Proportional Action:
action in which contribution to output is proportional to deviation at input (deviation = difference between controlled variable and setpoint).
Derivative Action:
action in which contribution to output is proportional to rate of variation input deviation.
Integral Action:
action in which contribution to output is proportional to integral of time of input deviation.
Influence of Proportional, Derivative and Integral actions on response of process under control
• An increase in P.B. reduces oscillations but increases deviation.
• A reduction in P.B. reduces the deviation but provokes oscillations of the controlled variable (the system tends to be unstable if P.B. value is too low).
• An increase in Derivative Action corresponds to an increase in Derivative Time, reduces deviation and prevents oscillation up to a critical value of
Derivative Time, beyond which deviation increases and prolonged oscillations occur.
• An increase in Integral Action corresponds to a reduction in Integral Time, and tends to eliminate deviation between the controlled variable and the
setpoint when the system is running at rated speed.
If the Integral Time value is too long (Weak integral action), deviation between the controlled variable and the setpoint may persist.
Contact GEFRAN for more information on control actions.
11 • CONTROL ACTIONS
12 • MANUAL TUNING
A) Enter the setpoint at its working value.
B) Set the proportional band at 0.1% (with on-off type setting).
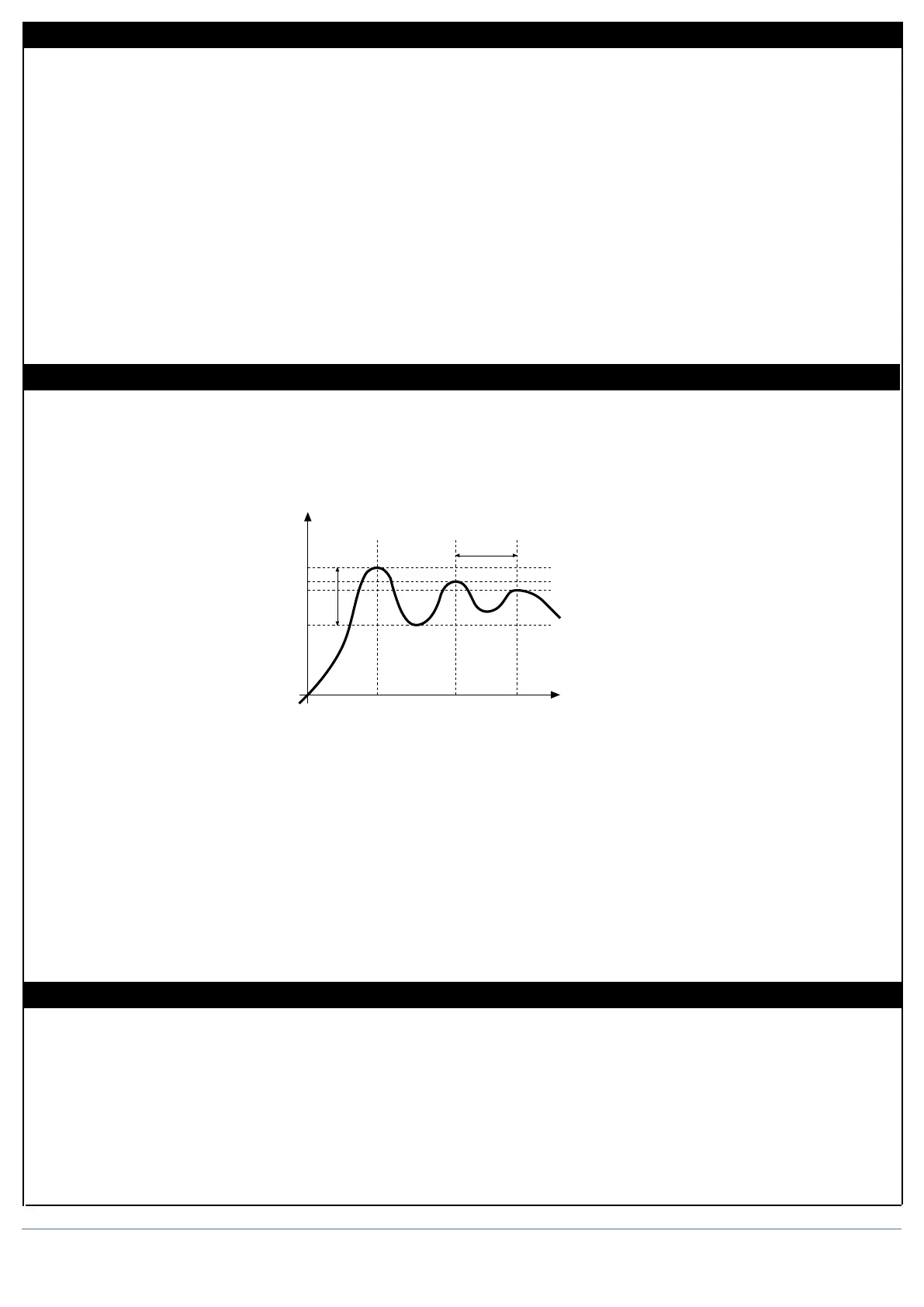
C) Switch to automatic and observe the behavior of the variable. It will be similar to that in the figure:
D) The PID parameters are calculated s follows: Proportional band
Peak
P.B.= ---------------------------------------- x 100
V max - V min
(V max - V min) is the scale range.
Integral time: It = 1.5 x T
Derivative time: dt = It/4
E) Switch the unit to manual, set the calculated parameters. Return to PID action by setting the appropriate relay output cycle time, and switch back to
Automatic.
F) If possible, to optimize parameters, change the setpoint and check temporary response. If an oscillation persists, increase the proportional band.
If the response is too slow, reduce it.
Process
Variable
Time
T
Peak
13 • SOFTWARE ON / OFF SWITCHING FUNCTION
How to switch the unit OFF: hold down the “F” and “Raise” keys simultaneously for 5 seconds to deactivate the unit, which will go to the OFF state while
keeping the line supply connected and keeping the process value displayed. The SV display is OFF.
All outputs (alarms and controls) are OFF (logic level 0, relays de-energized) and all unit functions are disabled except the switch-on function and digital
communication.
How to switch the unit ON: hold down the “F” key for 5 seconds and the unit will switch OFF to ON. If there is a power failure during the OFF state, the
unit will remain in OFF state at the next power-up (ON/OFF state is memorized).
The function is normally enabled, but can be disabled by setting the parameter Prot = Prot +16. This function can be assigned to a digital input (d.i.F.1 or
d.i.F.2) and excludes deactivation from the keyboard.
1380090G_MHW_1600-1800P_04-2013_ENG

 Loading...
Loading...











