Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor DEVELOPER’S QUICK START GUIDE
27
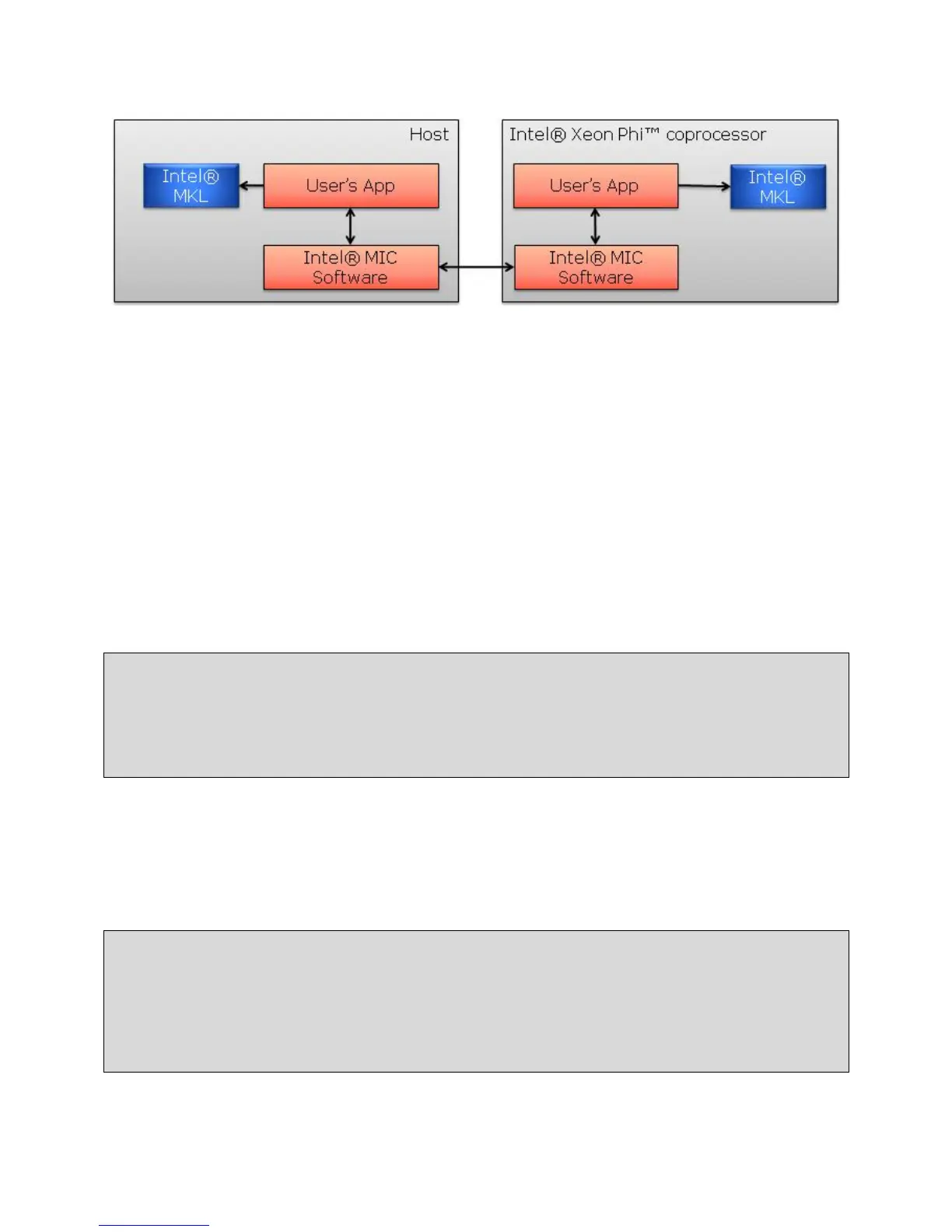
Figure 3.1: Using MKL Native Acceleration with Offload
SGEMM Sample
Using SGEMM routine from BLAS library
Sample Code – sgemm
Step 1: Initialize the matrices, which in this example need to be global variables to make use of data
persistence.
Step 2: Send the data over to the Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor using #pragma offload. In this
example, the free_if(0) qualifier is used to make the data persistent on the Intel® Xeon Phi™
Coprocessor.
#define PHI_DEV 0
#pragma offload target(mic:PHI_DEV) \
in(A:length(matrix_elements) free_if(0)) \
in(B:length(matrix_elements) free_if(0)) \
in(C:length(matrix_elements) free_if(0))
{
}
Code Example 14: Sending the Data to the Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor
Step 3: Call sgemm inside the offload section to use the “Native Acceleration” version of Intel® MKL on
the Intel® Xeon Phi™ Coprocessor. The nocopy() qualifier causes the data copied to the card in step 2
to be reused.
#pragma offload target(mic:PHI_DEV) \
in(transa, transb, N, alpha, beta) \
nocopy(A: alloc_if(0) free_if(0)) nocopy(B: alloc_if(0) free_if(0)) \
out(C:length(matrix_elements) alloc_if(0) free_if(0)) // output data
{
sgemm(&transa, &transb, &N, &N, &N, &alpha, A, &N, B, &N,
&beta, C, &N);
}
Code Example 15: Calling sgemm Inside the Offload Section
 Loading...
Loading...











