RAID implementation
RAID implementation improves data storage reliability and performance.
Redundant array of independent disks (RAID) is a method of configuring multiple
drives in a storage subsystem for high availability and high performance. The
collection of two or more drives presents the image of a single drive to the system.
If a single device failure occurs, data can be read or regenerated from the other
drives in the array.
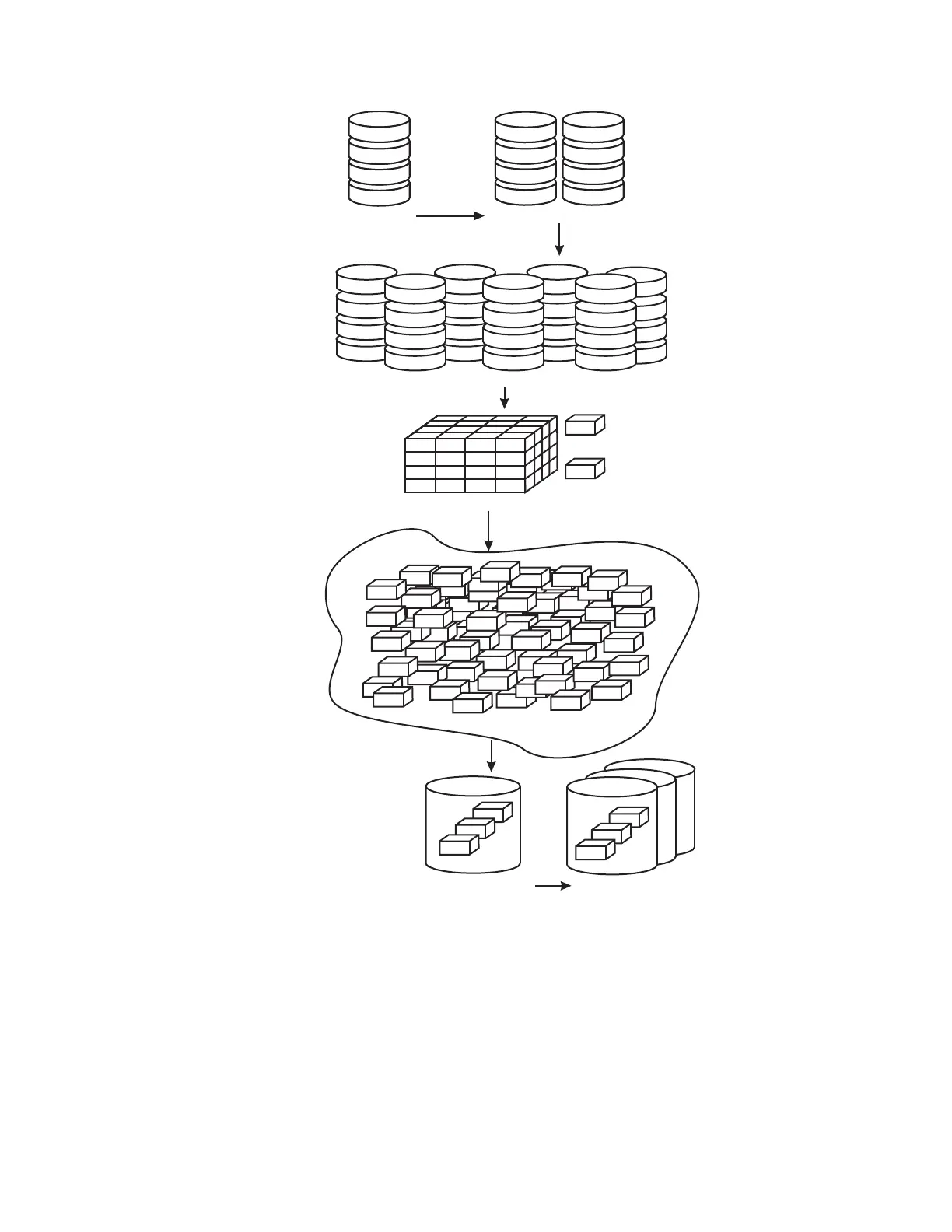
Disk
ArraySite
Array
Rank
Extents
=CKDMod1ExtentinIBM
Systemzenvironments
=FB1GBinanOpen
systemsHost
Virtualization
ExtentPool
Extents
LogicalVolume
VolumeGroup
VolumeGroups
MapHoststo
Volumes
f2d00137
Figure 10. Logical configuration sequence
Chapter 1. Overview 31
 Loading...
Loading...











