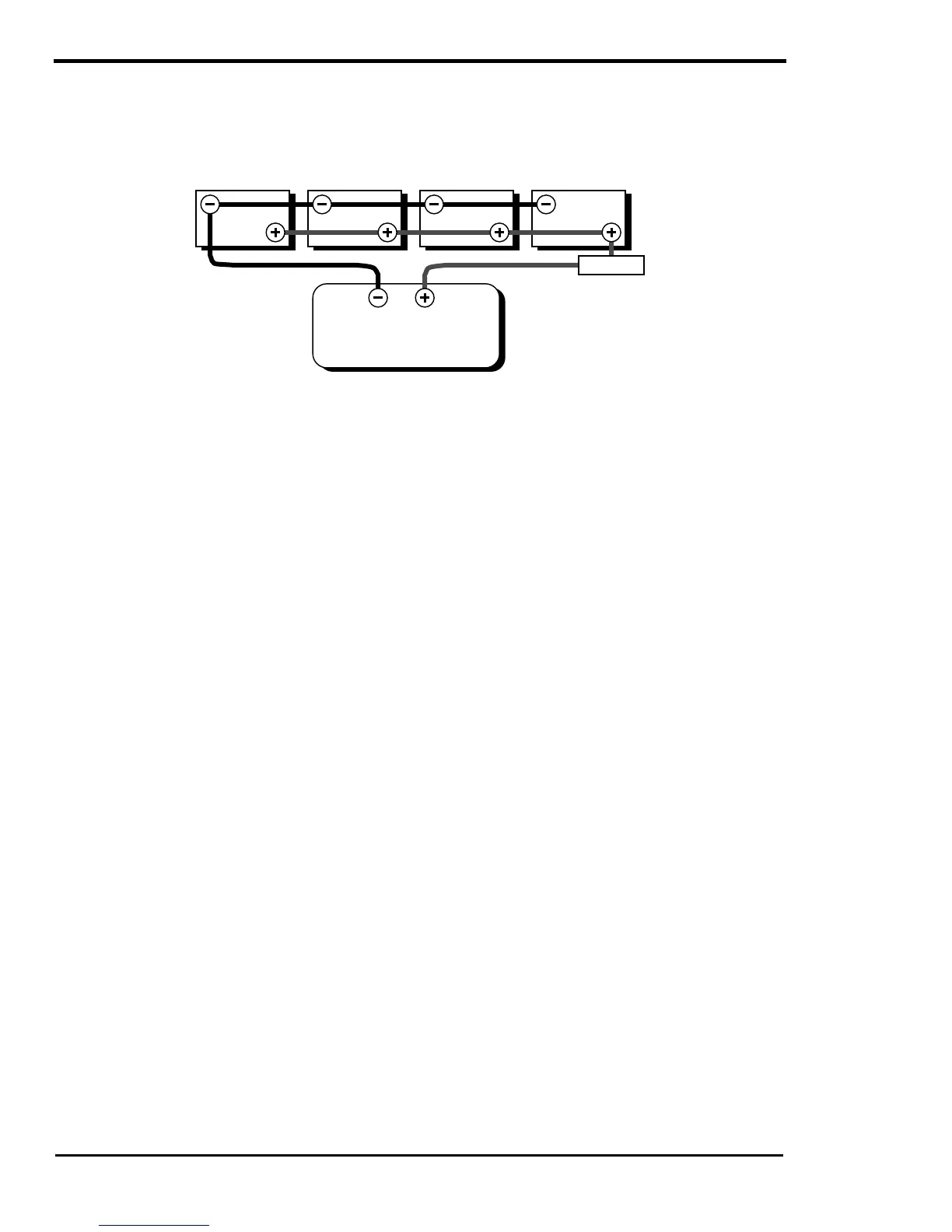
Methods for connecting batteries in series, parallel, or series-parallel.
Guide to diagnosing and resolving inverter issues based on symptoms.
Troubleshooting battery charger issues and error indications.
Troubleshooting specific error causes and their solutions.
Default and adjustable settings for 12 VDC models.
Default and adjustable settings for 24 VDC models.
Default and adjustable settings for 48 VDC models.
Details of the product warranty, coverage, and exclusions.
Procedure for returning products for warranty or repair service.











