02.00 Function descriptions
SIEMENS AG 6RX1700-0AD76 9-11
SIMOREG DC Master Operating Instructions
9.4.1 Definitions
Ramp-up = Acceleration from low, positive to high, positive speeds (e.g. from 10% to 90%) or from
low, negative to high, negative speeds (e.g. from -10% to -90%)
Ramp-down =Deceleration from high, positive to low, positive speeds (e.g. from 90% to 10%) or from
high, negative to low, negative speeds (e.g. from -90% to -10%)
On transition from negative to positive speeds, e.g. -10% to +50%:
From -10% to 0 = ramp-down and
From 0 to +50% = ramp-up and vice versa
Ramp-up time refers to the time required by the ramp-function generator to reach the 100% output
value, with a lower and upper transition rounding of 0 and a step change in the input
quantity from 0 to 100% or from 0 to -100%. The rate of rise at the output is the same in
response to smaller step changes in the input quantity.
Ramp-down time refers to the time required by the ramp-function generator to reach the 100% output
value, with a lower and upper transition rounding of 0 and a step change in the input
quantity from 100% to 0 or from -100% to 0. The rate of rise at the output is the same in
response to smaller step changes in the input quantity.
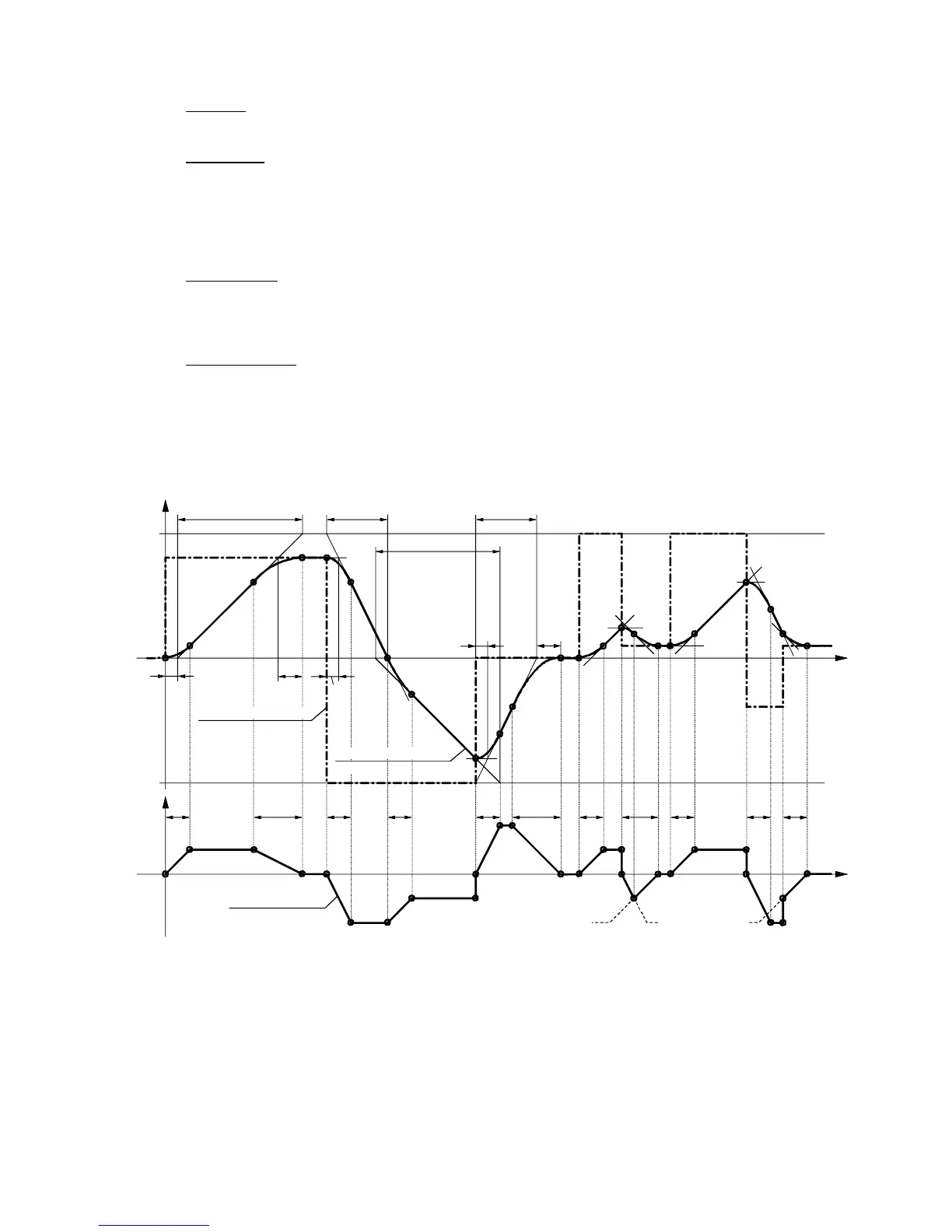
9.4.2 Operating principle of ramp-function generator
HLZ
HLZ
RLZ RLZ
AR
ER
AR 1)
AR AR ARER
2) AR
3)
AR/2 ER/2
AR/2
AR/2 ER/2
(K0192)
(K0190)
K0190
K0192
100%
-100%
K0191
(dv/dt)
t
t
dy/dt (K0191)
Ramp generator setpoint
Ramp generator outout
HLZ ... Ramp-up time (H303, H307, H311), RLZ ... Ramp-down time (H304, H308, H312)
AR ... Lower transition rounding (H305, H309, H313), ER ... Upper transition rounding (H306, H310, H314)
1) Transition from ramp-down gradient to ramp-up gradient
2) The lower rounding switches to the upper rounding before the maximum ramp-down gradient is reached
3) Due to the input step change, only the last part of the upper transition rounding is executed here

 Loading...
Loading...











