21
Basic Concepts Section 2-1
2-1-2 Basic Information on Instructions
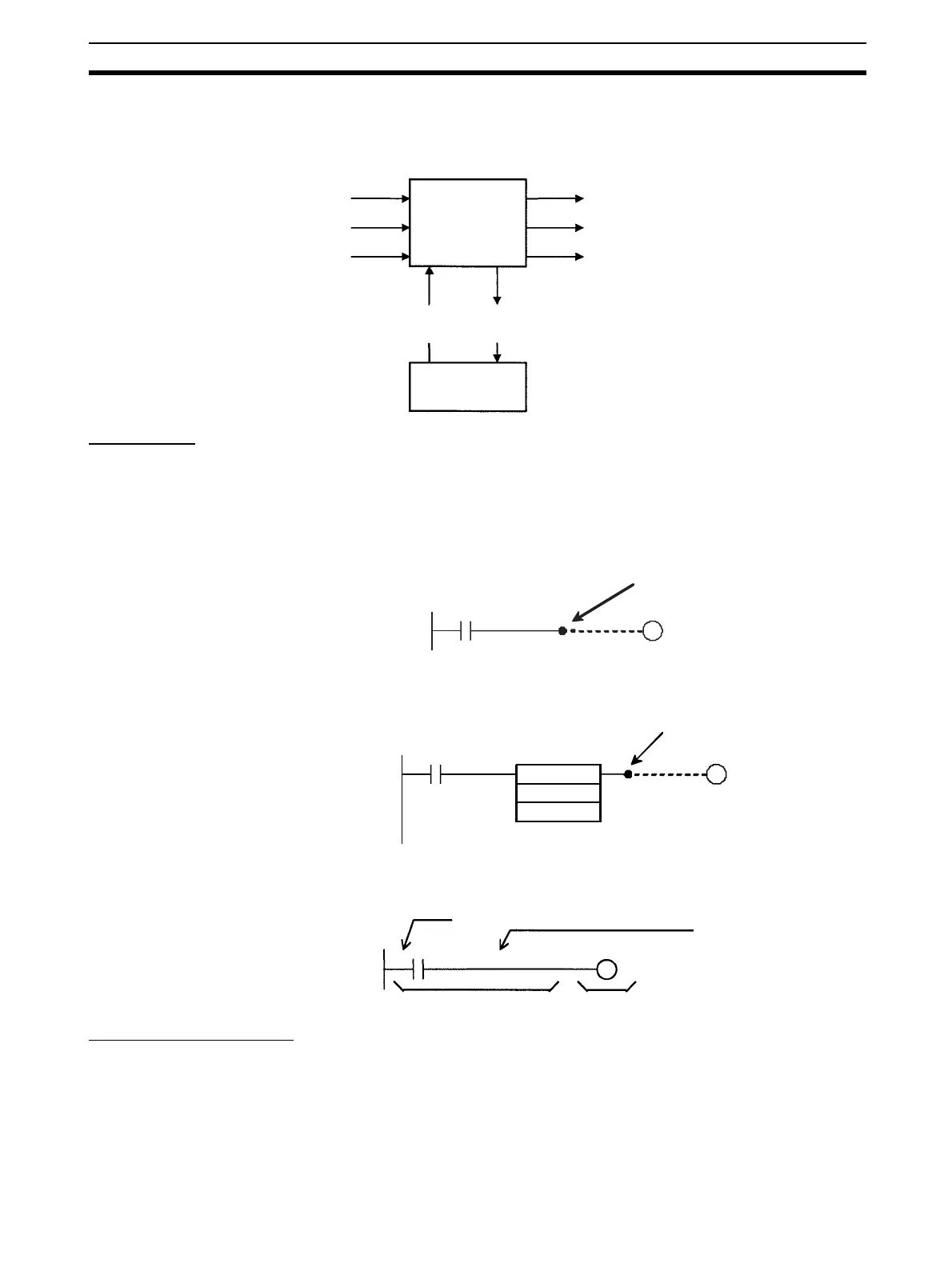
Programs consist of instructions. The conceptual structure of the inputs to and
outputs from an instruction is shown in the following diagram.
Power Flow
The power flow is the execution condition that is used to control the execute
and instructions when programs are executing normally. In a ladder program,
power flow represents the status of the execution condition.
Input Instructions • Load instructions indicate a logical start and outputs the execution condi-
tion.
• Intermediate instructions input the power flow as an execution condition
and output the power flow to an intermediate or output instruction.
Output Instructions Output instructions execute all functions, using the power flow as an execution
condition.
Instruction Conditions
Instruction conditions are special conditions related to overall instruction exe-
cution that are output by the following instructions. Instruction conditions have
a higher priority than power flow (P.F.) when it comes to deciding whether or
not to execute an instruction. An instruction may become not be executed or
may act differently depending on instruction conditions. Instruction conditions
Power flow (P.F., execution condition)
Instruction condition
Flags
Operands
(sources)
Operands
(destinations)
Memory
Instruction
*1: Input instructions only.
*2: Not output for all instructions.
Power flow (P.F., execution condition)*
1
Instruction condition*
2
Flag
Outputs the
execution condition.
=
D00000
#1215
Outputs the
execution condition.
LD power flow
Input block Output block
Power flow for
output instruction

 Loading...
Loading...










