01A01-21
MF 400 Xtra
Introduction
01
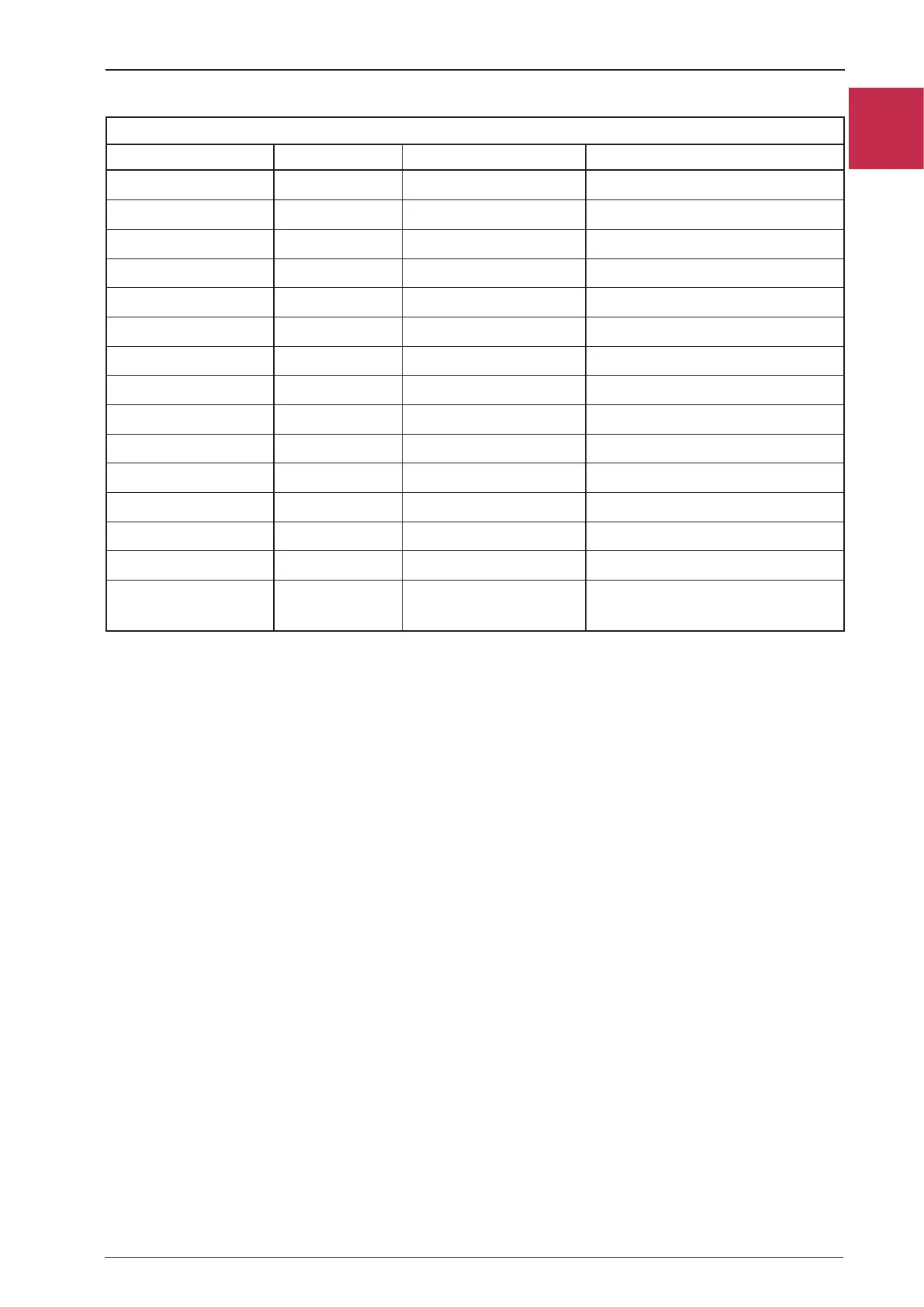
2. Equivalence between units - Imperial and SI systems
Quantities Units
IMPERIAL SYSTEM INTERNATIONAL SYSTEM - SI PRACTICAL OR DERIVED UNITS
Distance foot m mm, cm, km
Area foot³ m² mm², cm², km², ha, alqueire...
Volume foot³ m³ mm³, cm³, l, gallon
Mass lb kg g
Specific mass lb/foot³ kg/m³ g/cm³, g/l, kg/l
Specific volume foot³/lb m³/kg cm³/g, l/kg
Power lbf newton - N kgf, dyne
Speed foot/s m/s km/h, m/min
Speed grad/s rad/s rpm, rps
Torque lbf.foot N.m m.kgf, cm.kgf
Ideal pressure lbf/foot² N/m² (or Pa kgf/m², kgf/cm², kgf/mm²
Flow rate foot³/s m³/s m³/h, l/h, l/min, l/s
Time s s min, h
Energy lbf.foot J kgf.m
Power Btu W hp, cv
3. Prefixes of technical units
To form multiples or sub-multiples of a base unit,
simply add the desired prefix/symbol in front of
it.
To multiply the unit volt by 1000: kilo + volt =
kilovolt and k + V = kV.
To divide the unit volt by 1000: milli + volt
= millivolt and m + V = mV.
These prefixes can also be used with non-SI
units:
millibar, kilocalorie, megaton, hectoliter, etc
For historical reasons, the name of the basic unit
of mass has a prefix: kilogram. For this reason,
multiples and submultiples of this unit are
formed using the gram.

 Loading...
Loading...











