ENGLISH
22
MAINTENANCE WORK ON CHASSIS AND ENGINE
»
1
2
3
5 mm
min.
1 mm
4
5
1
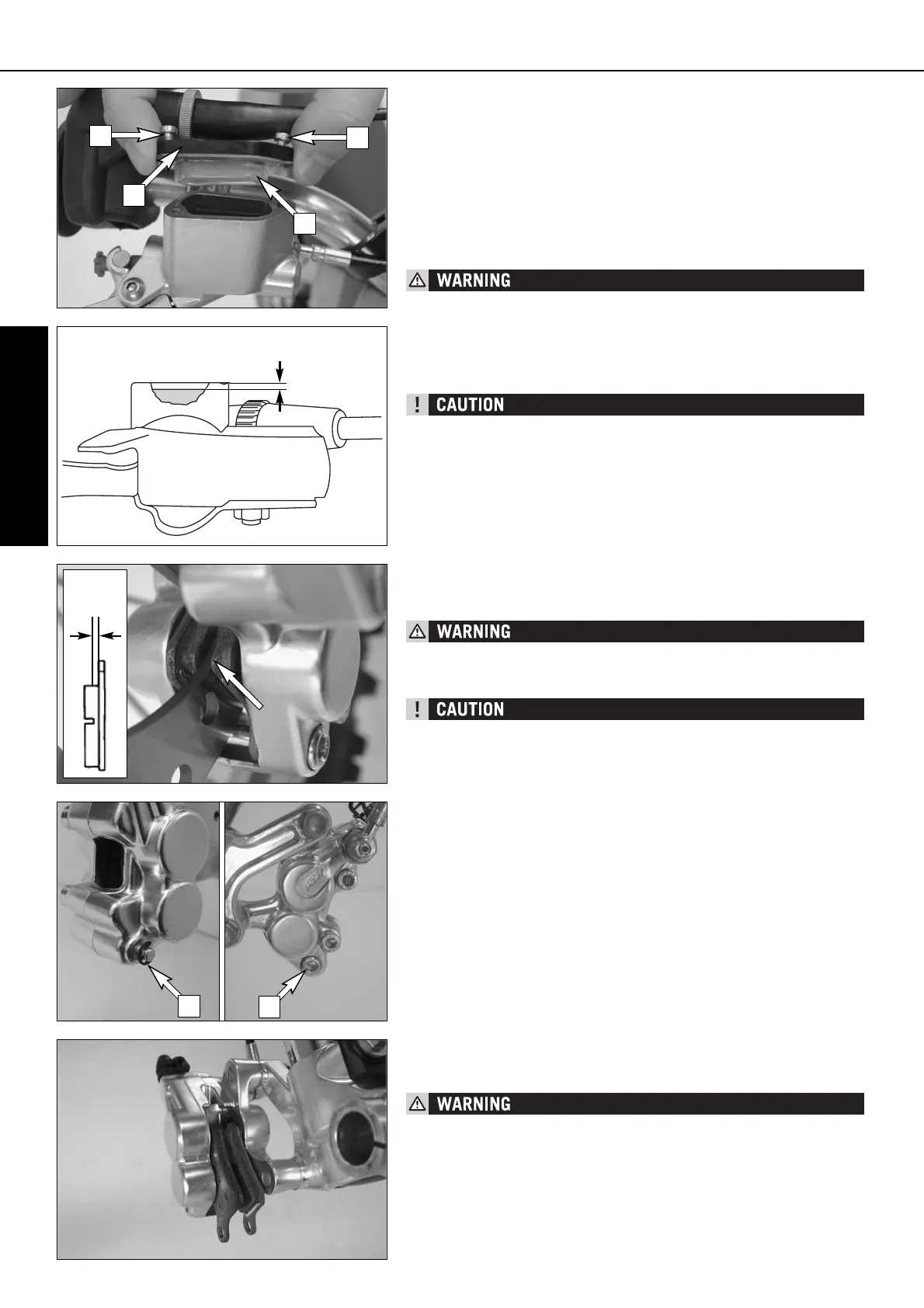
Checking the brake fluid level/ refilling *
The brake fluid reservoir is combined with the hand brake cylinder on the
handlebar. To check the brake fluid level, press the brake pistons back into
the basic position. Move the hand brake cylinder in a horizontal position, remove
the screws [1] and the cover [2] with the diaphragm [3]. The brake fluid level
should be 5 mm below the upper edge of the reservoir (see drawing),
otherwise add DOT 5.1 brake fluid (e.g. Motorex Brake Fluid DOT 5.1) up to
5 mm below the upper edge of the reservoir.
Mount the diaphragm, the cover and the screws and actuate the hand brake
lever until you feel the point of pressure again. Wipe off any overflowing or
spilled brake fluid with water.
– Actuate the hand brake lever until you feel the point of pressure again.
– Never use DOT 5 brake fluid! It is based on silicone oil and of a purple
color. Seals and brake hoses must be especially adapted to it.
– Store brake fluid out of reach of children.
– Brake fluid can cause skin irritation. Avoid contact with skin and eyes. If you
get brake fluid in your eyes, rinse with plenty of water and consult a doctor.
– Don’t let brake fluid get in contact with paint, it is an effective paint remover.
– Use only clean brake fluid taken from a tightly sealed container.
Checking front brake pads
Inspect the brake pads from in front of the vehicle. The linings must be at
least 1 mm (0.04 in) thick.
At their most worn point brake pad linings should not be thinner than 1 mm
(0.04 in), otherwise they could lead to brake failure. For your own safety don’t
put off having your brake pads changed.
If the brake pads are replaced too late so that the lining is partly or entirely
worn, the steel components of the brake pad will rub against the brake disc,
thereby imparing the braking effect and destroying the brake disc.
Replacing the front brake pads *
Remove the front wheel (see front wheel chapter).
Press brake shoes apart with a suitable screwdriver to put the brake pistons
in their basic position.
Remove the lock washer [4] from the screw as well as fixing screw [5] and
take the brake shoes out of the brake caliper. Clean brake caliper thoroughly
with compressed air.
Mount the right brake shoe and fix with screw. Mount the left brake shoe and
tighten the screw to 4 Nm. Mount the lock washer. Align brake shoes, mount
front wheel (see chapter: Mounting the front wheel).
– It is very important to keep the brake disk free from oil and fatty matters.
Otherwise, the braking effect would be strongly reduced.
– After assembly, check if circlips have been fitted correctly.
– Do not unscrew any other screws on the brake caliper or you will have to
bleed the brake system.
– After working on the brake system always operate the hand brake lever to
apply the brake pads to the brake disk and create a point of pressure.