x! 0 ≦ x ≦ 69 (x is an integer)
nPr
0 ≦ n < 1 × 10
10
, 0 ≦ r ≦ n (n, r are integers)
1 ≦ {n!/(n-r)!} < 1 × 10
100
nCr
0 ≦ n < 1 × 10
10
, 0 ≦ r ≦ n (n, r are integers)
1 ≦ n!/r! < 1 × 10
100
or 1 ≦ n!/(n-r)! < 1 × 10
100
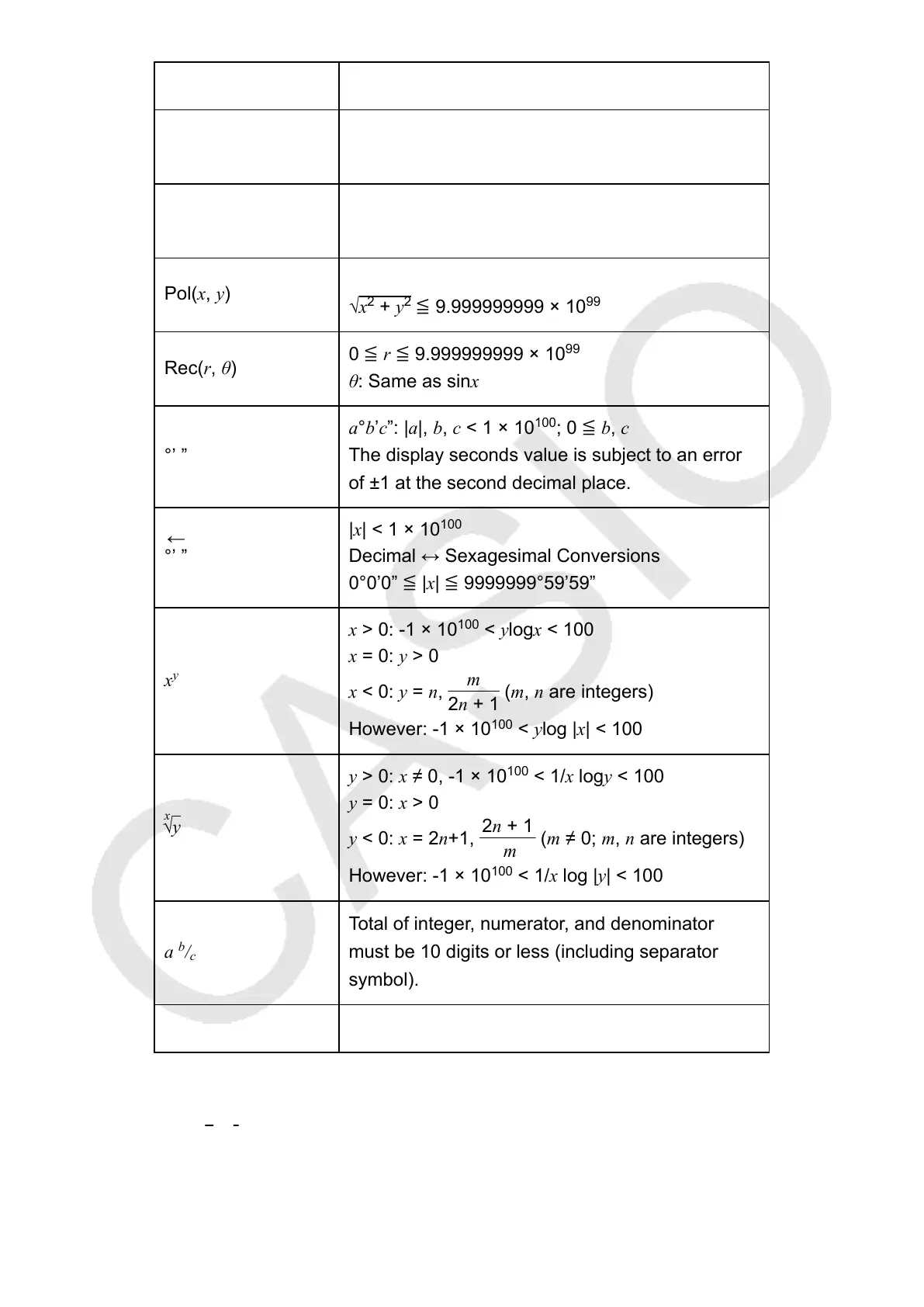
Pol(x, y)
|x|, |y| ≦ 9.999999999 × 10
99
√x
2
+ y
2
≦ 9.999999999 × 10
99
Rec(r, θ)
0 ≦ r ≦ 9.999999999 × 10
99
θ: Same as sinx
°’ ”
a°b’c”: |a|, b, c < 1 × 10
100
; 0 ≦ b, c
The display seconds value is subject to an error
of ±1 at the second decimal place.
°’ ”
←
|x| < 1 × 10
100
Decimal ↔ Sexagesimal Conversions
0°0’0” ≦ |x| ≦ 9999999°59’59”
x
y
x > 0: -1 × 10
100
< ylogx < 100
x = 0: y > 0
x < 0: y = n,
m
2n + 1
(m, n are integers)
However: -1 × 10
100
< ylog |x| < 100
x
√y
y > 0: x ≠ 0, -1 × 10
100
< 1/x logy < 100
y = 0: x > 0
y < 0: x = 2n+1,
2n + 1
m
(m ≠ 0; m, n are integers)
However: -1 × 10
100
< 1/x log |y| < 100
a
b
/
c
Total of integer, numerator, and denominator
must be 10 digits or less (including separator
symbol).
RanInt#(a, b) a < b; |a|, |b| < 1 × 10
10
; b - a < 1 × 10
10
• Precision is basically the same as that described under "Calculation
Range and Precision", above.
• x
y
,
x
√y,
3
√ , x!, nPr, nCr type functions require consecutive internal
calculation, which can cause accumulation of errors that occur with each
calculation.
78
 Loading...
Loading...