5
Bird Dual-Split type
Bird Dual-Split Type
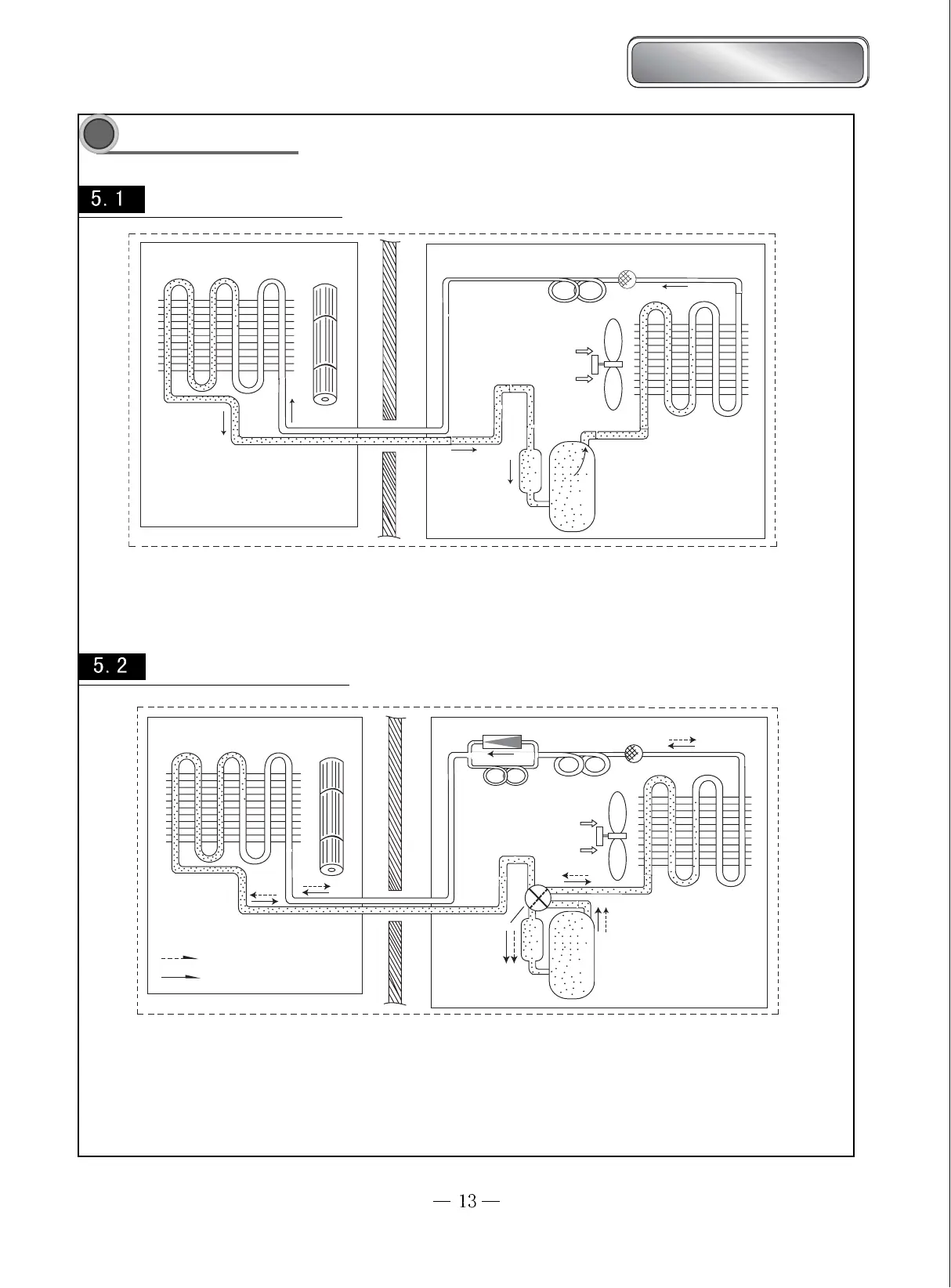
Cooling system diagram
Cooling system diagram for cooling only type
Evaporator
Cross flow fan
Filter
Capillary
Axial flow fan
Condenser
Compressor
Gas-liquid separator
When the power is on, indoor and outdoor units will start to run. The compressor sucks low-pressure refrigerant gas from the evaporator
of
indoor unit and then discharges high-temperature, high-pressure refrigerant gas into outdoor condenser. Then air exchanges the heat with outdoor air
and becomes refrigerant liquid. The liquid is throttled by the capillary and changes into low-temperature and low-pressure liquid and then flows
into indoor evaporator. Then liquid exchanges the heat with the required air and changes into low-temperature and low-pressure refrigerant gas.
The cycle introduced above goes on and on, and the demanded low temperature environment is maintained.
Cooling system diagram for cooling/heating type
Evaporator
Cross flow fan
One-way valve
Main capillary
Filter
Auxillary capillary
Axial flow fan
Condenser
E lectromagnetic
4-way valve
Gas-liquid separator
Compressor
Heating
Cooling
When the power is on, indoor and outdoor units will start to run. When the system operates in cool mode, the compressor sucks low-temperature, low-
pressure refrigerant gas from indoor evaporator and then discharges high-temperature, high-pressure refrigerant gas into outdoor heat exchanger. With
the help of axial flow fan, the gas transfers its latent heat into outdoor air and becomes high-pressure refrigerant liquid. The liquid is throttled by the
capillary and changes into low-temperature and low-pressure liquid and then flows into indoor heat exchanger. With the help of centrifugal fan, the
liquid evaporates into low-temperature refrigerant gas and indoor air is cooled down. The refrigerant gas is sucked into the compressor and the cycle
introduced above goes on and on, and the demanded low temperature environment is maintained.
When the system operates in heat mode, 4-way valve changes its way and the refrigerant flows into the reversible cycle as the cool mode. The
r
e frigerant discharges its latent heat in the indoor heat exchanger, and sucks heat from outdoor heat exchanger and forms the heat pump cycle.
T his cycle goes on and on, and the demanded high temperature environment is maintained.

 Loading...
Loading...











