-93-
Design & installation Guide For McQuay MDS Multi System
4.4 Design, Processing and Installation of Condensated Drain Pipe
4.4.1 Design of Condensated Piping
Size selection of main pipe and vertical pipe of condensated water
Choose the pipe size according to the condensated water flow from the main pipe of indoor unit
and the following table; Suppose the condensated water flow of 1 HP is 2L/h, then the condensated
water flow of 3# 2HP and 2# 3HP is calculated as follows:
2
L/h x 2(HP) x 3(sets) +2L/h x 3(HP) x 2(sets) = 24L/h.
Note:
Suppose the moisture is 10% in the pipe.
After the header pipe, the pipe should be larger or equal to VP30.
1
/1
0
0
4HP
25
25
Air vent pipe
25
2HP
2HP
Condensate pipe
group of multiple units
30 or more
Pipe mouth facing downward
to prevent foreign matters
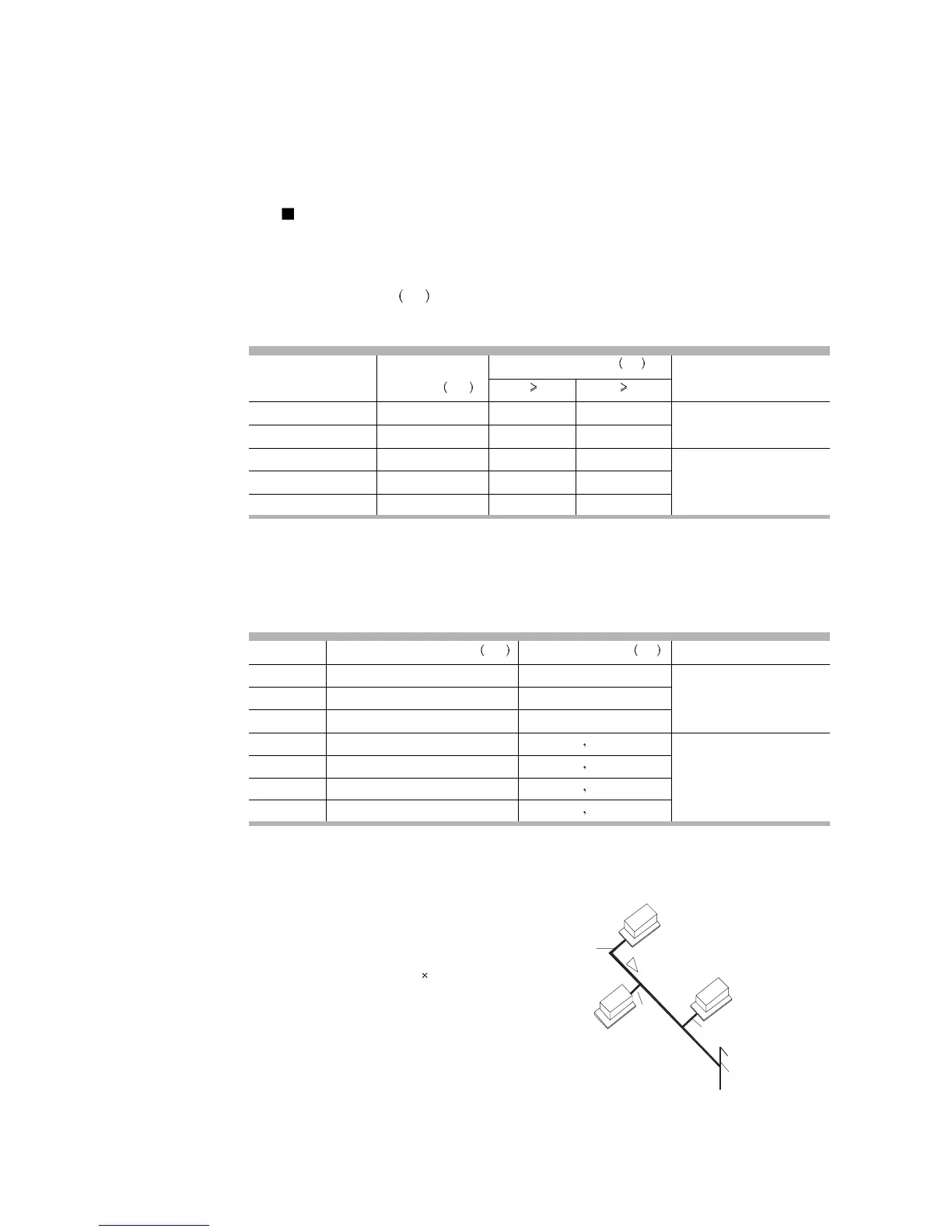
For example, The condensate pipe of one 2HP
and two 4HP indoor units are connected to a
pipe as shown on the right, and its water drain-
age capacity is:
4L/h + 8L/h 2=20L/h
So the horizontal vertical pipe diameter shall be
30 or more, and the diameter of the vertical
diameter shall not be less than that of the hori-
zontal vertical pipe.
Main horizontal pipe Vs condensated water flow rate
JIS
Polyethylene pipe allowable flow rate L/h
Remark
diameter mm slope 1/50 slope 1/100
VP20 20 39 27 unsuitable for the
VP25 25 70 50 header pipe
VP32 31 125 88
VP40 40 247 175 Suitable for the header pipe
VP50 51 473 334
Note:
The vertical pipe should be larger than VP30
Vertical pipe Vs condensated water flow rate
JIS Polyethylene pipe diameter mm allowable flow rate L/h Remark
VP20 20 220
unsuitable for
VP25 25 410
the header pipe
VP30 31 730
VP40 40 1 440
VP50 51 2 760
Suitable for the header pipe
VP65 67 5 710
VP75 77 8 280

 Loading...
Loading...