102
Instruction book
9096 3321 00
This table indicates that distilled or demineralised water should never be used, as their RSI is
>11.
The RSI is only indicating the equilibrium of scaling - descaling. A cooling water showing good RSI
conditions can still be unsuitable due to other factors.
2. pH
The effect of pH is already included in the Rysnar index, but the pH itself has some additional limitations: For
GA units, the pH should be >6.8.
3. Total dissolved solids (TDS)
This is the sum of all ions in the water. It can be derived from the dry residue after evaporation (but not
including suspended solids), or it can be estimated from the electrical conductivity.
In a closed system, the limit is described by:
TDS < 3000 mg/l
In an open system, TDS < 450 mg/l
4. Chlorides (Cl-)
Chloride ions will create pitting corrosion on stainless steel. Their concentration should be limited:
Closed cooling system: Chlorides < 500 ppm
Open cooling system: Chlorides < 150 ppm
However, if the water is scaling, lower limits should be used. (See The Rysnar stability index (RSI)).
5. Free chlorine (Cl
2
)
Continuously, a level of 0.5 ppm should not be exceeded. For shock treatments, a maximum limit of 2 ppm
for maximum 30 minutes/day applies.
6. Sulphates (SO4—)
Closed cooling system: Sulphates < 400 ppm Open cooling system: Sulphates < 150 ppm
7. Carbonate hardness
Closed cooling system: 50-1000 ppm CaCO
3
Open cooling system: 50-500 ppm CaCO
3
HCO3
-
/ SO4
2-
should be > 1
8. Ammonia
< 0.5 ppm
9. Copper
< 0.5 ppm
10. Iron and Manganese
Iron < 0.2 ppm
Manganese < 0.1 ppm
11. Organics
No algae.
No oil.
12. Suspended solids
Non-soluble particles, size < 1mm:
< 10 ppm
13. Oxygen
< 0.2 ppm
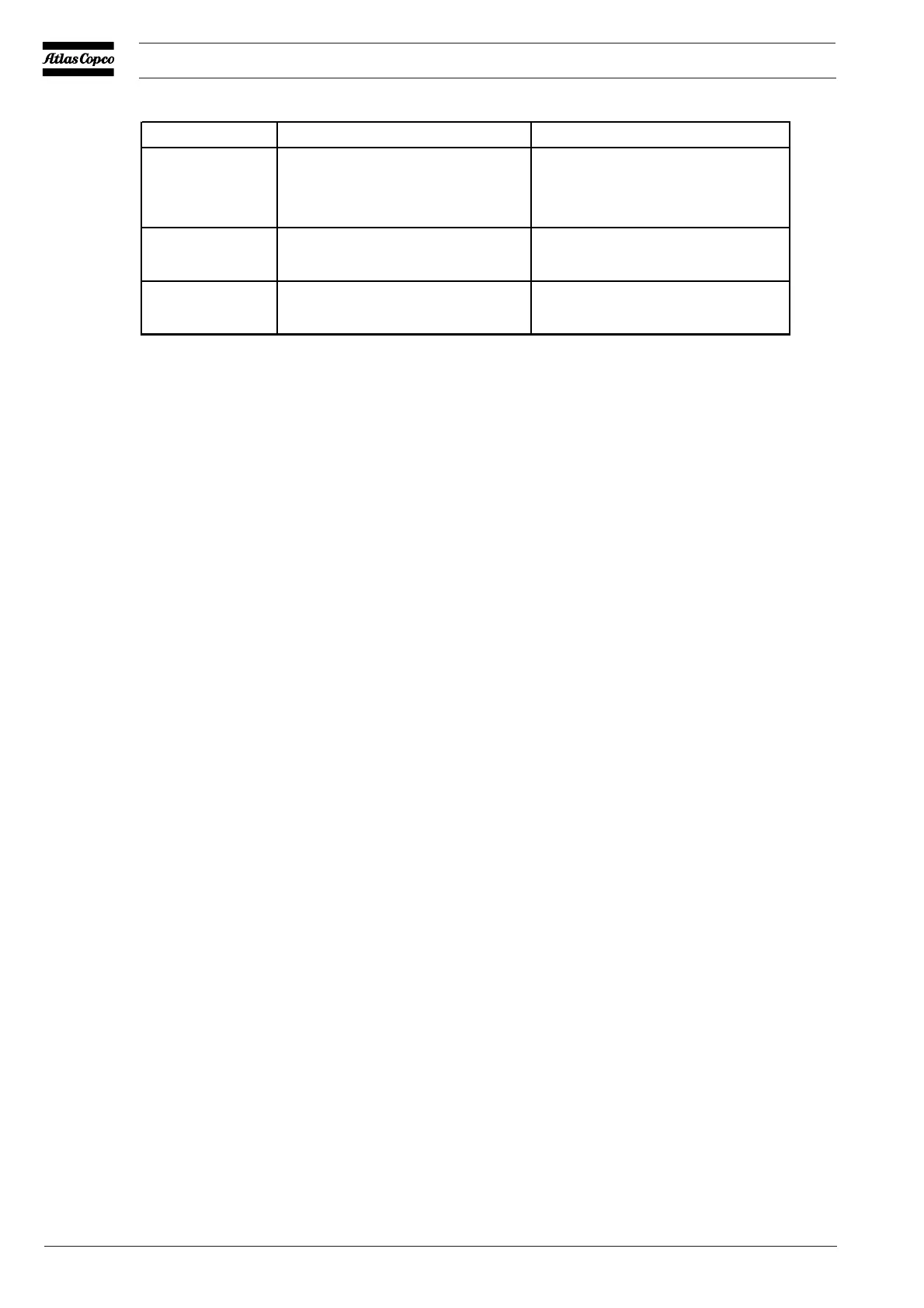
RSI Tendency of the water Action
7.6 < RSI < 9.0 Strong corrosion Regular control necessary, use
of corrosion inhibitor
recommended
9.1 <RSI<11 Very strong corrosion Regular control necessary, use
of corrosion inhibitor required
RSI > 11 Very strong corrosion in the
complete water circuit
Water should not be used

 Loading...
Loading...











