Data storage values
TS3500 Tape Library documentation displays data storage values using both
decimal (base-10) prefixes and binary (base-2) units of measurement.
Decimal units such as K, MB, GB, and TB have commonly been used to express
data storage values, though these values are more accurately expressed using
binary units such as KiB, MiB, GiB, and TiB. At the kilobyte level, the difference
between decimal and binary units of measurement is relatively small (2.4%). This
difference grows as data storage values increase, and when values reach terabyte
levels the difference between decimal and binary units approaches 10%.
To reduce the possibility of confusion, the TS3500 Tape Library documentation
represents data storage using both decimal and binary units. Data storage values
are displayed using the following format:
#### decimal unit (binary unit)
By this example, the value 512 terabytes is displayed as:
512 TB (465.6 TiB)
Table 2 compares the names, symbols, and values of the binary and decimal units.
Table 3 shows the increasing percentage of difference between binary and decimal
units.
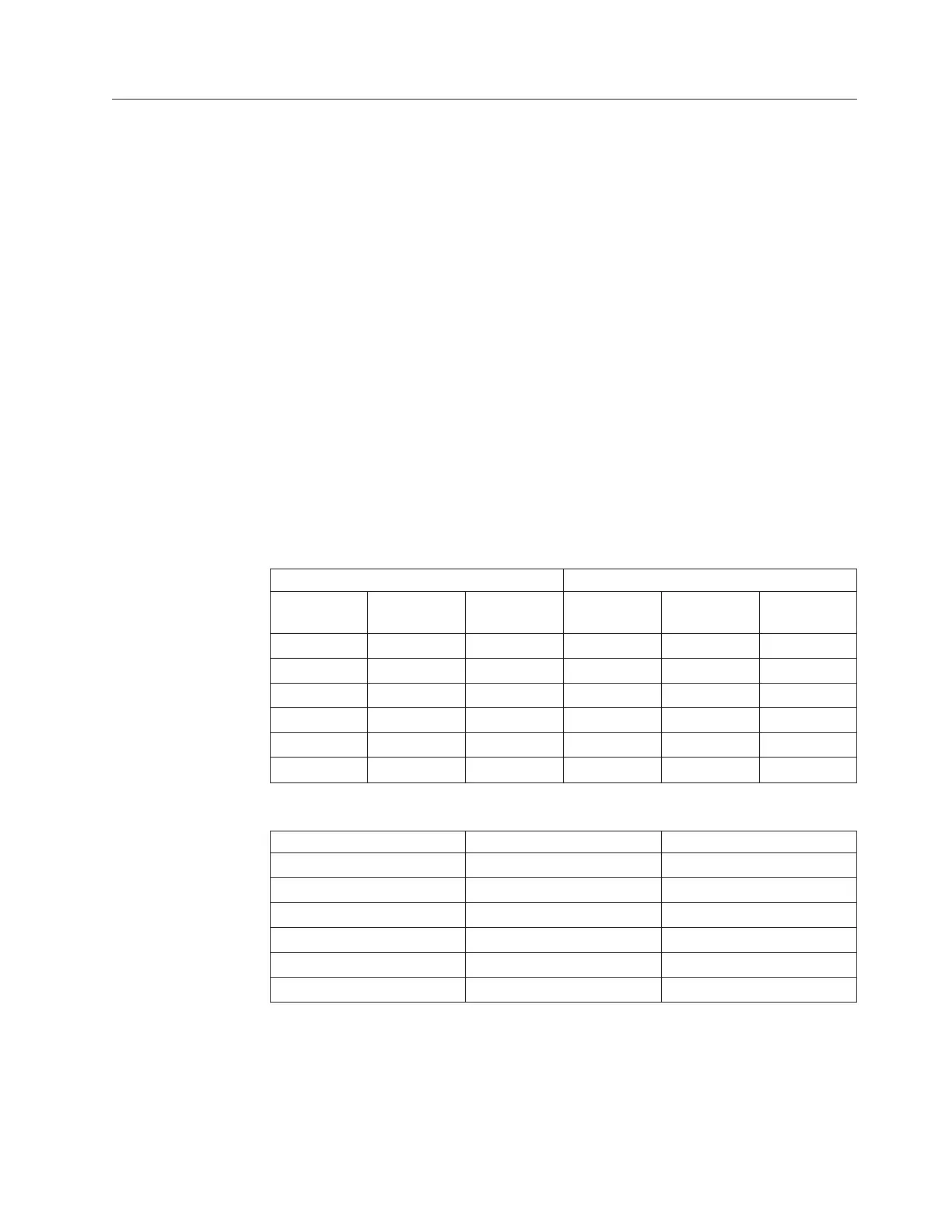
Table 2. Comparison of binary and decimal units and values
Decimal Binary
Name Symbol Value
(base-10)
Name Symbol Value
(base-2)
kilo K 10
3
kibi Ki 2
10
mega M 10
6
mebi Mi 2
20
giga G 10
9
gibi Gi 2
30
tera T 10
12
tebi Ti 2
40
peta P 10
15
pebi Pi 2
50
exa E 10
18
exbi Ei 2
60
Table 3. Percentage difference between binary and decimal units
Decimal Value Binary Value Percentage Difference
100 kilobytes (KB) 97.65 kibibytes (KiB) 2.35%
100 megabytes (MB) 95.36 mebibytes (MiB) 4.64%
100 gigabytes (GB) 93.13 gibibytes (GiB) 6.87%
100 terabytes (TB) 90.94 tebibytes (TiB) 9.06%
100 petabytes (PB) 88.81 pebibytes (PiB) 11.19%
100 exabytes (EB) 86.73 exbibytes (EiB) 13.27%
About this publication xxiii
 Loading...
Loading...











