68
Diagnostic function
Diagnostic function
The diagnostic function monitors and checks that the
EDC system is functioning correctly (including the
boost pressure and engine coolant temperature
(ECT)).
The diagnostic function has the following tasks:
● To detect and locate malfunctions
● To inform that malfunctions have been detected
● To assist in fault-tracing
● To protect the engine and ensure suitability for
manoeuvering when serious malfunctions have
been detected
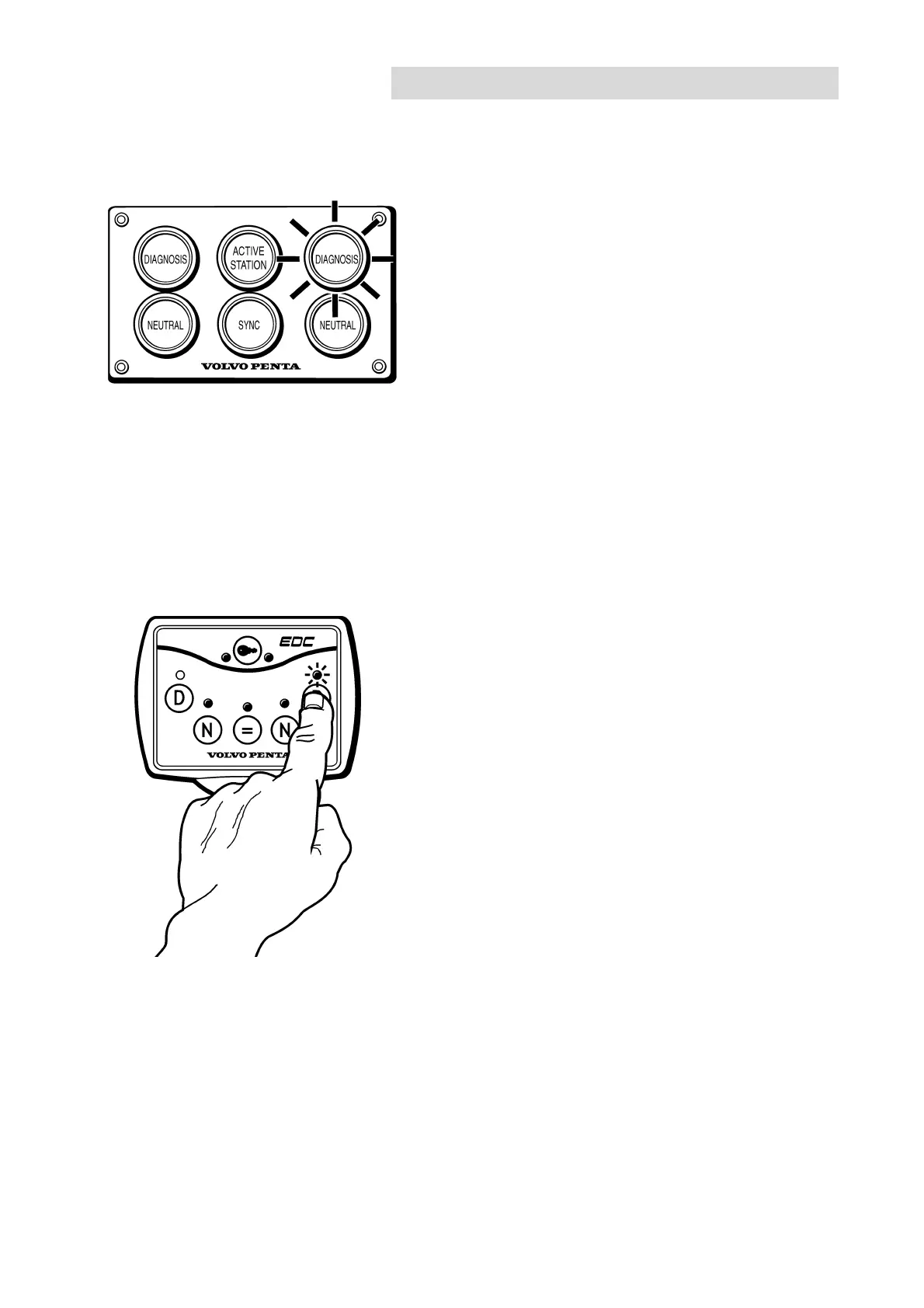
Malfunction alerts
The indicator for the diagnostic button starts to flash if
the diagnostic function registers malfunction in the
EDC system.
Note! High engine coolant temperature (ECT) is only
indicated via the warning lamp and the acoustic
alarm.
Assistance when fault-tracing
A diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is flashed out if the
diagnostic button is pressed and then released. This
code can be found in the list of DTCs with information
about cause, consequences and corrective action.
The diagnostic function affects the engine as
follows when:
1. The diagnostic function has detected a minor fault
which will not damage the engine:
Consequence: The engine is unaffected
2. The diagnostic function has detected a serious
fault that will not result in immediate damage to
the engine (high engine coolant temperature
(ECT) for example):
Consequence: Engine power is reduced until the
relevant value normalizes.
3. The diagnostic function has detected a serious
fault that will cause engine break down:
Consequence: Engine stops
4. The diagnostic function has detected a serious
fault that will prevent engine operation:
Consequence: The gear is disengaged and the
engine speed (RPM) is set to 1000 rpm.
Emergency shifting is still possible: See the “Trou-
bleshooting” chapter.

 Loading...
Loading...