8
Glossary
Ambient Operating Temperature
The ambient temperature at which a device can be used in the con-
tinuously operated state.
Ambient Storage Temperature
The ambient temperature at which a device, without power applied,
maybestoressafely.
Automatic Reset
To automatically return the timer to the “0” state after the lapse of
given time.
Dielectric Strength
The maximum voltage a dielectric can withstand without rupturing.
DOWN Display Digital Timer
Thetimerwhose display progresses indescendingsequence(from
thesetvalueto0).
Electrical Reset/External Reset
To reset timer by applying a required voltage to the reset circuit.
Electrical Life Expectancy
A life expectancy of a timer when the control output of the timer is
operated to switch the specified voltage/current load connected to
the control output.
Holding Time
The period of time from the completion of the time-limit operation to
the start of the reset operation.
Humidity
The ambient humidity at which a device can be used in the continu-
ously operated state.
Instantaneous Contact
The contact that performs instantaneous operation.
Instantaneous Operation
The operation to place the output in the ON or OFF state upon ap-
plication of the required voltage to the operating circuit.
Insulation Resistance
Theresistanceofferedbyaninsulatingmaterialtotheflowofcurrent
resulting from an impressed DC voltage.
Integrating Operation
The operation to obtain an output when the sum of the operating
times stopped or released by gate signals coincides with the set
time.
Malfunction Durability Shock
The threshold of shock beyond which a device can no longer oper-
ate properly by satisfying the prescribed ratings.
Malfunction Durability Vibration
The threshold of vibration beyond which a device can no longer op-
erate properly by satisfying the prescribed ratings.
Manual Reset
To mechanically reset the timer by manual operation.
Mechanical Durability Shock
The threshold of shock beyond which an abnormality is expected to
occur in the appearance or function of a device.
Mechanical Durability Vibration
Thethresholdofvibrationbeyond whichanabnormality is expected
to occur in the appearance or function of a device.
Mechanical Life Expectancy
A life expectancy of a timer when the control output of the timer is
operated under no load condition.
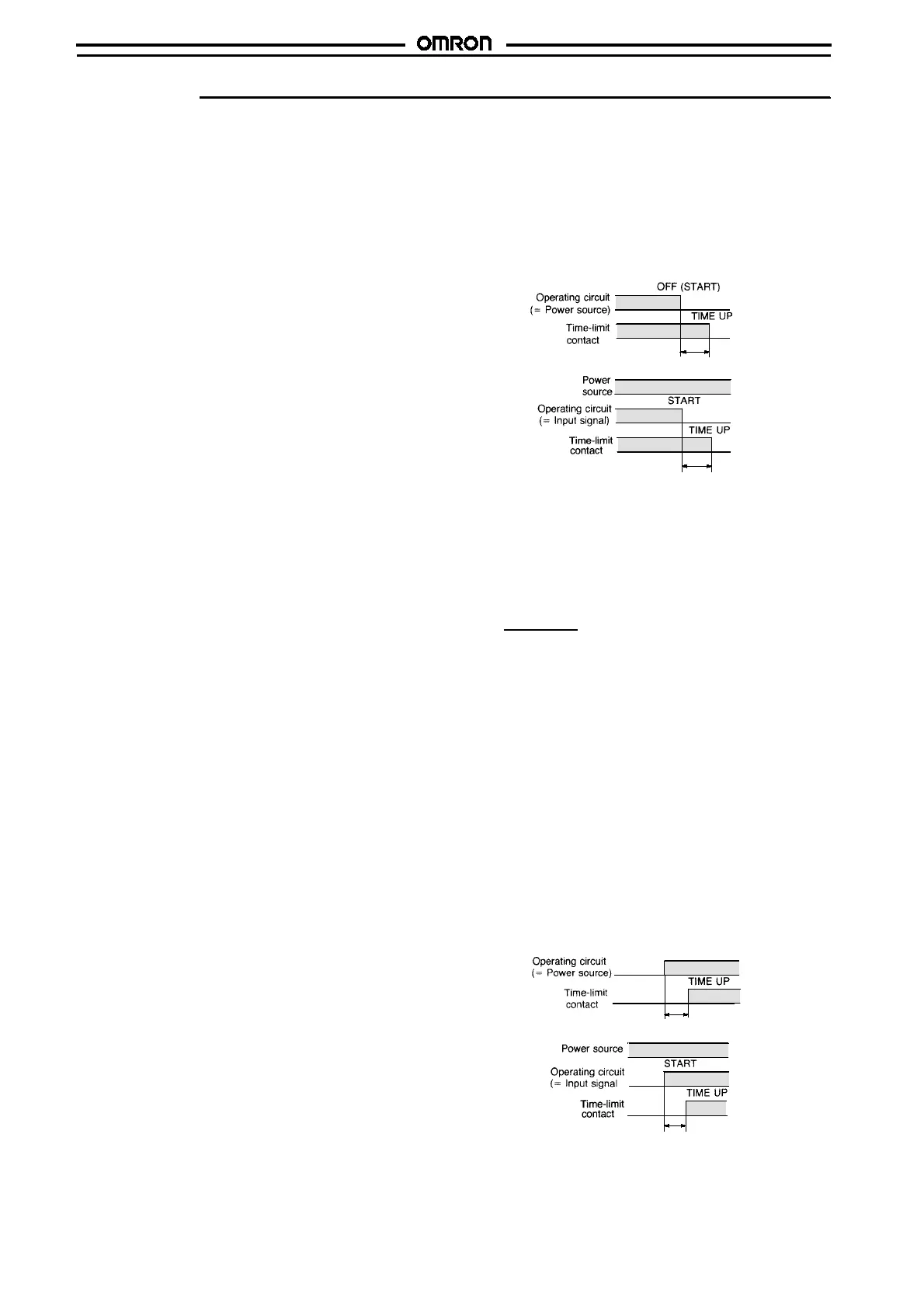
OFF-delay Timer
An output signal is generated upon application of a voltage to the
operating circuit. The output signal is removed after the lapse of a
given preset time from the interruptionof the voltage being supplied
to the operating circuit. The timer remains in the OFF state until the
re-application of the voltage to the operating circuit.
This timer is also available in two types; one with a power supply
also serving as an operating circuit, and the other with separate
power supply and operating circuit. With the former type, restric-
tions are placed on the available types, operate time, etc.
(a) When the operating circuit is a power source
(b) When the operating circuit is an input signal source
T
T
OFF Time
The period of time from the start of the timer’s reset operation until
the application of a required voltage to the operating circuit.
OFF Time Characteristic
A change in operating time when the operate time in a given OFF
time and the OFF time are changed.
Formula for calculation:
OFF time characteristic
=
!
x 100 (%)
TM x 3 -- TM
3
TMs
where,
TM
3
: Average value of operating times measured during the
OFF time of 1 second.
TM x 3: Average value of operating times measured during the
OFF time which causes the maximum deviation from TM
3
which the OFF time range of 1 hour from the specified re-
setting time.
TMs: Maximum scale time
ON-delay Timer
An output signal is generated after the lapse of a given preset time
from the application of voltage to the operating circuit.
The output signal is held until the operating circuit is turned off, and
is removed upon turning off the operating circuit, causing the timer
to return to its operable state.
This timer is available in two types; one with a power supply also
serving as an operating circuit, and the other, with separate power
supply and operating circuit.
In the case of motor timers, the latter type provides an higherrepeat
accuracy.
(a) When the operating circuit is a power source
(b) When the operating circuit is an input signal source
T
T
 Loading...
Loading...