2.2 Air system
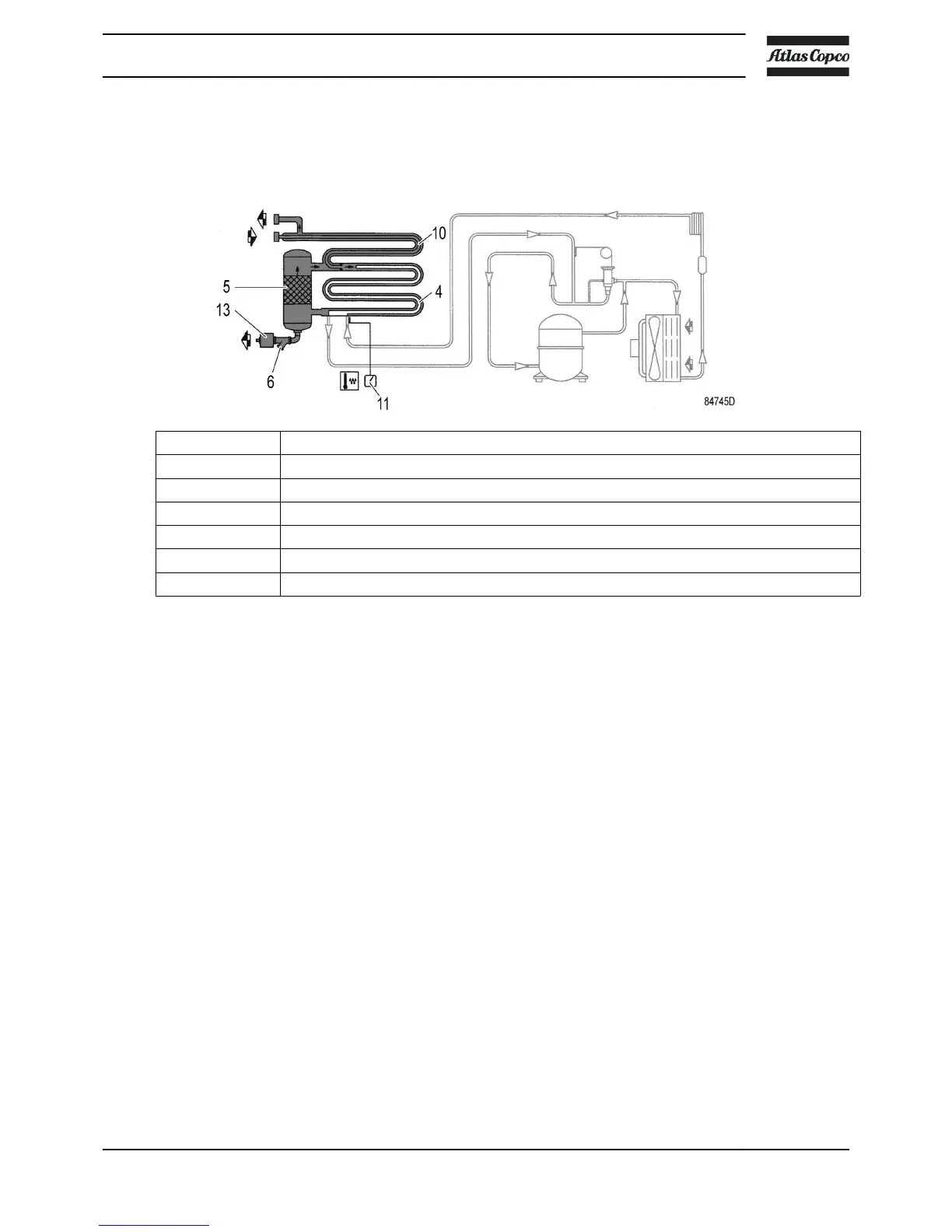
Air flow diagram
Reference Name
4 Evaporator
5 Condensate separator
6 Impurity trap
10 Heat exchanger
11 Digital dewpoint indicator
13 Condensate drain
Description
Compressed air enters heat exchanger (10) and is cooled by the outgoing, cold, dried air. Water in the
incoming air starts to condense. The air then flows through heat exchanger/evaporator (10 and 4) where the
refrigerant evaporates, causing the air to be cooled further to close to the evaporating temperature of the
refrigerant. More water in the air condenses. The cold air then flows through separator (5) where all the
condensate is separated from the air. The condensate is automatically drained in the condensate drain.
The cold, dried air flows through heat exchanger (10) where it is warmed up by the incoming air to
approximately 10˚C (18˚F) below the incoming air temperature.
Condensation in the air net cannot occur unless the air is cooled to below the pressure dewpoint, indicated
by the dewpoint indicator (11).
Instruction book
2920 7112 40 11

 Loading...
Loading...