5.6 Operators
The following are the operators used for calculations, which involves variables.
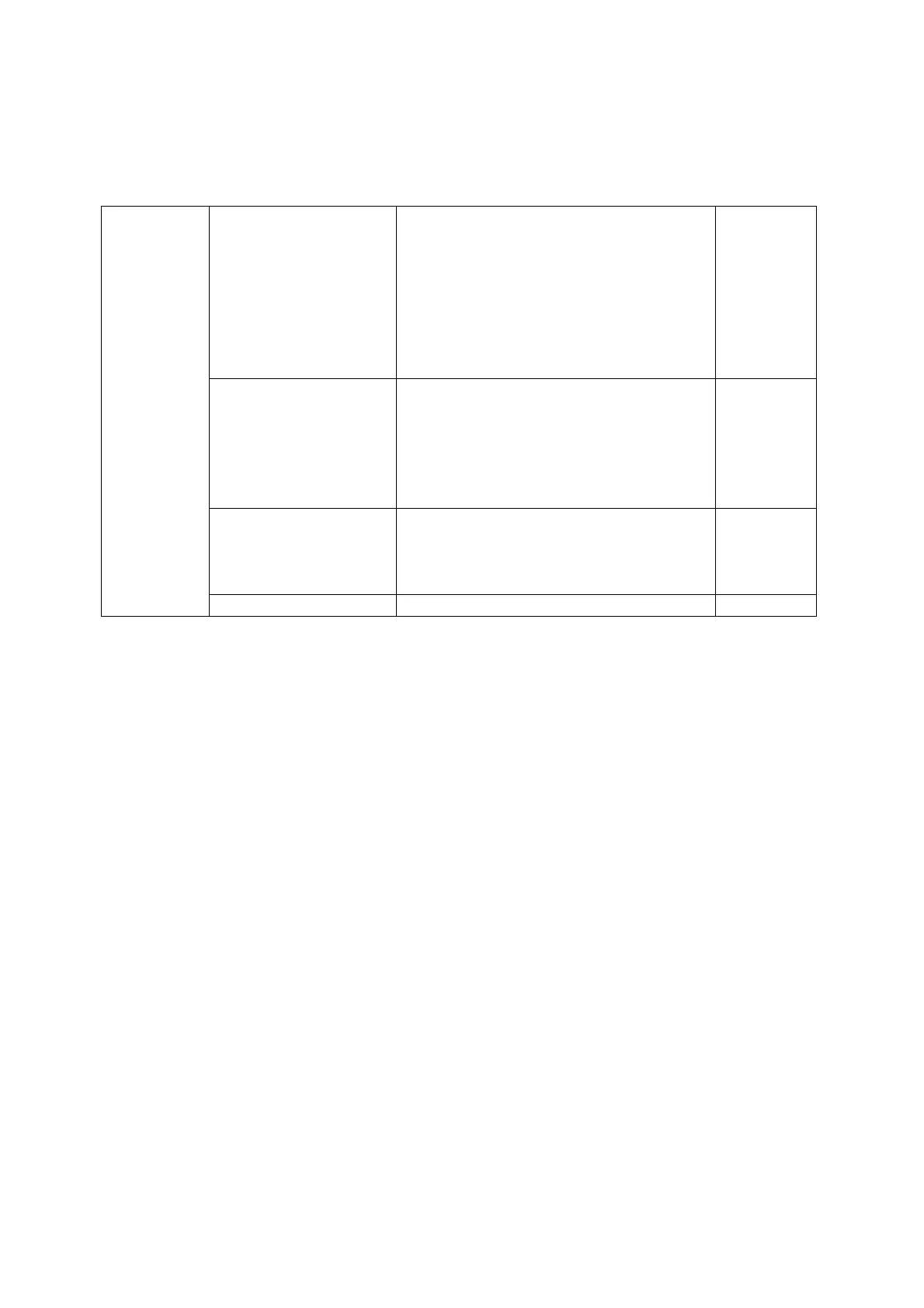
Signs
Addition
Subtraction
Multiplication
Division
Power
Integer division
Integer remainder of integer division
Equal to
Does not equal
Less than
Grater than
Less than or equal to
Grater than or equal to
=
<>, ><
<
>
=>, <=
=>, >=
Negation
Logical product
Logical sum
Exclusive OR
Relational operators
Relational operations can be performed only when the operators are both strings or
both numeric values.
With strings, character codes are compared one-by-one from the beginning of the
strings. This is to say that the first position of string A is compared to the first position
of string B, the second position of string A with the second position of string B, etc.
The result of the comparison is based upon the character codes of the first difference
between the strings detected, regardless of the length of the strings being compared.
EXAMPLES:
A<B (character code for A less than that for X)
A>B (character code for X greater than that for A)
A result of -1 is returned when the result of a relational operation is true (condition
met), while 0 is returned when the return is false (conditions not met)
EXAMPLE:
10 PRINT 10>3 -1 returned because 10>3 is true
20 PRINT 7>1 0 returned because 7<1 is false
30 PRINT “ABC”=3XYZ” 0 returned because ABC=XYZ is false
40 END
 Loading...
Loading...