Although the buffer does not prevent the PULL instruction from accessing elements
placed on the stack before the buffer was created, it is a way for an exec to create
a temporary extension to the stack. The buffer allows an exec to:
1. Use the QUEUE instruction to insert elements in FIFO order on a stack that
already contains elements.
2. Have temporary storage that it can delete easily with the DROPBUF command.
An exec can create multiple buffers before dropping them. Every time MAKEBUF
creates a new buffer, the REXX special variable RC is set with the number of the
buffer created. Thus if an exec issues three MAKEBUF commands, RC is set to 3
after the third MAKEBUF command.
Note: To protect elements on the stack, an exec can create a new stack with the
NEWSTACK command. For information about the NEWSTACK command,
see “Protecting Elements in the Data Stack” on page 147.
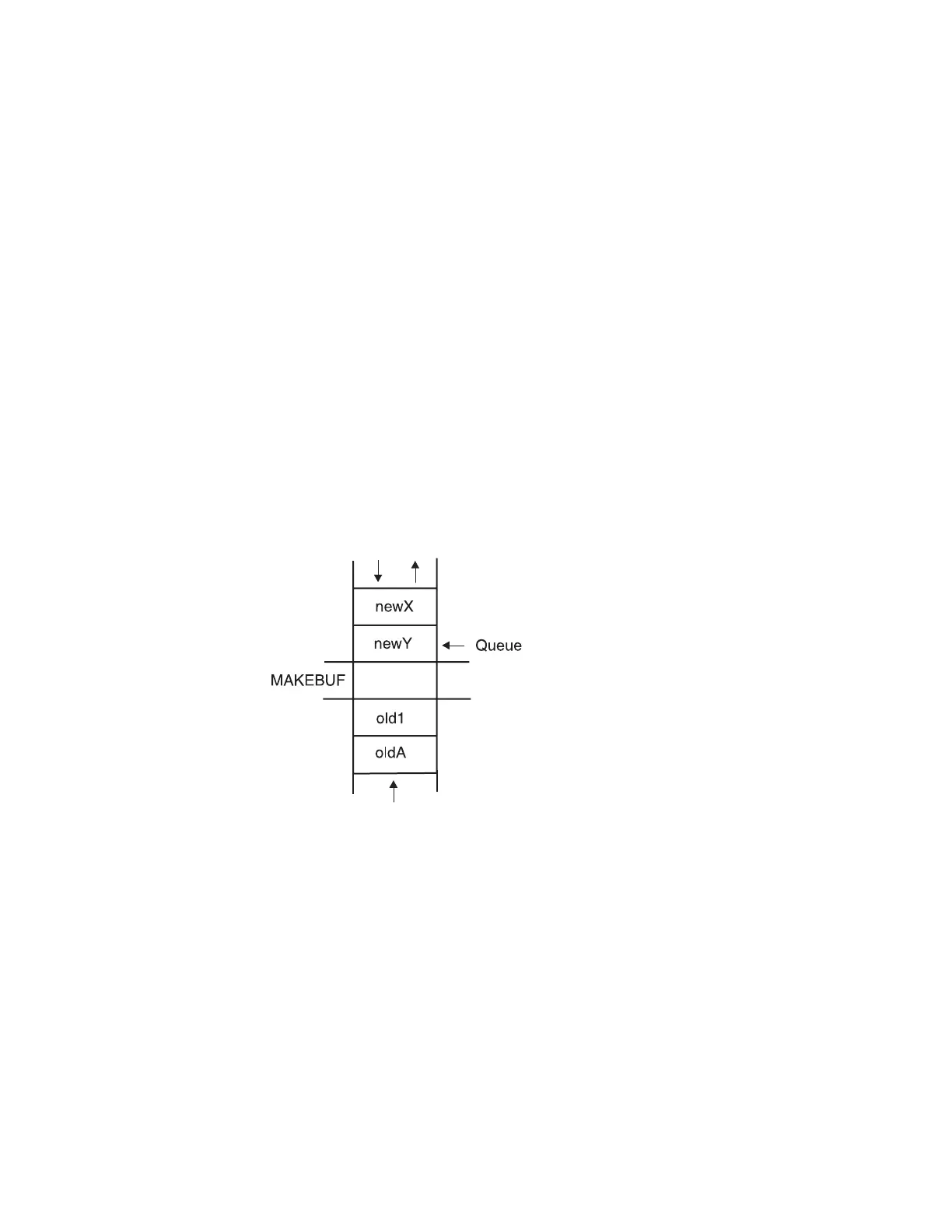
Creating a Buffer with the MAKEBUF Command
To create a buffer on the data stack before adding more elements to the stack, use
the TSO/E REXX MAKEBUF command. All elements added to the data stack after
the MAKEBUF command are placed in the buffer. Below the buffer are elements
placed on the stack before the MAKEBUF command.
Instructions that could be used to create the illustrated buffer are as follows:
'MAKEBUF'
PUSH 'newX'
QUEUE 'newY'
Removing Elements from a Stack with a Buffer
The buffer created by MAKEBUF does not prevent an exec from accessing
elements below it. After an exec removes the elements added after the MAKEBUF
command, then it removes elements added before the MAKEBUF command was
issued.
Using the previous illustration, when the exec issues three PULL instructions, the
following elements are removed from the data stack.
newX
newY
old1
Creating a Buffer on the Data Stack
Chapter 11. Storing Information in the Data Stack 143

 Loading...
Loading...











