15
METAL CUTTING
When cutting metal, always clamp down the material. Be careful to move the saw along slowly. Use
lower speeds. Do not twist, bend, or force the blade. If the saw jumps or bounces, use a blade with
finer teeth. If the blade is clogged when cutting soft metal, use a blade with coarser teeth.
For easier cutting, lubricate the blade with a stick of cutting wax, if available, or use cutting oil when
cutting steel. Never use gasoline!! Thin metal should be sandwiched between two pieces of wood or
tightly clamped onto a single piece of wood (wood on top of the metal). Draw the cut lines or design on
the top piece of wood.
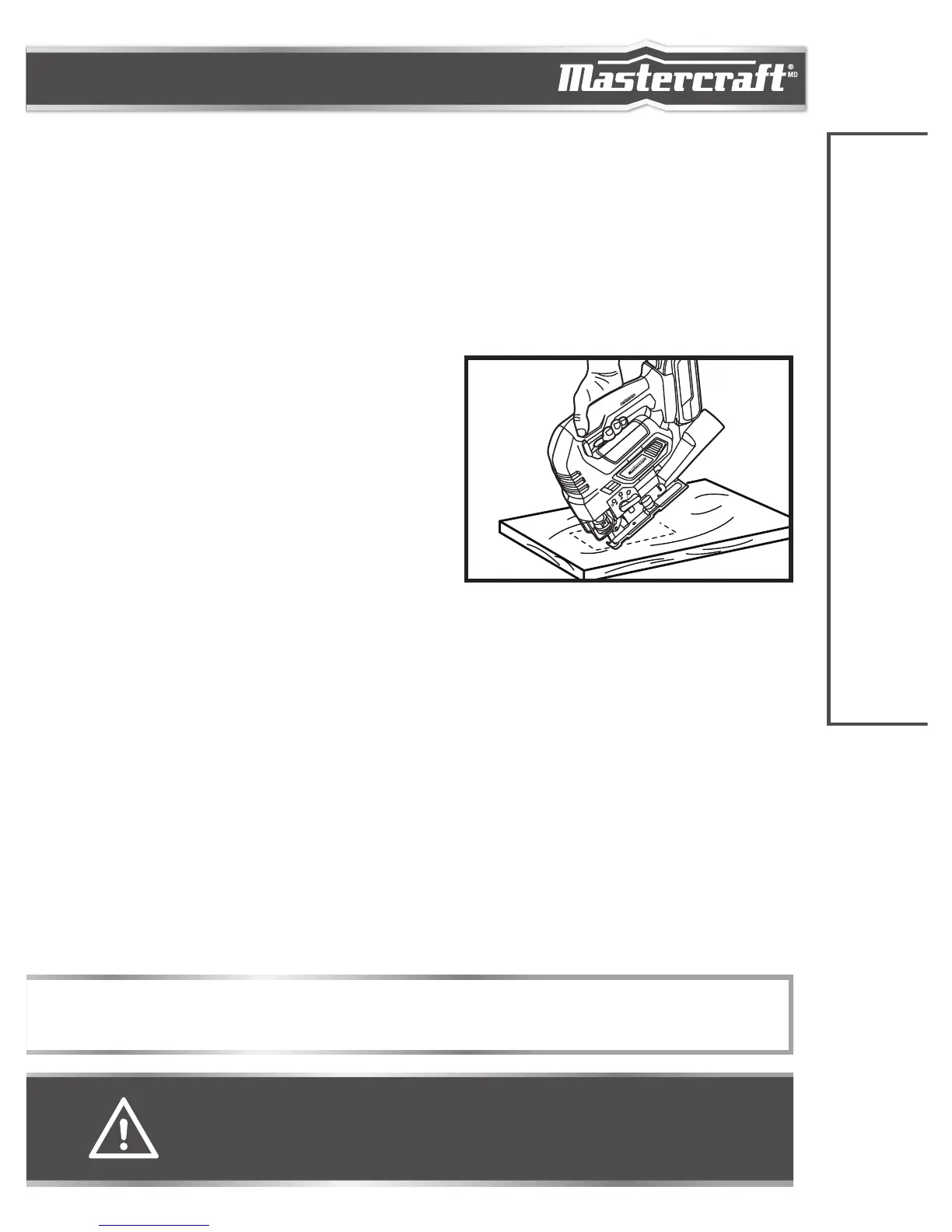
PLUNGE CUTTING
(fig 10)
Plunge cutting is useful and time-saving for making
rough openings in soft materials. It makes it
unnecessary to drill a hole for an inside or pocket cut.
1. Draw cutting lines for the opening.
2. Hold the saw firmly and tilt it forward so the toe of the
shoe plate rests on the workpiece.
3. Make sure that the blade is well clear of the workpiece.
4. With the toe of the shoe plate held firmly against the
workpiece to prevent side wobble, start the saw and then gradually lower the blade into the workpiece.
5. When the blade touches the workpiece, continue pressing down on the toe of the shoe plate.
6. Slowly pivot the saw like a hinge until the blade cuts through the workpiece and the shoe plate rests flat on
the workpiece.
7. Then begin sawing in the usual manner along the cut line.
OPERATING INSTRUCTIONS
WARNING!
• Before attempting to use this tool, become familiar with all of its operating features and safety requirements.
• Always securely and support the workpiece. Always maintain proper control of the jigsaw. Failure to clamp and
support the workpiece and loss of control of the saw could result in serious injury.

 Loading...
Loading...