BSD-340-user-guide-eng, Doc. 1004474-2, 2020-09-18,
Autronica Fire and Security AS
Page 13
3.7 Raise loop and store topology in loop driver
a. Type #si and enter in the Command input window to raise loop and save topology to
EEPROM
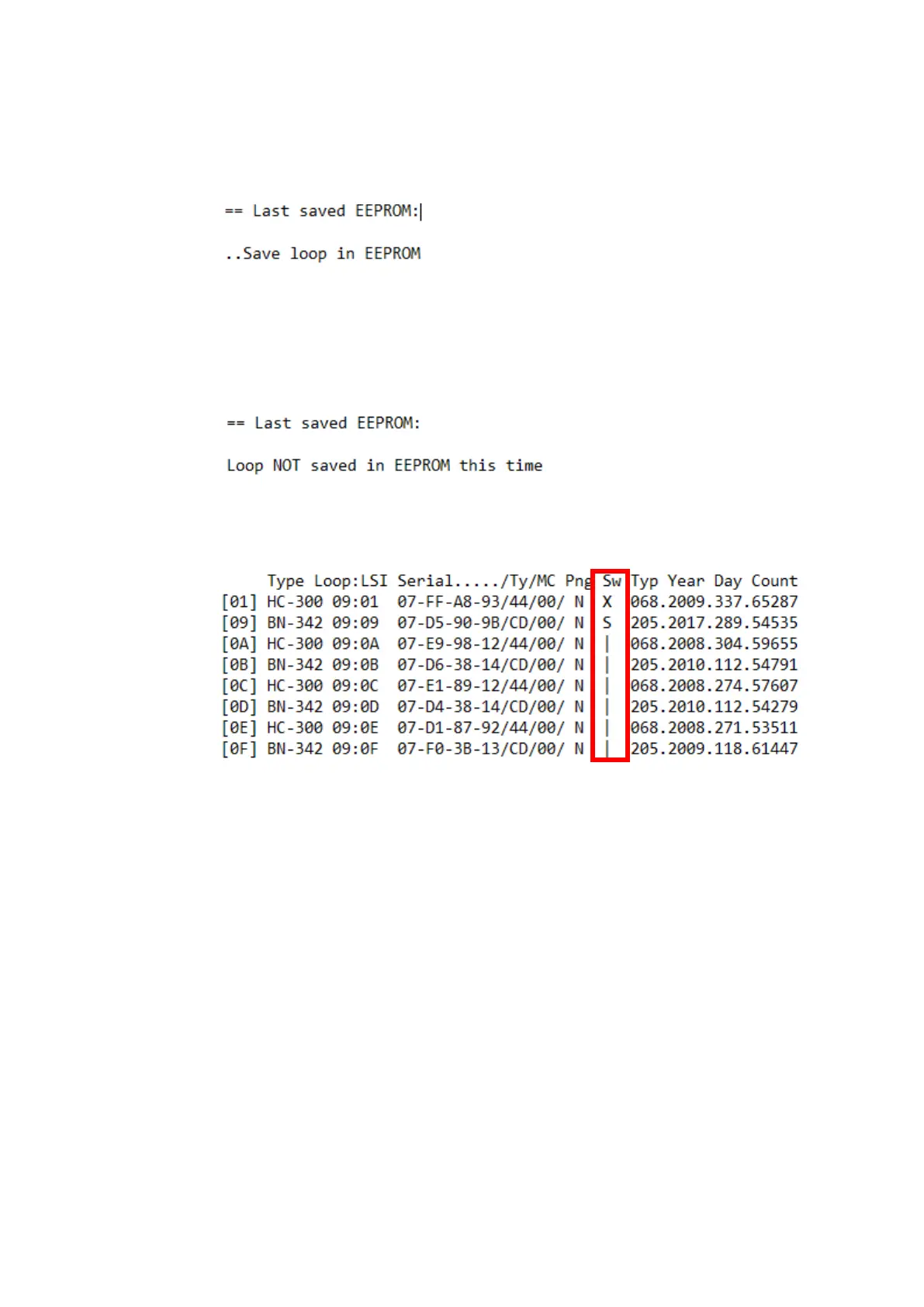
b. The loop raise should end with a message like this
If loop is successfully saved to EEPROM, proceed to step d.
c. Resolving failed save of topology
i. If there are devices on the loop which fail to start, or that there are loop breaks on the
loop, a fail message is reported: “Loop Not saved in EEPROM this time” will be printed
in terminal (see figure below)
ii. Since the powerloop requires to have a saved topology to work, use the print
topology #prntop command to get a printout of the topology and fault messages to
help resolve any faults.
iii. Note the symbol | in the Sw column. Different symbols may be used:
| = closed switch, X = open switch, ? = unit missing, S = Short circuit
In the example above there is a short between detector 1 and 2. In the SW column
the first detector states an X, which means that it has not been able to close the loop
switch. On detector 2 it is stated an S for short (towards detector 1)
iv. Investigate the loop and connections and resolve any faulty wiring or connections.
v. Type #si and enter in the Command Input Window to try a loop raise again after you
have investigated faults indicated on the topology after the last run of "si.
d. After loop has been successfully saved you can verify the saved loop, Type #prntop and
enter in the Command input window to list saved topology (output as in figure below)

 Loading...
Loading...