3. Instruction Set
API
Mnemonic Operands Function
SS2
SX2
19 D
BIN P
Convert BCD to BIN
Type
OP
Bit Devices Word devices Program Steps
X Y M S K H KnX
KnY
KnM
KnS
T C D E F
BIN, BINP: 5 steps
DBIN, DBINP: 9 steps
SS2
SX2
SS2
SX2
SS2
SX2
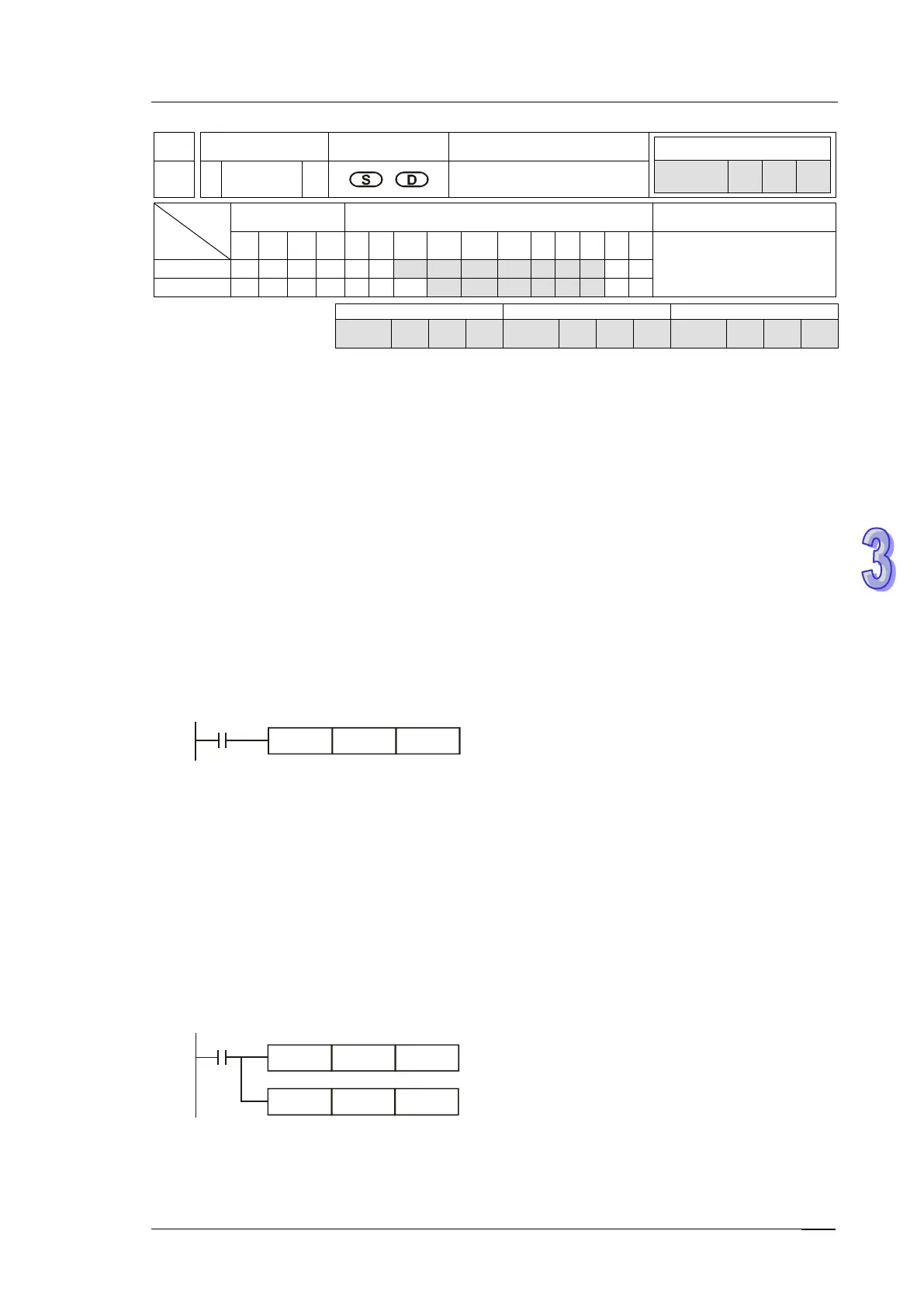
Operands:
S: Source of data D: Conversion result
Explanations:
1. The content in S (BCD value) is converted into BIN value and stored in D.
2. The valid range of source S: BCD (0 to 9,999), DBCD (0 to 99,999,999)
3. If the content of S is not a valid BCD value, an operation error will occur, error flags M1067
and M1068 = ON, and D1067 holds error code H0E18.
4. If operand S and D use index register F, only 16-bit instruction is available.
5. Flags: M1067 (Program execution error), M1068 (Execution error locked), D1067 (error code)
Program example:
When X0 = ON, the BCD value of K1M0 will be converted to BIN value and stored in D10.
Points to note:
6. When PLC needs to read an external DIP switch in BCD format, BIN instruction has to be first
adopted to convert the read data into BIN value and store the data in PLC.
7. On the contrary when PLC needs to display a value on a BCD format 7-segment displayer,
BCD instruction is required to convert the internal data into BCD value then sent the value to
the displayer.
8. When X0 = ON, the BCD value of K4X20 is converted into BIN value and sent to D100. The
BIN value of D100 will then be converted into BCD value and sent to K4Y20.
BCD D100 K4Y20
X0
BIN D100K4X20
 Loading...
Loading...