Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor DEVELOPER’S QUICK START GUIDE
23
The code shown below is an example of a single host CPU thread attempting to offload the reduction code to
the Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor using OpenMP in the offload construct.
float OMP_reduction(float *data, int size)
{
float ret = 0;
#pragma offload target(mic) in(size) in(data:length(size))
{
#pragma omp parallel for reduction(+:ret)
for (int i=0; i<size; ++i)
{
ret += data[i];
}
}
return ret;
}
Code Example 5: C/C++: Using OpenMP in Offloaded Reduction Code
real function FTNReductionOMP(data, size)
implicit none
integer :: size
real, dimension(size) :: data
real :: ret = 0.0
!dir$ omp offload target(mic) in(size) in(data:length(size))
!$omp parallel do reduction(+:ret)
do i=1,size
ret = ret + data(i)
enddo
!$omp end parallel do
FTNReductionOMP = ret
return
end function FTNReductionOMP
Code Example 6: Fortran: Using OpenMP* in Offloaded Reduction Code
Parallel Programming on the Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor: OpenMP* + Intel® Cilk™ Plus
Extended Array Notation
The following code sample further extends the OpenMP example to use Intel Cilk Plus Extended Array
Notation. In the following code sample, each thread uses the Intel Cilk Plus Extended Array Notation
__sec_reduce_add() built-in reduction function to use all 32 of the Intel® MIC Architecture’s 512-bit vector
registers to reduce the elements in the array.
float OMPnthreads_CilkPlusEAN_reduction(float *data, int size)
{
float ret=0;
#pragma offload target(mic) in(data:length(size))
{

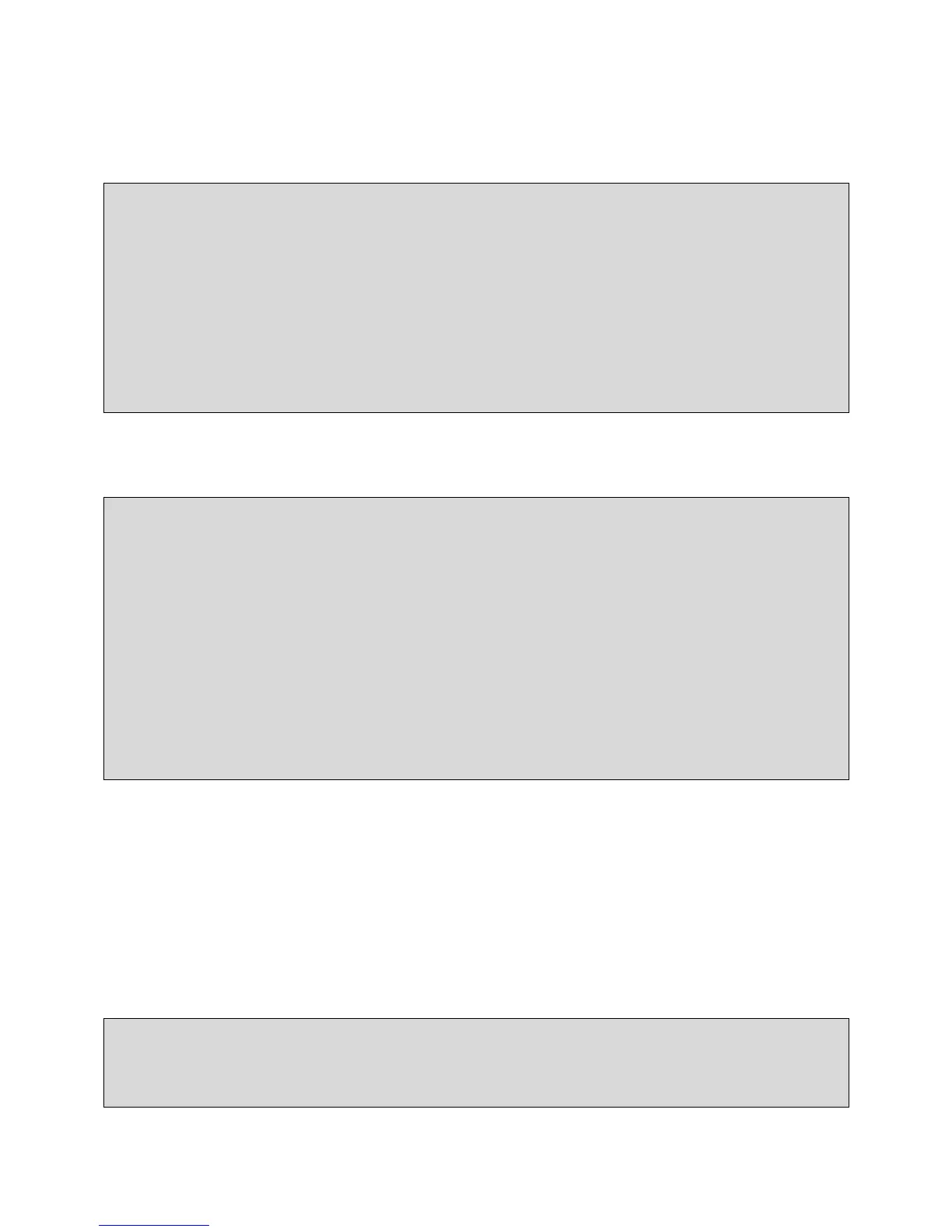 Loading...
Loading...











