10
O
perating the AZ3 mount
Azimuth ne adjustment
Altitude ne adjustment
Azimuth locking knob
Fig.g
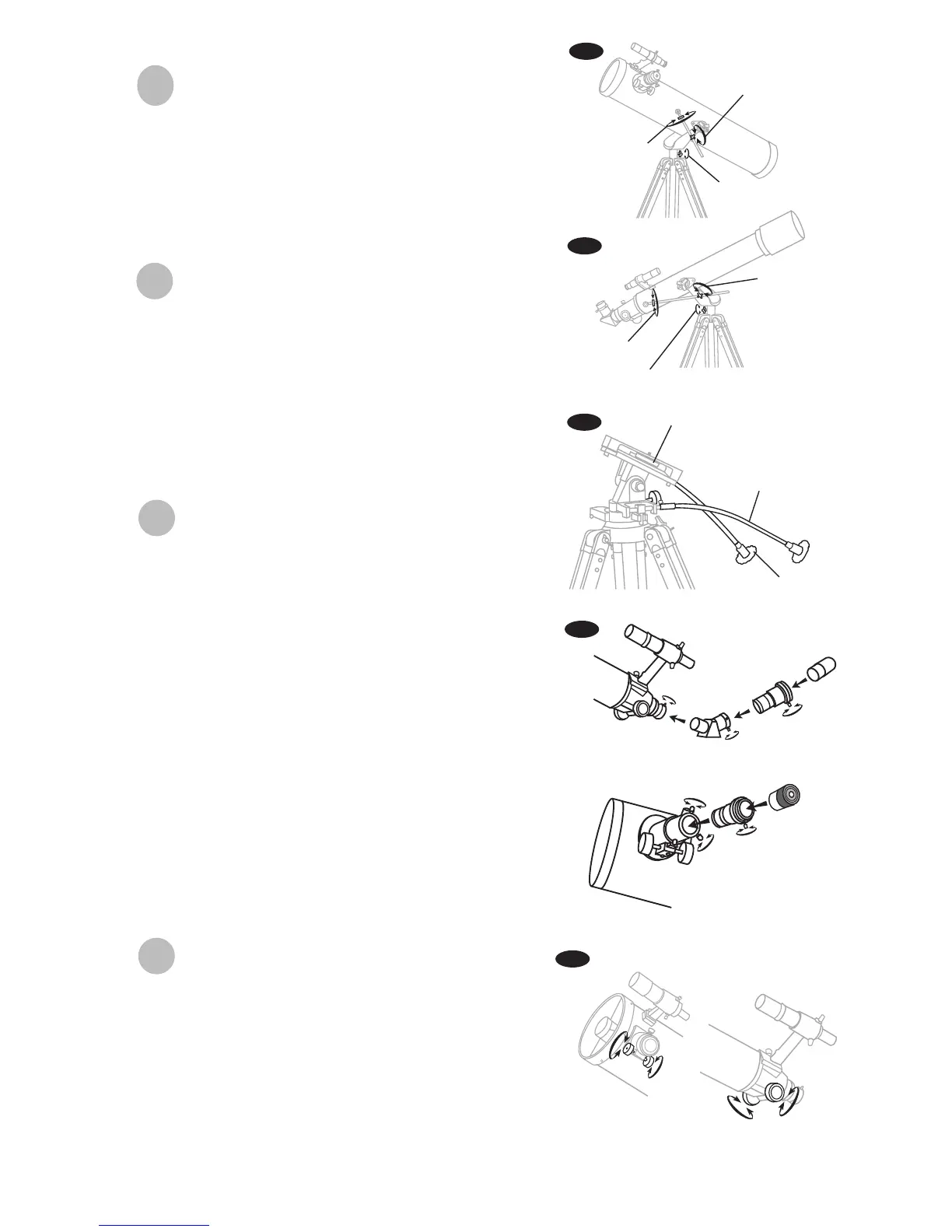
Using the Barlow lens
F
ocusing
Fig.k
This mount has controls for movement in altitude (up-down) and
azimuth (left-right). Coarse azimuth movement is controlled by a
locking knob located near the tripod head for left-right rotation.
Loosen the knob to make large direction changes then lock it for
ne adjustments. Coarse Altitude movement is controlled by a
friction bolt. Use the micro-adjustment control cables to make small
altitude and azimuth movements such as centreing objects in view.
The micro-adjustment controls have limited travel so it is best to
centre them on their threads before making a coarse adjustment
(Fig.i).
A Barlow is a negative lens which increases the magnifying power
of an eyepiece, while reducing the eld of view. It expands the
cone of the focussed light before it reaches the focal point, so that
the telescope's focal length appears longer to the eyepiece.
The Barlow is inserted between the focuser and the eyepiece in a
reector, and usually between the diagonal and the eyepiece in a
refractor or a catadioptric (Fig.j). With some telescopes, it can also
be inserted between the focuser and the diagonal, and in this
position it gives even greater magnication. For example, a 2X
Barlow when inserted after the diagonal can become 3X when
placed in front of the diagonal.
In addition to increasing magnication, the benets of using a
Barlow lens include improved eye relief, and reduced spherical
aberration in the eyepiece. For this reason, a Barlow plus a lens
often outperform a single lens producing the same
magnication. However, it is greatest value may be that a Barlow
can potentially double the number of eyepiece in your collection.
Slowly turn the focus knobs (Fig.k), one way or the other, until the
image in the eyepiece is sharp. The image usually has to be nely
refocused over time, due to small variations caused by
temperature changes, exures, etc. This often happens with short
focal ratio telescopes, particularly when they haven't yet reached
outside temperature. Refocusing is almost always necessary when
you change an eyepiece or add or remove a Barlow lens.
Fig.j
Barlow
Diagonal
Eyepiece
(Refracting Telescopes)
(Reflecting Telescopes)
Barlow
Eyepiece
Altitude adjustment
Azimuth adjustment
Altitude ne
adjustment
Operating the AZ1/AZ2 mount
Azimuth adjustment
Altitude ne
adjustment
Altitude adjustment
Fig.h
Fig.i
This telescope has an altitude(up-down)-azimuth(left-right) mount
to control telescope movements. Loosen the azimuth lock knob to
make left-right direction movements then tighten to lock. Loosen
the altitude lock knob to make course up-down changes. Altitude
ne adjustments can be made by rotating the knurled wheel on
the altitude ne adjustment rod after tightening the altitude lock
knob. (AZ1: Fig.g, AZ2: Fig.h)

 Loading...
Loading...