1840-10
To input the latitude
1. Use H and J to move the cursor to the position in the latitude you want
to change.
2. Use L and K to cycle through the range of settings at the position where
the cursor is located.
• Holding down L or K cycles through the settings at high speed.
• Any latitude greater than 90°00'00" is automatically converted to 90°00'00"
when you save it.
3. Repeat steps 1 and 2 to set the latitude you want.
To input the longitude
1. Use H and J to move the cursor to the position in the longitude you want
to change.
2. Use L and K to cycle through the range of settings at the position where
the cursor is located.
• Holding down L or K cycles through the settings at high speed.
• Any longitude greater than 180°00'00" is automatically converted to
180°00'00" when you save it.
3. Repeat steps 1 and 2 to set the longitude you want.
To change a numeric setting
1. Use H and J to move the cursor to the digit you want to change.
2. Use L and K to cycle through the numbers from 0 to 9.
• Holding down L or K cycles through the numbers at high speed.
3. Repeat steps 1 and 2 to make all the settings you want.
Position
N 00 00' 00"
N 00 00' 00"
N 00 00' 00"
N 00 00' 00"
N 00 00' 00"
N 00 00' 00"
N 00 00' 00"
Setting Range
N or S
0 to 9
0 to 9
0 to 5
0 to 9
0 to 5
0 to 9
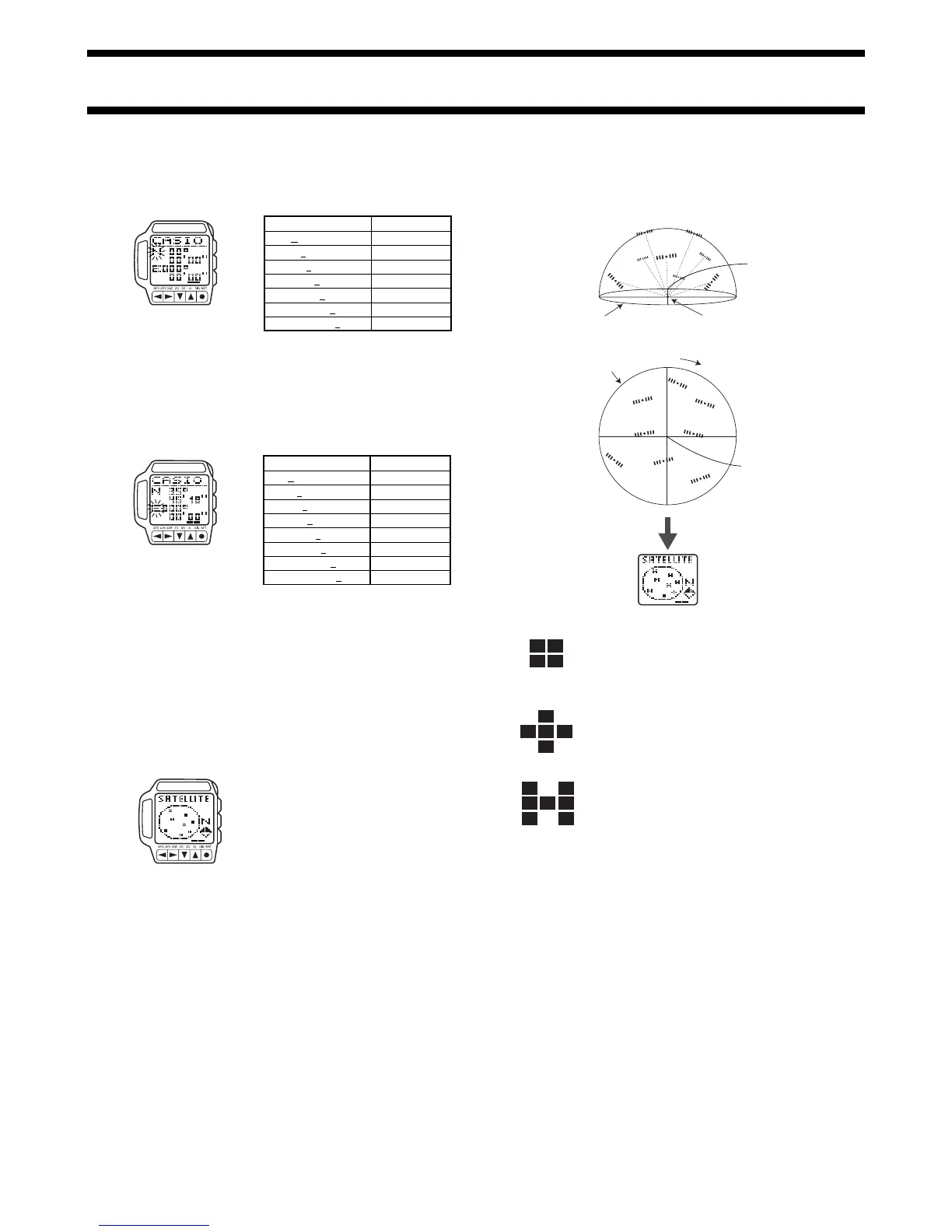
Displaying GPS Satellite Information
You can use the following procedure to display the position and the receive
status of GPS satellites that are currently overhead.
To display GPS satellite information
1. In any mode, press the MENU button to
display the Menu Screen.
2. Use L and K to highlight SATELLITE,
and then press ●.
• Satellite information appears immediately
if a GPS measurement operation is
already in progress.
• If a GPS measurement operation is not in
progress, the message WAIT remains on
the display as data is being collected.
• In the case of a GPS Continuous Mode measurement operation, the screen
data is refreshed every second. To refresh the display in other GPS
measurement modes, press MENU to return to the Menu Screen and then
press ● again.
Satellite Information Display
The following shows the meaning of the satellite marks that appear on the
display.
Satellite Marks
Searching
This mark indicates a satellite from which the watch
is standing by to receive a signal. The positions of
these satellites are determined using almanac data
for the current latitude, longitude, and time.
Tracking
This mark indicates a satellite that is currently being
tracked by the watch. Signal receipt for these
satellites is enabled.
Busy
This mark indicates a satellite from which ephemeris
data (information about the position of the host
satellite and the satellite clock time) is being
received. It indicates the satellites that the watch is
using for position measurement.
Datums
Since the Earth is neither flat nor a perfect sphere or even an ellipsoid, a wide
variety of spheroid models (mostly ellipses) were developed with different
major and minor axes. An ellipsoid, in addition to the various control points
required to relate how the ellipsoid lies in relation to the Earth constitutes a
map datum.
When various countries mapped their areas, each usually used its own datum
to provide accuracy in a specific area. Though some datums share the same
ellipsoid, they use different control points, which results in differing datums.
The development of air travel between countries created the need for a single
global datum, which is identified according to their World Geodetic System
(WGS) names. The constellation of GPS satellites uses WGS 84 to describe
coordinates. It should be noted that errors of several hundred meters can
occur if coordinates of one datum are referred to in another datum without
converting them first.
Maps and Gridlines
Most maps are marked with horizontal and vertical lines that form a
grid
. The
squares of a map’s grid are called
grid cells
or
grid squares
.
The gridlines of some maps are spaced a number of inches or millimeters
apart, while others have gridlines spaced a number of minutes of latitude and
longitude. It is this latter type of map with
latitude and longitude based
gridlines
that can be used with the Map Screen of your GPS watch for
positioning.
Position
E 100 00' 00"
E 100 00' 00"
E 100 00' 00"
E 100 00' 00"
E 100 00' 00"
E 100 00' 00"
E 100 00' 00"
E 100 00' 00"
Setting Range
E or W
0 or 1
0 to 9
0 to 9
0 to 5
0 to 9
0 to 5
0 to 9
 Loading...
Loading...