ZXR10T600/T1200UserManual(IPv6Volume)
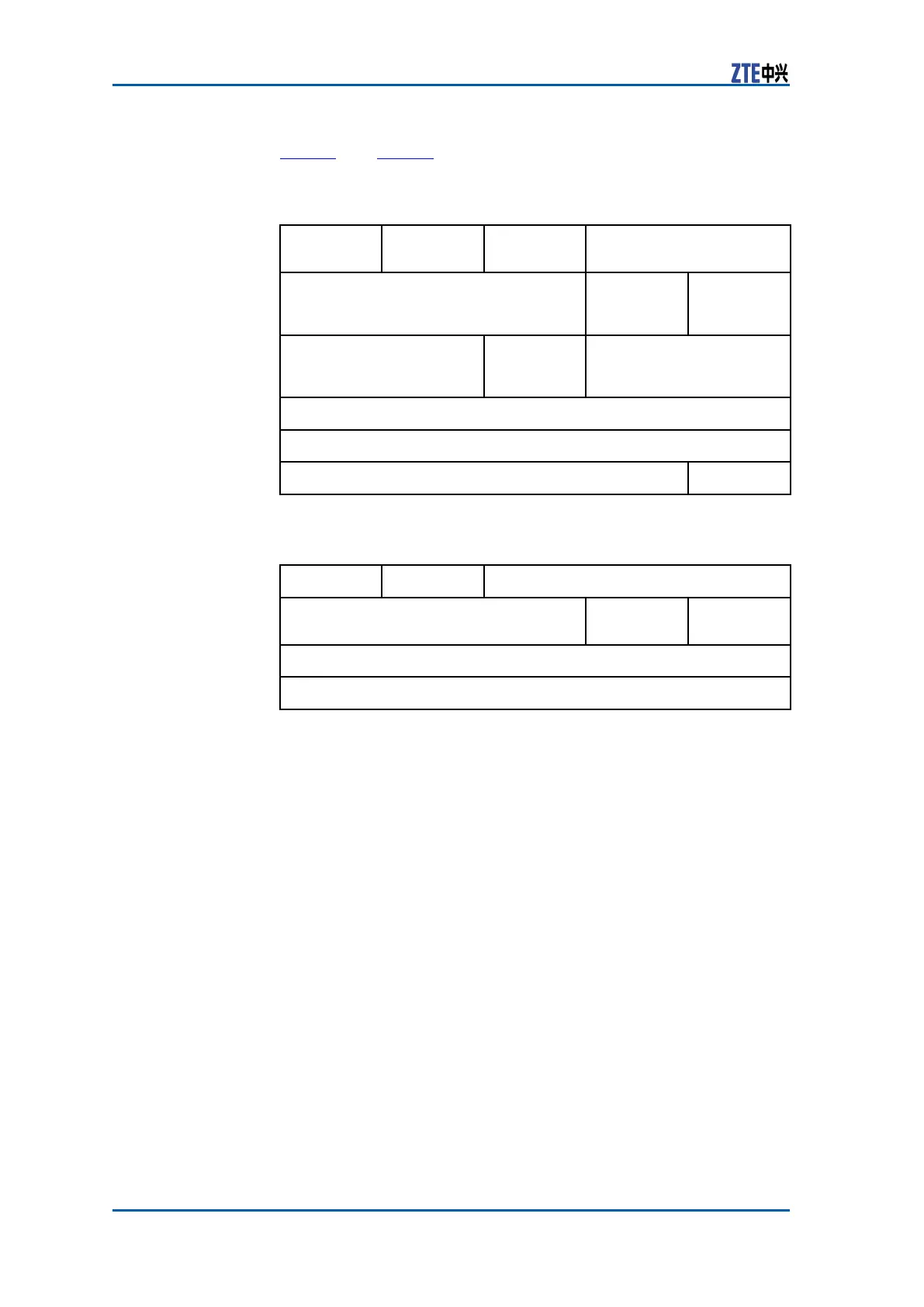
Table1andTable2aretheheaderformatsofIPv4andIPv6re-
spectively.(Numbersinthetablesrefertobitnumbers.)
TABLE1IPV4HEADERFORMAT
4-Version4–Header
Length
8-Service
Type
16-DataPacketLength
16–Identier
4–Flags
12-
Fragmented
Offset
8–TimetoLive(TTL)
8–T rans-
missionPro-
tocol
16–HeaderChecksum
32-SourceAddress
32-DestinationAddress
24–Options
8-Padding
TABLE2IPV6HEADERFORMAT
4-Version4–Priority24–FlowLabel
16–PayloadLength
8–Next
Header
8–HOP
Limit
128-SourceAddress
128-DestinationAddress
IPv6headerissimplerthanIPv4headerinstructurebecausemany
eldsinIPv4headerthatarenotfrequentlyusedaredeletedfrom
IPv6header ,andputintoitsoptionsandheaderextension,which
aredenedmorestrictly.
�IPv4containsteneldswithxedlength,twoaddressspaces
andsomeoptions,whileIPv6containsonlysixeldsandtwo
addressspaces.
�AlthoughIPv6headeroccupies40bytes,whichis1.6times
ofIPv4headerwith24-bytes,itdoesnotconsumetoomuch
memorycapacityduetoitsxedlength(thelengthoftheIPv4
headerisvariable).
�ThefollowingsixeldsaredeletedfromIPv4header:header
length,typeofservice,identier ,ags,fragmentedoffsets
andheaderchecksum.Namesandsomefunctionsofthe
threeeldsoftotallength,protocolandTimetoLive(TTL)
arechanged,anditsoptionalfunctionsiscompletelychanged.
Apartfromthis,twoeldsareadded:priorityandowlabel.
�IPv6headerformatisgreatlysimplied,whicheffectivelypares
downoverheadofprocessingheaderbyarouterorswitch.At
thesametime,IPv6enhancesthesupporttotheextension
headerandoptions,whichnotonlyallowsmoreefcientfor-
warding,butalsoprovidessufcientsupportsforfutureload
ofnewapplicationstonetworks.EachIPv6packetcanhave0,
4CondentialandProprietaryInformationofZTECORPORATION

 Loading...
Loading...