JOHNSON CONTROLS6
FORM 150.68-EG1 (0212)
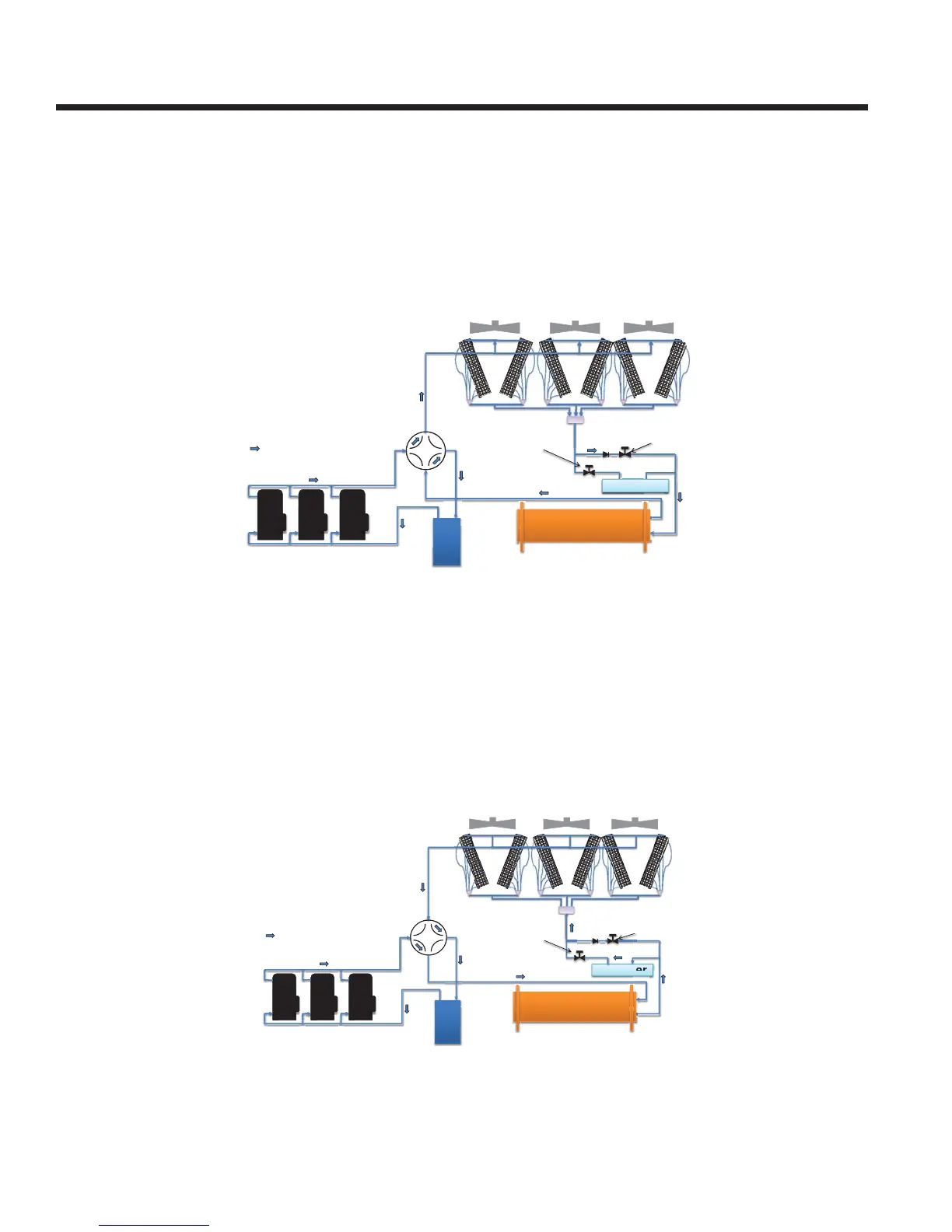
Refrigerant Flow Block Diagrams
COOLING MODE
Low pressure liquid refrigerant enters the heat exchanger and is evaporated and superheated by the heat energy absorbed
from the chilled liquid. Low pressure vapor enters the compressor, via the four-way reversing valve and accumulator,
where pressure and superheat are increased. The high pressure vapor is fed to the ambient coils and fans - via the four
way reversing valve which changes the direction of the refrigerant fl ow and the function of the heat exchanger to cooling
mode - where heat is removed. The fully condensed and subcooled liquid passes through the expansion valve (cooling)
where pressure is reduced and further cooling takes place before returning to the heat exchanger.
HEATING MODE
Liquid refrigerant enters the ambient coil and is fully evaporated and superheated by the energy absorbed from the ambient
air. Low-pressure superheated refrigerant vapor passes through the four-way reversing valve - which changes the direction
of the refrigerant fl ow and the function of the heat exchanger to heating mode - and the accumulator and enters the
compressor, where pressure and superheat are increased. High-pressure superheated refrigerant vapor enters the refrigerant
to water plate heat exchanger where heat is rejected to the water. The high-pressure liquid refrigerant, leaving the heat
exchanger passes through the liquid receiver and enters thermostatic expansion valve (heating) where the refrigerant and
subsequently cooled before returning to the ambient coil.
Defrost Operation
When ice builds up on the ambient coils defrost is initiated by operating the machine in a cooling mode. Each of the two
refrigerant circuits will be defrosted one at a time. When defrost is operative the circuit operating in heating mode is in balance
with the circuit operating in defrost (cooling). Therefore, heat energy is not removed from the hot water system.
Ambient Coils
(Condenser)
Refrigerant flow
Compressors
Heat Exchanger
(Evaporator)
4-way valve
Accumulator
Receiver
TXV
(heating)
TXV
(cooling)
Ambient Coils
(Evaporator)
Refrigerant flow
Compressors
Heat Exchanger
(Condenser)
4-way valve
Accumulator
Receiver
TXV
(heating)
TXV
(cooling)

 Loading...
Loading...