page 11808D turning and milling Service guide
车削与铣削
车削与铣削车削与铣削
车削与铣削 第
第第
第页
页页
页 服务指南
服务指南服务指南
服务指南
硬件故障
硬件故障硬件故障
硬件故障
服务案例
服务案例服务案例
服务案例
检查机床数据 MD30200 设置(主轴有编码器设为 , 无编码器设为 )
检查连接线之间是否存在干扰(强弱电连接线最好分开)
若故障为:主轴无法转动 / PPU 屏幕提示“等待主轴”
故障现象描述
故障现象描述故障现象描述
故障现象描述:
1.主轴无法转动 / PPU 屏幕提示等待主轴,且屏幕中无报警提示。
2.屏幕有主轴数值,实际主轴不动,且屏幕中无报警提示。
3.主轴转度不稳定(时快时慢)
诊断步骤
检查 PPU 后侧主轴接口 X54
1.接口是否松动或损坏
2.启动主轴后用万用表测量 X54 的引脚 1 和
9,观察是否有电压输出
检查 主轴与变频器的连接电缆是否完好
如果上述检查之后故障仍然存在,则很可能是系统主板 (PPU) 损坏,需要
进行更换或维修
若故障为:屏幕有主轴转速数值,实际主轴不动
检查机床数据 MD30130 / MD30240 / MD30134 / MD32250 / MD32260 /
MD35150 的设置是否正确
1.MD30130=1 / MD30240=2
2.MD30134 → 主轴输出极性(可在 0~2 之间设置)
0 →双极性,1 / 2 → 单极性(由实际情况确定)
3.MD32250=100 / MD32260与实际电机额定转速保持一致
情况1
检查所使用的主轴变频器是否出现故障
情况2
若故障为:主轴转度不稳定(时快时慢)
情况3
检查 PPU 后侧 X54 接口
1.接线是否松动
2.是否接触不良
检查主轴变频器连接线是否松动 / 变频器是否故障
主轴故障
主轴故障主轴故障
主轴故障
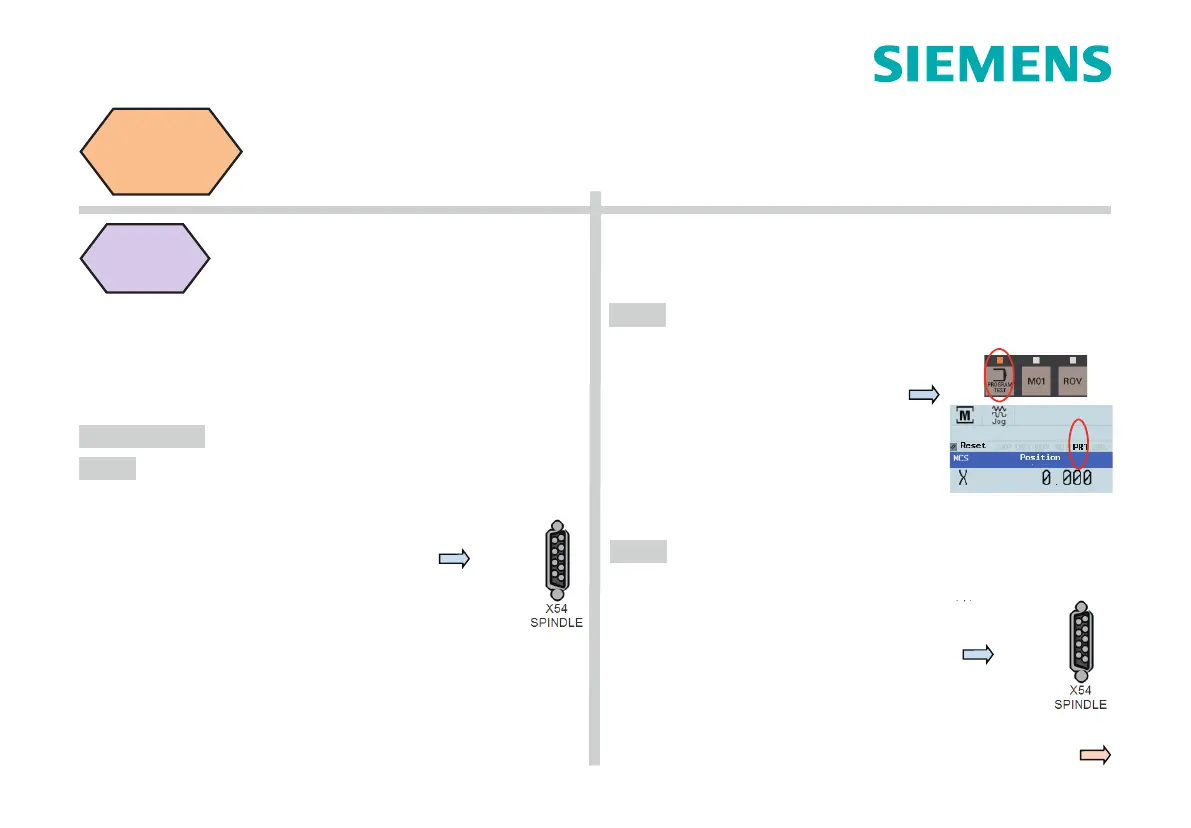
检查 PPU 上是否处于程序测试状态
1.MCP 上的“程序测试”按键指示灯是
否点亮(不可点亮)
2.PPU 屏幕上“PRT”指示符是否激活
(不可激活)
如故障仍存在,可根据“情况”中提及的检查步骤顺次进行检查
车削与铣削
车削与铣削车削与铣削
车削与铣削 第
第第
第页
页页
页 服务指南
服务指南服务指南
服务指南
硬件故障
硬件故障硬件故障
硬件故障
服务案例
服务案例服务案例
服务案例
检查机床数据 MD30200 设置(主轴有编码器设为 , 无编码器设为 )
检查连接线之间是否存在干扰(强弱电连接线最好分开)
若故障为:主轴无法转动 / PPU 屏幕提示“等待主轴”
故障现象描述
故障现象描述故障现象描述
故障现象描述:
1.主轴无法转动 / PPU 屏幕提示等待主轴,且屏幕中无报警提示。
2.屏幕有主轴数值,实际主轴不动,且屏幕中无报警提示。
3.主轴转度不稳定(时快时慢)
诊断步骤
检查 PPU 后侧主轴接口 X54
1.接口是否松动或损坏
2.启动主轴后用万用表测量 X54 的引脚 1 和
9,观察是否有电压输出
检查 主轴与变频器的连接电缆是否完好
如果上述检查之后故障仍然存在,则很可能是系统主板 (PPU) 损坏,需要
进行更换或维修
若故障为:屏幕有主轴转速数值,实际主轴不动
检查机床数据 MD30130 / MD30240 / MD30134 / MD32250 / MD32260 /
MD35150 的设置是否正确
1.MD30130=1 / MD30240=2
2.MD30134 → 主轴输出极性(可在 0~2 之间设置)
0 →双极性,1 / 2 → 单极性(由实际情况确定)
3.MD32250=100 / MD32260与实际电机额定转速保持一致
情况1
检查所使用的主轴变频器是否出现故障
情况2
若故障为:主轴转度不稳定(时快时慢)
情况3
检查 PPU 后侧 X54 接口
1.接线是否松动
2.是否接触不良
检查主轴变频器连接线是否松动 / 变频器是否故障
主轴故障
主轴故障主轴故障
主轴故障
检查 PPU 上是否处于程序测试状态
1.MCP 上的“程序测试”按键指示灯是
否点亮(不可点亮)
2.PPU 屏幕上“PRT”指示符是否激活
(不可激活)
如故障仍存在,可根据“情况”中提及的检查步骤顺次进行检查
Spindle
fault
Fault description:
1. The spindle cannot move, the PPU screen shows the waiting for spindle
signal and the screen has no alarm prompt.
2. The screen has spindle values, but the actual spindle cannot move and
the screen has no alarm prompt.
3. The spindle angle of rotation is not steady (varies during rotation).
If the fault is
:
The spindle cannot move, the PPU screen shows
the waiting for spindle signal.
If the fault is
:
Th
e screen has spindle values, but the actual
spindle cannot move.
If the fault is
:
The spindle angle of rotation is not steady (varies
during rotation)
Check whether there is an interference between the connections (it is
better to separate thicker and thinner wires).
Check the interface of X54 on the back of the PPU
1.Whether the interface is loose.
2.Whether the connections have a faulty contact.
Please ch
eck whether the connection of the spindle converter is
loose or whether the converter is damaged.
Please check whether the PPU is in the program
test state.
1. Whether the indicator light of the
“
Program test
”
key on MCP is on or not (it
should not be on).
2. Whether the
“
PRT
”
indicator on the PPU
screen is activated or not (it should not be acti-
Use the diagnostic steps of
“
Case1
”
mentioned
above to check the
spindle if the fault still
exists.
Check the settings of machine data MD30200 (spindle is set to 1 if it has an
encoder, otherwise 0).
Check the spindle interface of X54 on the back of the PPU
1. Whether the interface is loose or damaged.
2. Measure pins 1 and 9 of X54 with a multi-meter after
starting the spindle, then observe if there is voltage output.
Check whether the connection cable between the PP
U,
spindle and encoder is good.
Check whether the settings of machine data MD30130/MD30240/MD30134/
MD32250/MD32260/MD35150 are correct.
1. MD30130 = 1 / MD30240 = 2
2. MD30134 - spindle output polarity (set between 0 ~ 2 )
0-dual polarity, 1/2-single polarity (depends on the actual situation)
3. MD32250 = 100 / MD32260, it is consistent with actual motor rated
speed.
Check whether the spindle converter sh
ows a fault or not.
Replacement and maintenance are necessary if the fault still exists after
the above inspection, because it is probable that the PPU is damaged.
Diagnostic steps
Case1
Case2
Case3
Service case
of hardware
fault

 Loading...
Loading...




















