Page 4
Heat is extracted from the air by blowing air through a finned radiator, known as the evaporator,
with a fan. The extracted energy from the air is transferred into the refrigerant which circulates
around the evaporator. The heat pump then converts this low grade heat to a high grade by
compressing the refrigerant using the compressor. The compression of the refrigerant
increases the pressure and the temperature. This high grade heat is then transferred to the
heating system via another heat exchanger known as the condenser. The heat can now be
used to provide space heating and DHW. The pressure of the refrigerant is then released
through a throttling valve known as the expansion valve which also causes the temperature to
drop and allows the cycle to start over again.
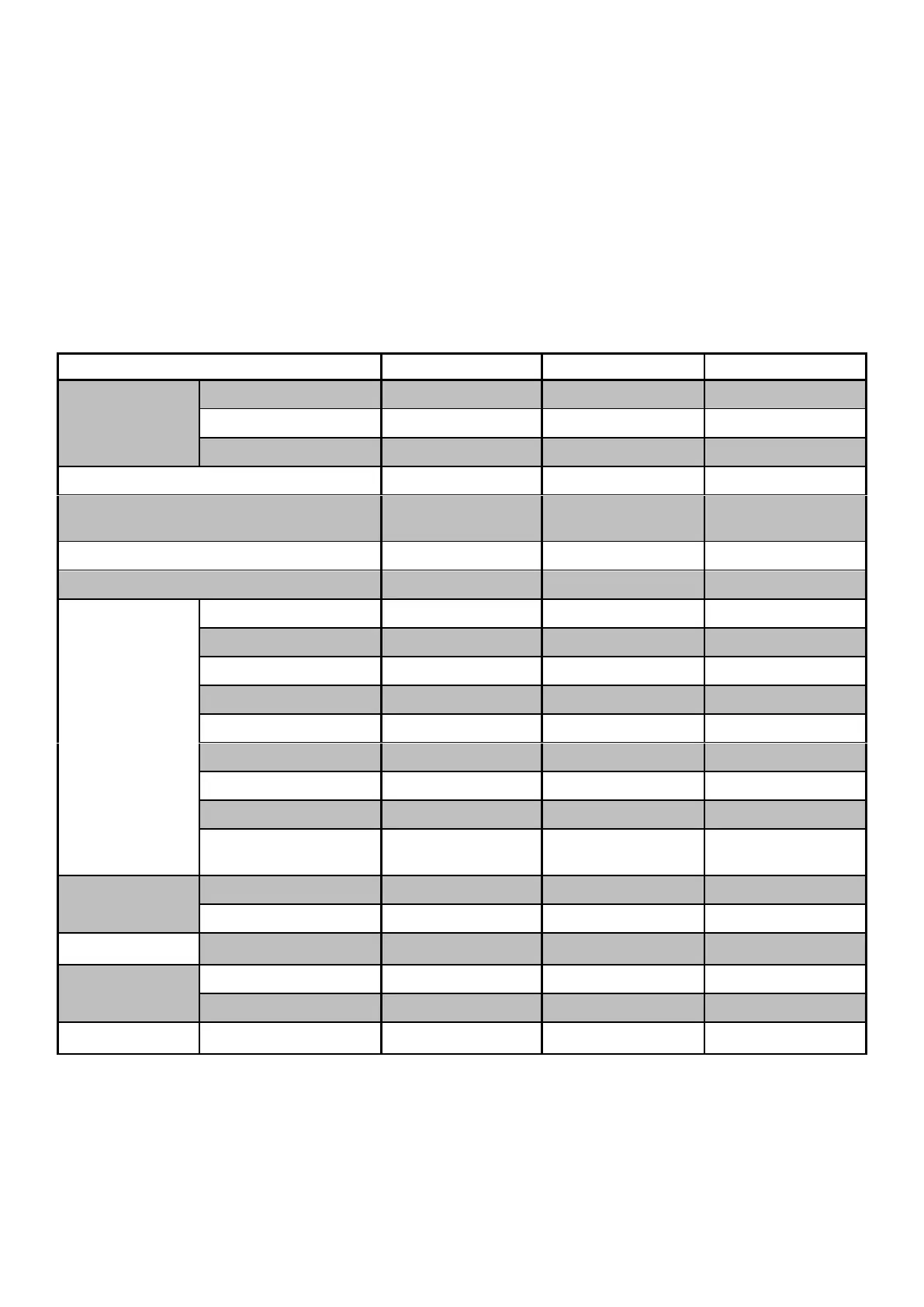
1.4 Product Data
Table 1 Product data
Nominal Sound Level (dBA)*
ErP Efficiency Class
(35°C / 55°C)^
*Nominal Sound Levels have been independently tested in accordance with EN 12102.
^ ErP ratings have been independently tested in accordance with EN 14825.
+
This unit features an integrated immersion heater which if used requires an additional 14Amp supply.
 Loading...
Loading...