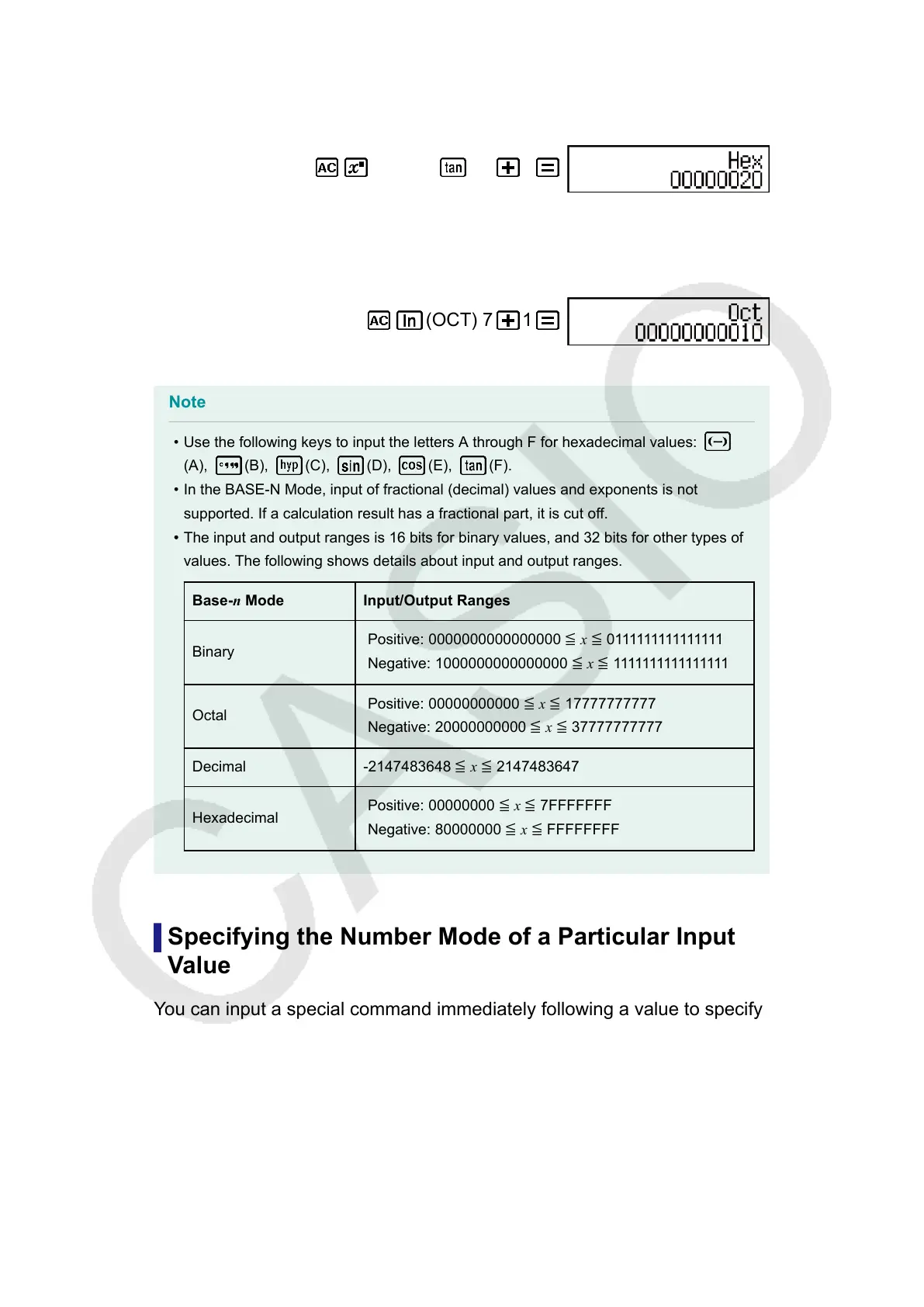
Example 2: Continuing from above, switch to the hexadecimal mode and
calculate 1F
16
+ 1
16
(HEX) 1 (F) 1
Example 3: Continuing from above, switch to the octal mode and
calculate 7
8
+ 1
8
(OCT) 7 1
Note
• Use the following keys to input the letters A through F for hexadecimal values:
(A), (B), (C), (D), (E), (F).
• In the BASE-N Mode, input of fractional (decimal) values and exponents is not
supported. If a calculation result has a fractional part, it is cut off.
•
The input and output ranges is 16 bits for binary values, and 32 bits for other types of
•
values. The following shows details about input and output ranges.
Base-n Mode
Input/Output Ranges
Binary
0000000000000000 ≦ x ≦ 0111111111111111
1000000000000000 ≦ x ≦ 1111111111111111
Octal
00000000000 ≦ x ≦ 17777777777
20000000000 ≦ x ≦ 37777777777
Decimal
-2147483648 ≦ x ≦ 2147483647
Hexadecimal
Specifying the Number Mode of a Particular Input
Value
You can input a special command immediately following a value to specify
the number mode of that value. The special commands are: d (decimal), h
(hexadecimal), b (binary), and o (octal).
Example: To calculate 10
10
+ 10
16
+ 10
2
+ 10
8
and display the result as a
decimal value
47

 Loading...
Loading...











