Chapter 2 Individual Operations
52
Chapter 2
Individual Operations
Filter Cube Motion Restricting Lever Functions
Lever position Filter cube switching
Position A
(push in by two
notches)
Locked
(filter cubes cannot be switched)
Position B
(push in by one
notch)
Switching between positions 1 and 2, or
between positions 3 and 4 only.
(The position at which the lever is pushed in
determines whether switching is for positions 1
and 2 or positions 3 and 4.))
Position C
(first click stop
position)
Free (switching possible)
A1
-
2
-
3
-
4
B1
-
2 / 3
-
4
C1
-
2
-
3
-
4
1
1
4
2
3
4
CUBE
A1
-
2
-
3
-
4
B1
-
2 / 3
-
4
C1
-
2
-
3
-
4
Lever position
15.2
Selecting Filters
A filter cube consists of three types of optical components: an
excitation filter (EX filter), a barrier filter (BA filter), and a dichroic
mirror (DM). Select the filter cube with the desired combination o
optical components to suit the characteristics of the specimen
and the fluorophore by referencing the properties of each filter.
You can select a combination of an excitation filter and a barrie
filter even if you are using the same excitation method.
Excitation filters, barrier filters, and dichroic mirrors can be
purchased separately.
Since excitation filters are exposed to strong light during
operations, they will deteriorate over time. Replace the filter at
intervals determined by usage.
UV-2A
EX 330-380
DM 400
BA 420
Filter cube
Spacer inside the filter cube
Some types of filter cubes cannot be inserted directly into the epi-fluorescence attachment.
Follow the procedure described in Chapter 3, Section 6 “Attaching a filter cube” to remove an internal spacer or
reverse the spacer before insertion.
Excitation filter (EX filter)
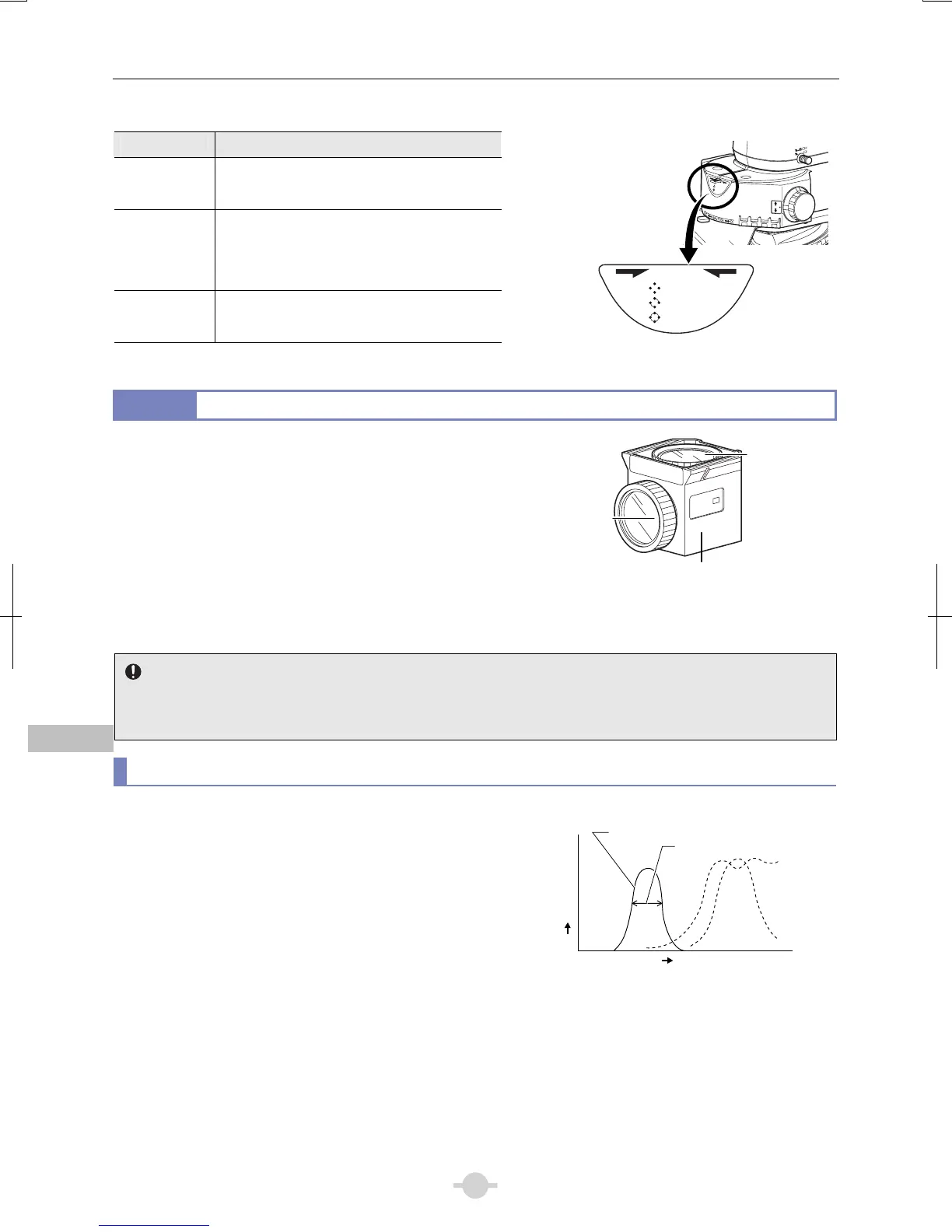
Excitation filters allow selective transmission of light (excitation
light) in the wavelength range required for fluorescent light
emissions from the specimen, blocking light of all othe
wavelengths. The range of wavelengths allowed to pass through
a filter is referred to as the bandwidth.
The bandwidth range of an excitation filter determines the
brightness of the fluorescent image, the generation o
autofluorescence (fluorescence resulting from substances othe
than the fluorophores), and degree of fading. The broader the
bandwidth, the greater the amount of excitation light irradiated
onto the specimen, thereby increasing the brightness. However,
this also increases the amount of autofluorescence and causes
faster color fading. Narrow bandwidth reduces the amount o
excitation light striking the specimen and causes the image to
appear darker, but reduces autofluorescence and fading. Fo
specimens with pronounced autofluorescence, use excitation
filters with a narrow bandwidth. (Note that this will make the
fluorescent image darker.)
Since excitation filters are exposed to strong light during
operations, they will deteriorate over time. Replace the filter at
intervals determined by usage.
EX filter bandwidth
Excitation filte
Barrier filte
Dichroic mirror (inside the cube)
EX filte
Bandwidth
Spectral
transmission
Wavelength
0

 Loading...
Loading...