orolia.com GSG-8 Getting Started Guide | 5
General Specifications
Intended Use:
Orolia GSG-8 Advanced GNSS Simulators are used to test GNSS receivers and GNSS systems by
generating GNSS signals, as they are transmitted by GNSS satellites. An RF output generates one of
the following: upper band GNSS signals, lower band GNSS signals, interference signals (including
jamming or spoofing), or additional antennas or vehicles (with SKYMUTI). A GPU provides signal
generation processing power, and an additional GPU allows more signals to be generated
simultaneously.
Power:
Line Voltage – 100-240 V
AC
, 50-60 Hz
Power Consumption – GSG-811: Idle – 80 W, Simulation – 200 W
GGG-842: Idle – 120 W, Simulation – 500 W
MAINS supply voltage fluctuations up to ±10% of the nominal voltage
Environmental:
Temperature - +0° C to +30° C (operating), -15° C to +50° C non-condensing @ 12,000 m (storage)
Humidity – 10% to 70% (non-condensing)
Altitude – max operating: 2000 m above sea level, max transport: 4,500 m above sea level
Pollution – Degree 2: Normally only nonconductive pollution occurs. Temporary conductivity caused
by condensation is to be expected.
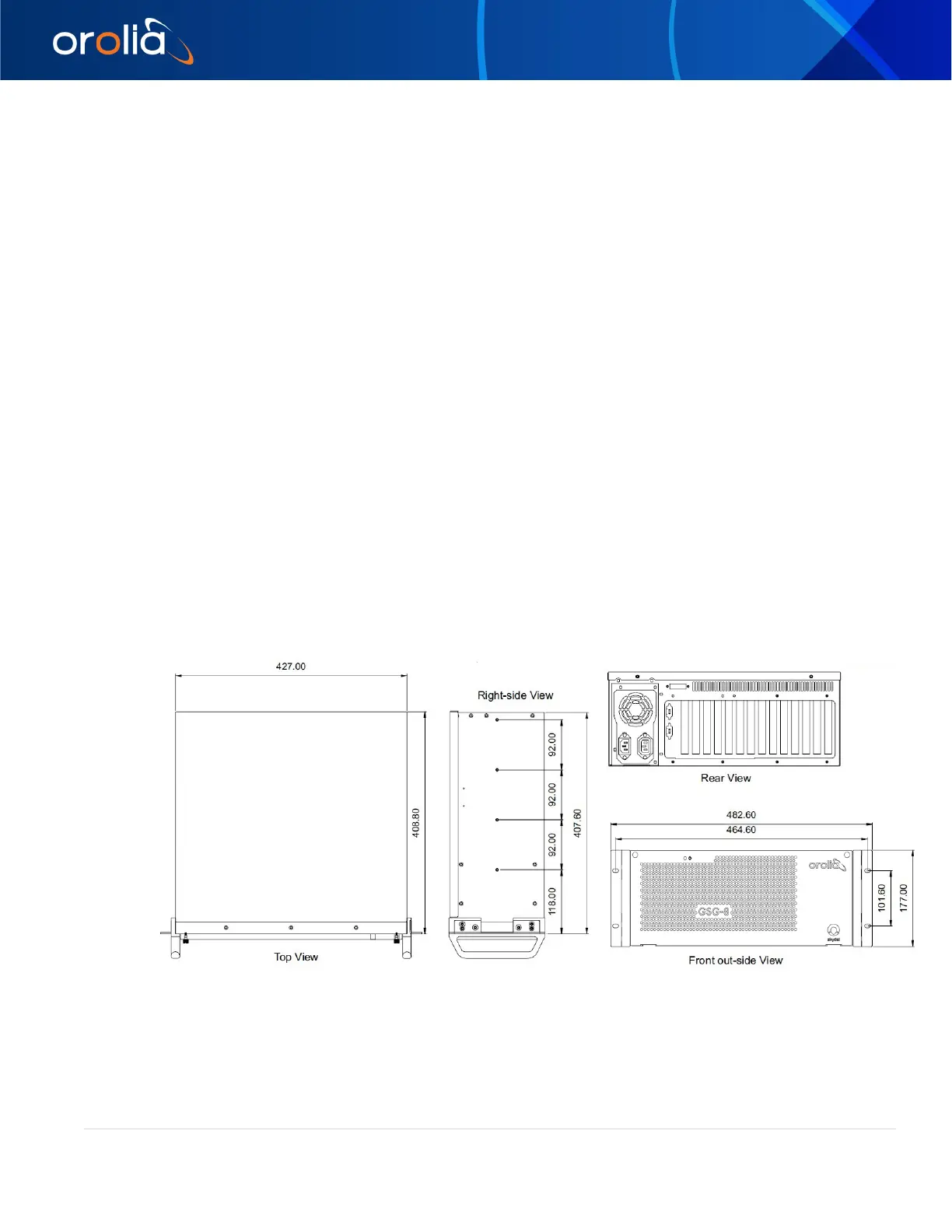
Mechanical:
Size: 4U Depth: 16 in (40.6 cm) Width: 19 in (48 cm)
Weight: 39.6 lbs. (18kg) Height: 7 in (18 cm)
Certifications:
Safety: EN/IEC 61010-1:2010
Emissions: EN 61326-1:2013, AS/NZ CISPR 32:2015, EN 55011:2009/A1:2010, EN61000-3-2:2014,
EN 61000-3-3:2013, FCC Part 15 Subpart B Class A ICES-003 Issue 6.
 Loading...
Loading...