29
EFI System
66 690 07 Rev. -- KohlerEngines.com
4. If voltage at plug was good, and there was continuity
across pump terminals, reconnect plug to pump,
making sure you have a good connection. Turn on
key switch and listen for pump to activate.
a. If pump starts, repeat steps 1 and 2 to verify
correct pressure.
b. If pump still does not operate, replace it.
Fuel Pressure Regulator
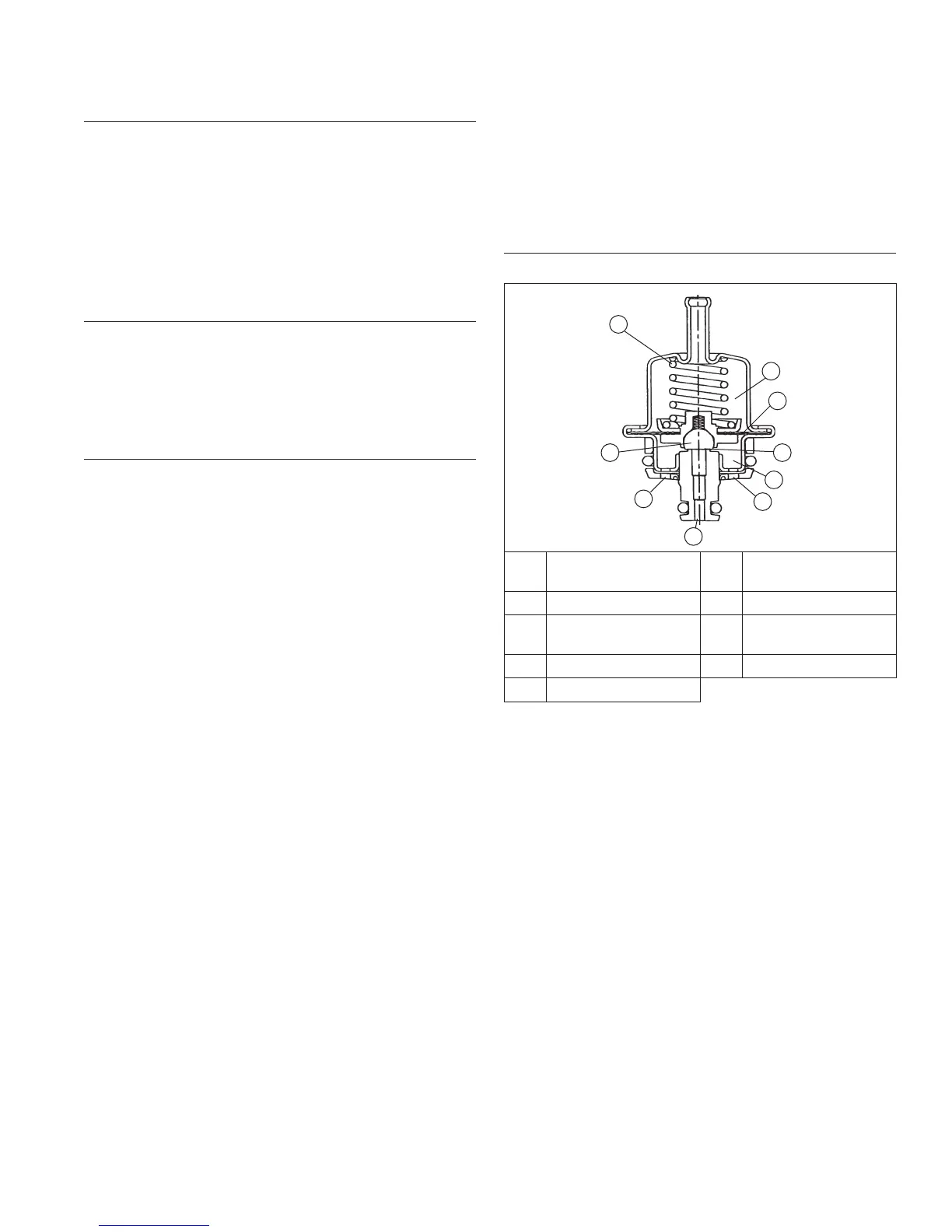
Fuel Pressure Regulator Details
B
A
C
I D
E
F
H
G
A Pressure Regulating
Spring
B Pressure Regulating
Chamber
C Diaphragm D Valve Seat
E
Fuel Chamber
F Outlet Port
(to fuel rail)
G Return Port (to tank) H Inlet Port
I
Valve
Depending on application, regulator may be located in
fuel tank along with fuel pump, or outside tank just down
line from pump. Regulator is a sealed, non-serviceable
assembly. If it is faulty, it must be separated from base/
holder assembly and replaced as follows:
1. Shut engine off, make sure engine is cool, and
disconnect negative (–) battery cable.
2. Depressurize fuel system through test valve in fuel
rail.
3. Access regulator assembly as required and clean
any dirt or foreign material away from area.
4. External Regulator:
a. Remove screws securing mounting bracket to
regulator housing. Remove O-ring and pull
regulator out of housing.
b. Remove snap ring and remove regulator from
base/holder.
Internal (In-Tank) Regulator:
Remove screws securing retaining ring and
regulator in base/holder assembly. Grasp and pull
regulator out of base/holder.
Wiring Harness
Wiring harness used in EFI system connects electrical
components, providing current and ground paths for
system to operate. All input and output signaling occurs
through a special all weather connector that attaches
and locks to ECU.
Condition of wiring, connectors, and terminal
connections is essential to system function and
performance. Corrosion, moisture, and poor connections
are more likely cause of operating problems and system
errors than an actual component.
Battery Charging System
EFI engines are equipped with either a 15 or 25 amp
charging system to accommodate combined electrical
demands of ignition system and specifi c application.
Charging system troubleshooting information is provided
in Electrical System.
FUEL COMPONENTS
Fuel Pump
Fuel pumps are non-serviceable and must be replaced
if determined to be faulty. If a fuel delivery problem
is suspected, make certain pump is being activated
through relay, all electrical connections are properly
secured, fuses are good, and a minimum of 7.0 volts
is being supplied. If during cranking, voltage drops
below 7.0 volts, a reduction of fuel pressure may occur
resulting in a lean starting condition. If required, testing
of fuel pump and relay may be conducted.
1. Connect black hose of Pressure Tester (part of EFI
Service Kit) to test valve in fuel rail. Route clear hose
into a portable gasoline container or equipment fuel
tank.
2. Turn on key switch to activate pump and check
system pressure on gauge. If system pressure of 39
psi ± 3 is observed, relay, fuel pump, and regulator
are working properly. Turn key switch off and
depress valve button on tester to relieve system
pressure.
a. If pressure is too high, and regulator is outside
tank (just down line from pump), check that return
line from regulator to tank is not kinked or
blocked. If return line is good, replace regulator
(see Regulator on page).
b. If pressure is too low, install in-line T between
pump and regulator and retest pressure at that
point. If it is too low there also, replace fuel pump.
3. If pump did not activate (step 2), disconnect plug
from fuel pump. Connect a DC voltmeter across
terminals in plug, turn on key switch and observe if a
minimum of 7 volts is present. If voltage is between
7 and 14, turn key switch off and connect an
ohmmeter between terminals on pump to check for
continuity.
a. If there was no continuity between pump
terminals, replace fuel pump.
b. If voltage was below 7, test wiring harness and
relay as covered in Electrical Relay section.

 Loading...
Loading...











