18 SR 430, SR 450
: Fit the nuts (arrows) and tighten
them down firmly.
4.2.2 Vacuum Test
Oil seals tend to fail when subjected
to a vacuum, i.e. the sealing lip lifts
away from the crankshaft during the
piston's induction stroke because
there is no internal counterpressure.
A test can be carried out with pump
0000 850 1300 to detect this kind of
fault.
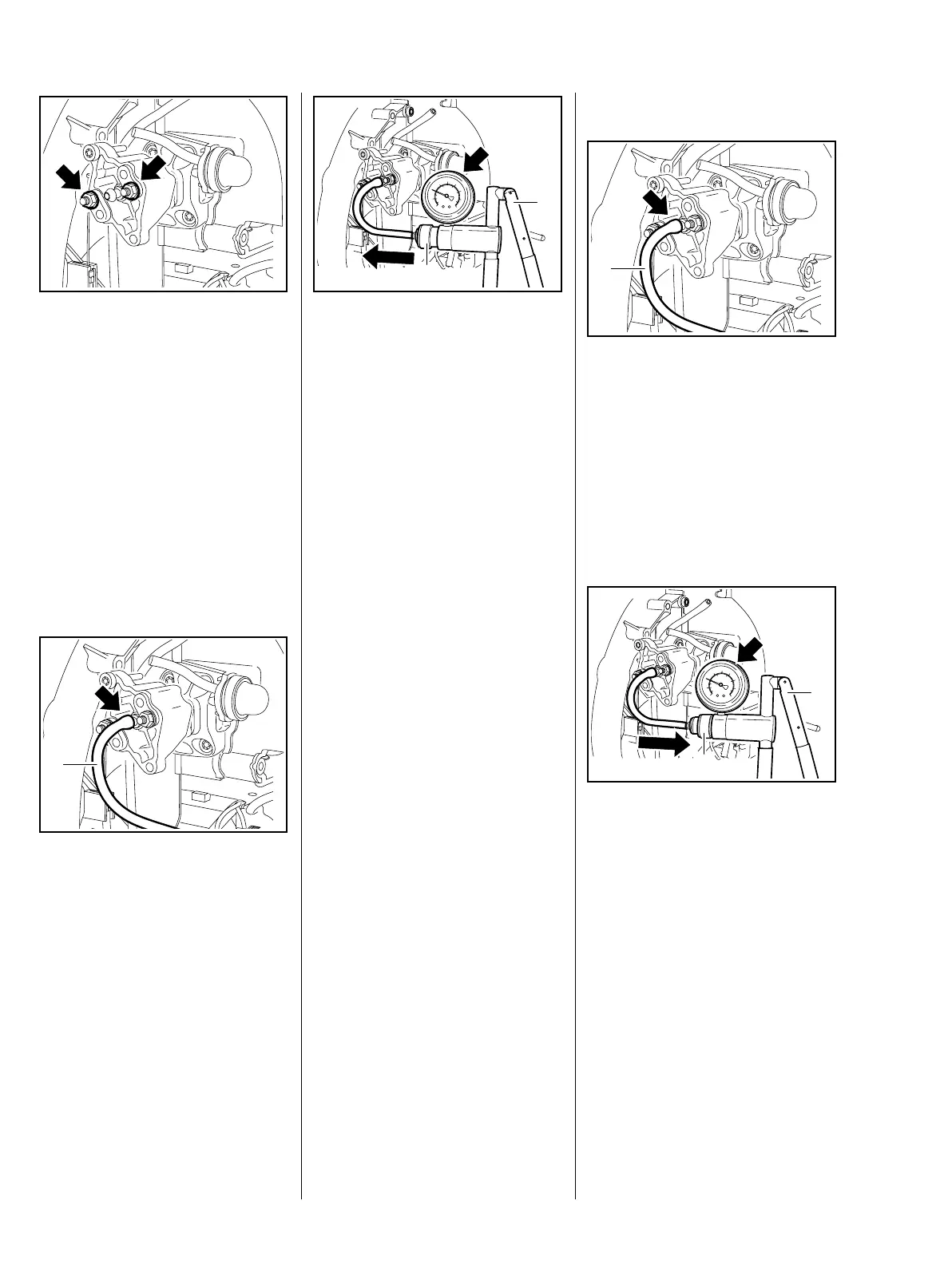
: Connect pressure hose (1) of
pump 0000 850 1300 to the
nipple (arrow).
0002RA015 TG0002RA016 TG
1
: Push ring (1) to the left.
: Operate the lever (2) until the
pressure gauge (arrow) indicates
a vacuum of 0.5 bar.
If the vacuum reading remains
constant, or rises to no more than
0.3 bar within 20 seconds, it can be
assumed that the oil seals are in
good condition.
However, if the pressure continues
to rise (reduced vacuum in the
engine), the oil seals must be
replaced, b 4.3.
– After finishing the test, push the
ring to the right to vent the pump.
– Continue with pressure test,
b 4.2.3
1
2
0002RA017 TG
4.2.3 Pressure Test
Carry out the same preparations as
for the vacuum test, b 4.2.2
– Always carry out the pressure
test after the vacuum test,
b 4.2.2
: Connect pressure hose (1) of
pump 0000 850 1300 to the
nipple (arrow).
: Push ring (1) to the right.
: Operate the lever (2) until the
pressure gauge (arrow) indicates
a pressure of 0.5 bar. If this
pressure remains constant for at
least 20 seconds, the engine is
airtight.
– If the pressure drops, the leak
must be located and the faulty
part replaced.
0002RA016 TG
1
1
2
0002RA018 TG