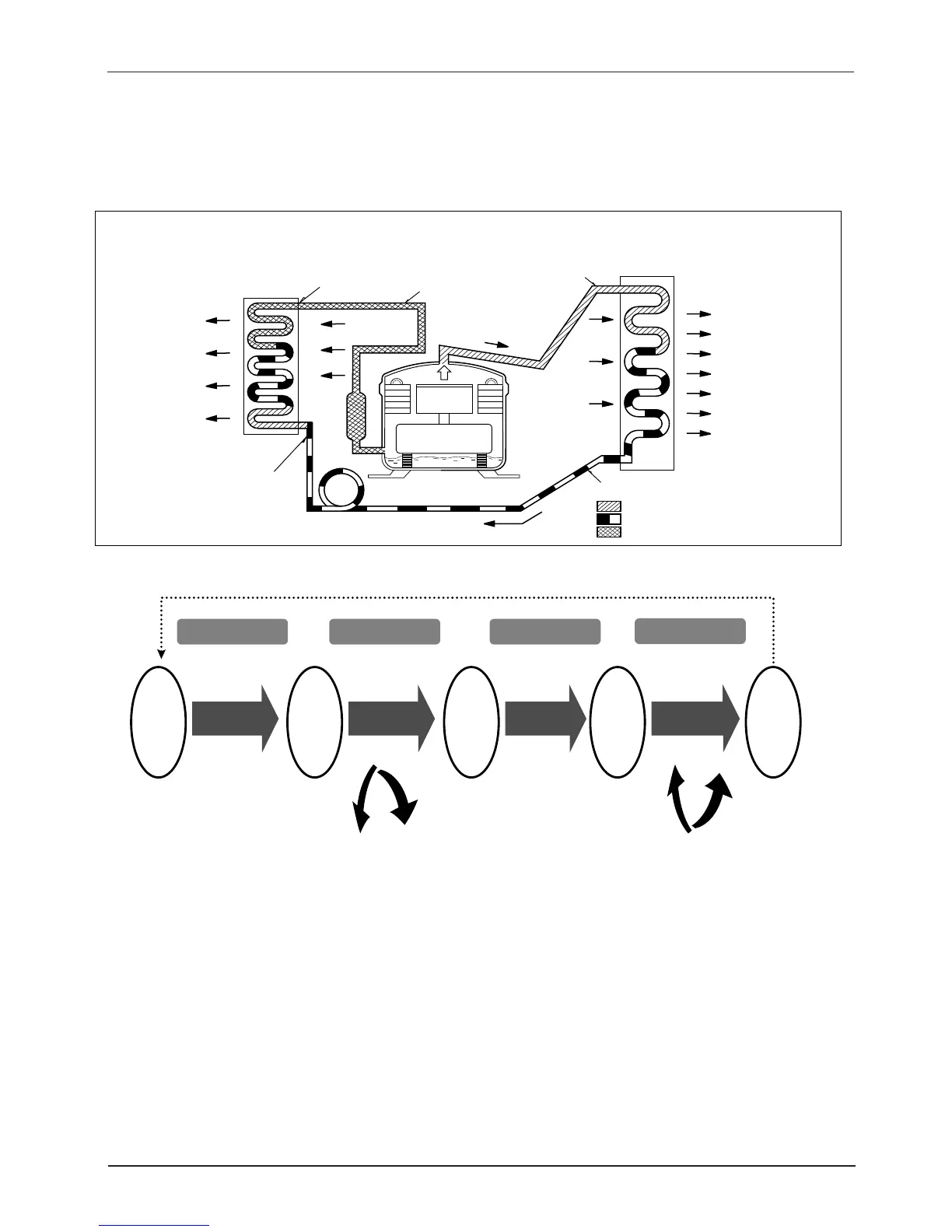
3.2 Refrigerating cycle
1) Refrigerating cycle
2) The principle of refrigerating cycle
3) The role of each cycle
(1) Compression : The gasified refrigerant evaporated is absorbed into compressor through the suction pipe,
and then compressed by a piston in cylinder and turned into a gas of high temperature and
high pressure which is able to be liquified in a room temperature.
(2) Liquification : The gas of high temperature and high pressure in compressor is cooled by air in condenser
and liquified by a condensing heat.
(3) Expansion : With passing through the capillary tube, the high pressure refrigerant liquified in condenser
turns into a low pressure condition, which is easy to evaporate.
(4) Evaporation : The liquid refrigerant of low temperature and low pressure passed though the capillary tube
absorbs the room air heat in evaporator and evaporates into a gas.

 Loading...
Loading...











