14
AMPERAGE TABLE/OVERCURRENT PROTECTION
The tables above provides the total connected heating element
load in amperes for branch circuit conductor and overcurrent
protection sizing. Single-phase heaters are two wire circuits.
Three-phase heaters are three wire circuits. In addition to the
foregoing, a grounded conductor is required.
The rating of the overcurrent protection must be computed
on the basis of 125% of the total connected load amperage.
Where the standard ratings and settings do not correspond
with this computation, the next higher standard rating or setting
should be selected.
HEATER CIRCUITS - ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODELS
The water heater’s electrical components are pictured and
identied in Figure 2 and Figure 3. The model and rating plate
illustration on page 4 identies heater circuit ratings. The
ELECTRONIC CONTROL model has two electrical circuits:
• The control circuit, which controls the electrical power to
heating elements, referring the following control circuit
diagram Figure 5. CCB Control Circuit Diagram - Electronic
Control Models.
• The power circuit, which is operated by the control circuit
carries the electrical load of the heating elements. The
following describes the heater circuits and includes
wiring diagrams for Delta configuration, refer to the
“WYE Conguration Insert” for water heaters operating at
380V/400V/416V/575V. All heater circuits are designed for
50/60 cycle alternating current.
CONTROL CIRCUIT - ELECTRONIC CONTROL MODELS
These models are equipped with an electronic control system.
The system includes a CCB (Central Control Board), an
immersion temperature probe with ECO for temperature
sensing and limiting, a UIM (User Interface Module) for user
interface & information display and element current sensors for
monitoring the power circuits. Refer to the control circuit label
on the water heater for details. The CCB is powered by a small
120V/24V transformer. The control circuit operates on 120V
supplied by a larger 100VA transformer. Standard equipment
includes control circuit fusing using two, 3 amp, class G fuses
with 600 volt rating. Do not substitute fuses of a different rating.
SEQUENCE OF OPERATION
1. When the control is powered, the UIM should display
mode information, water temperature, Operating Set Point,
heating status and operating mode.
2. If the control determines that the actual water temperature
inside the tank is below the programmed Operating Setpoint
minus the (1st)differential, a call for heat is activated.
3. After all safety checks are veried, the CCB (Central
Control Board) will energize contactor coils starting with
the lower bank of heating elements (each diagonal row of
three heating elements is considered a “bank” - see Figure
2) then energize the middle bank (if so equipped) and top
bank (if so equipped). The middle and top banks (if so
equipped) are energized according to programmed 2nd
and 3rd differential set points.
4. The control remains in the heating mode until the water
temperature reaches the programmed Operating Setpoint.
At this point the contactors will be de-energized in the
reverse order.
5. The control system now enters the standby operating
mode while continuing to monitor the water temperature
and the state of other system devices. If the water
temperature drops below the programmed Operating
Setpoint minus the (1st) differential, the control
will automatically return to step 2 and repeat the
heating cycle.
NOTE: See the Electronic Control Models Operation section for
more detailed information on temperature settings mentioned
above.
120-VAC CONTROL CIRCUIT TRANSFORMER CONNECTIONS
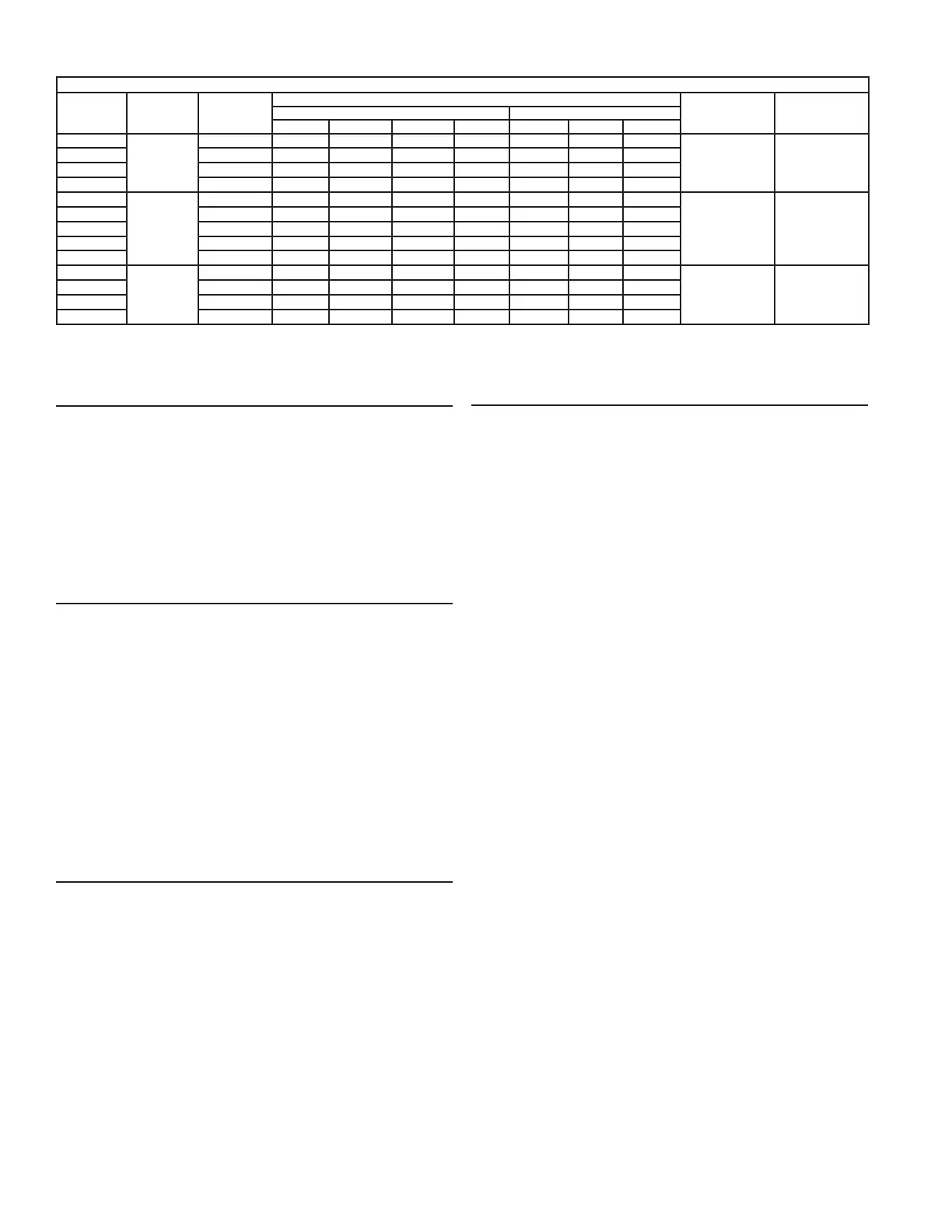
Table 6. Full Load Current for Various Congurations
kW
Input
Number Of
Elements
Element
wattage
Full Load Current In Amperes
Number Of Ther-
mostats
Number Of
Fuses
Single Phase Three Phase
208V 240V 277V 480V 208V 240V 480V
12
3
4000 58 50 44 25 34 29 15
3 6
13.5 4500 65 57 49 29 38 33 17
15 5000 73 63 55 32 42 37 18
18 6000 - - - 75 65 38 - - - 44 22
18
6
3000 87 - - - - - - - - - 50 - - - - - -
6 12
24 4000 116 100 87 50 67 58 29
27 4500 130 113 98 57 75 65 33
30 5000 145 125 109 63 84 73 37
36 6000 - - - 150 130 75 - - - 87 44
36
9
4000 173 - - - - - - - - - 100 - - - - - -
9 18
40.5 4500 195 169 147 85 113 98 49
45 5000 217 188 163 94 125 109 55
54 6000 - - - 225 195 113 150 130 65
Printed on 2/8/2018 9:05 AM CT

 Loading...
Loading...











