P
r
o
t
e
c
t
e
d
b
y
c
o
p
y
r
i
g
h
t
.
C
o
p
y
i
n
g
f
o
r
p
r
i
v
a
t
e
o
r
c
o
m
m
e
r
c
i
a
l
p
u
r
p
o
s
e
s
,
i
n
p
a
r
t
o
r
i
n
w
h
o
l
e
,
i
s
n
o
t
p
e
r
m
i
t
t
e
d
u
n
l
e
s
s
a
u
t
h
o
r
i
s
e
d
b
y
V
o
l
k
s
w
a
g
e
n
A
G
.
V
o
l
k
s
w
a
g
e
n
A
G
d
o
e
s
n
o
t
g
u
a
r
a
n
t
e
e
o
r
a
c
c
e
p
t
a
n
y
l
i
a
b
i
l
i
t
y
w
i
t
h
r
e
s
p
e
c
t
t
o
t
h
e
c
o
r
r
e
c
t
n
e
s
s
o
f
i
n
f
o
r
m
a
t
i
o
n
i
n
t
h
i
s
d
o
c
u
m
e
n
t
.
C
o
p
y
r
i
g
h
t
b
y
V
o
l
k
s
w
a
g
e
n
A
G
.
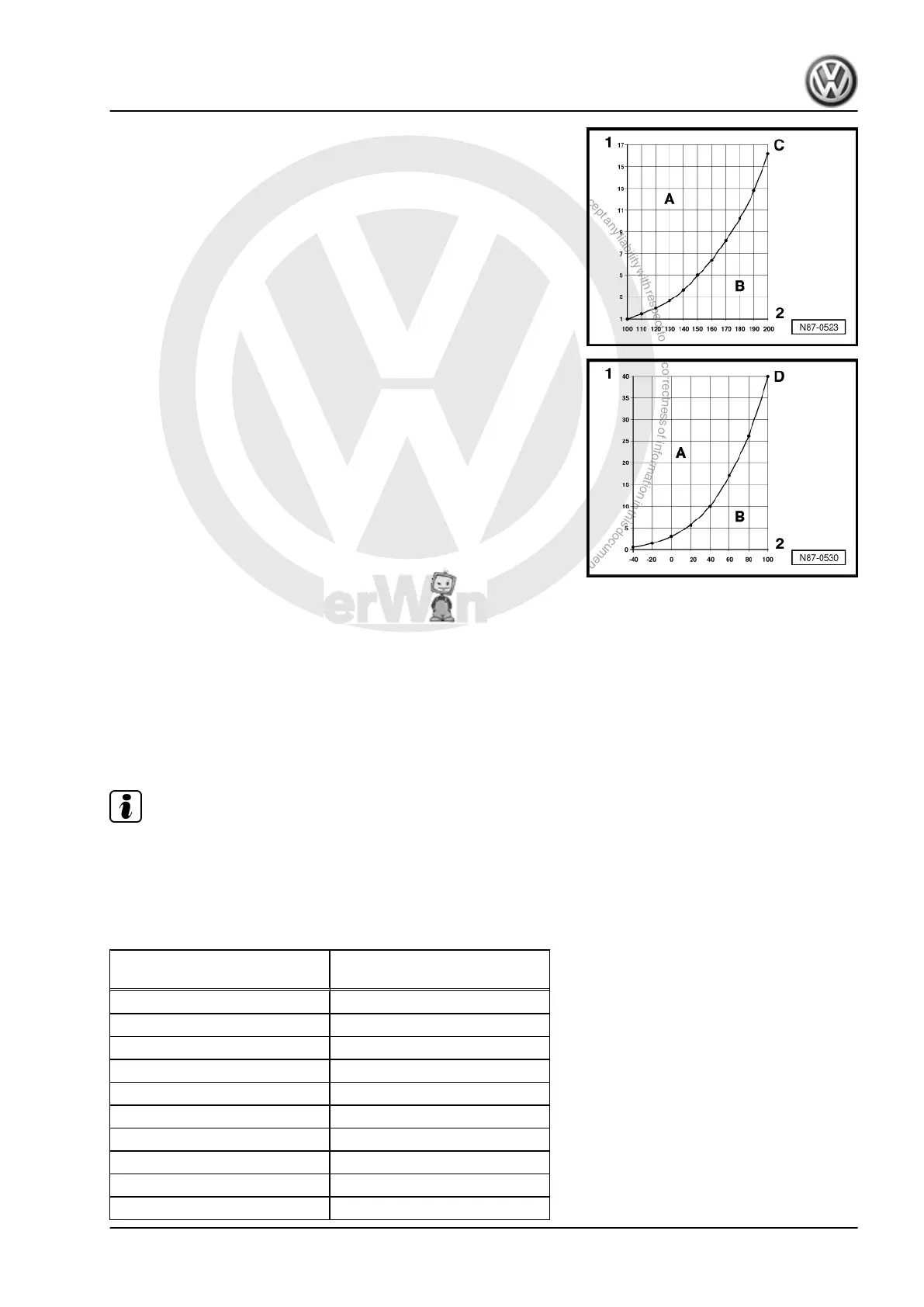
Vapour pressure curve for water
A - Liquid
B - Gaseous
C - Vapour pressure curve for water
1 - Pressure on the liquid in bar (absolute)
2 - Temperature in °C
Vapour pressure curve for refrigerant R134a
A - Liquid
B - Gaseous
D - Vapour pressure curve for refrigerant R134a
1 - Pressure on the liquid in bar (absolute)
2 - Temperature in °C
1.4 Vapour pressure table for refrigerant
R134a
The vapour pressure table for each refrigerant is published in the
literature for refrigeration engineers. This table shows the vapour
pressure exerted on the liquid column in the container for a given
temperature of the container.
Since a characteristic vapour pressure table is known for every
refrigerant, one can determine what refrigerant is present by
measuring pressure and temperature.
Note
Absolute pressure means that 0 bar corresponds to an absolute
vacuum. The normal ambient pressure (positive pressure) corre‐
sponds to 1 bar absolute pressure. On most pressure gauges, a
reading of 0 bar corresponds to an absolute pressure of one bar
(which is confirmed by the existence of a -1 bar marking beneath
the 0 scale marking).
Temperature in °C Pressure in bar (positive pres‐
sure) R134a
-45 -0.61
-40 -0.49
-35 -0.34
-30 -0.16
-25 0.06
-20 0.32
-15 0.63
-10 1.00
-5 1.43
0 1.92
Amarok 2011 ➤ , Beetle 2012 ➤ , Bora 1999 ➤ , CC 2010 ➤ , CC 2012 ➤ , ...
Air conditioning system with refrigerant R134a - Edition 10.2014
1. General notes on air conditioning systems 3

 Loading...
Loading...











