116 Cisco LAN Switching Configuration Handbook
1/1
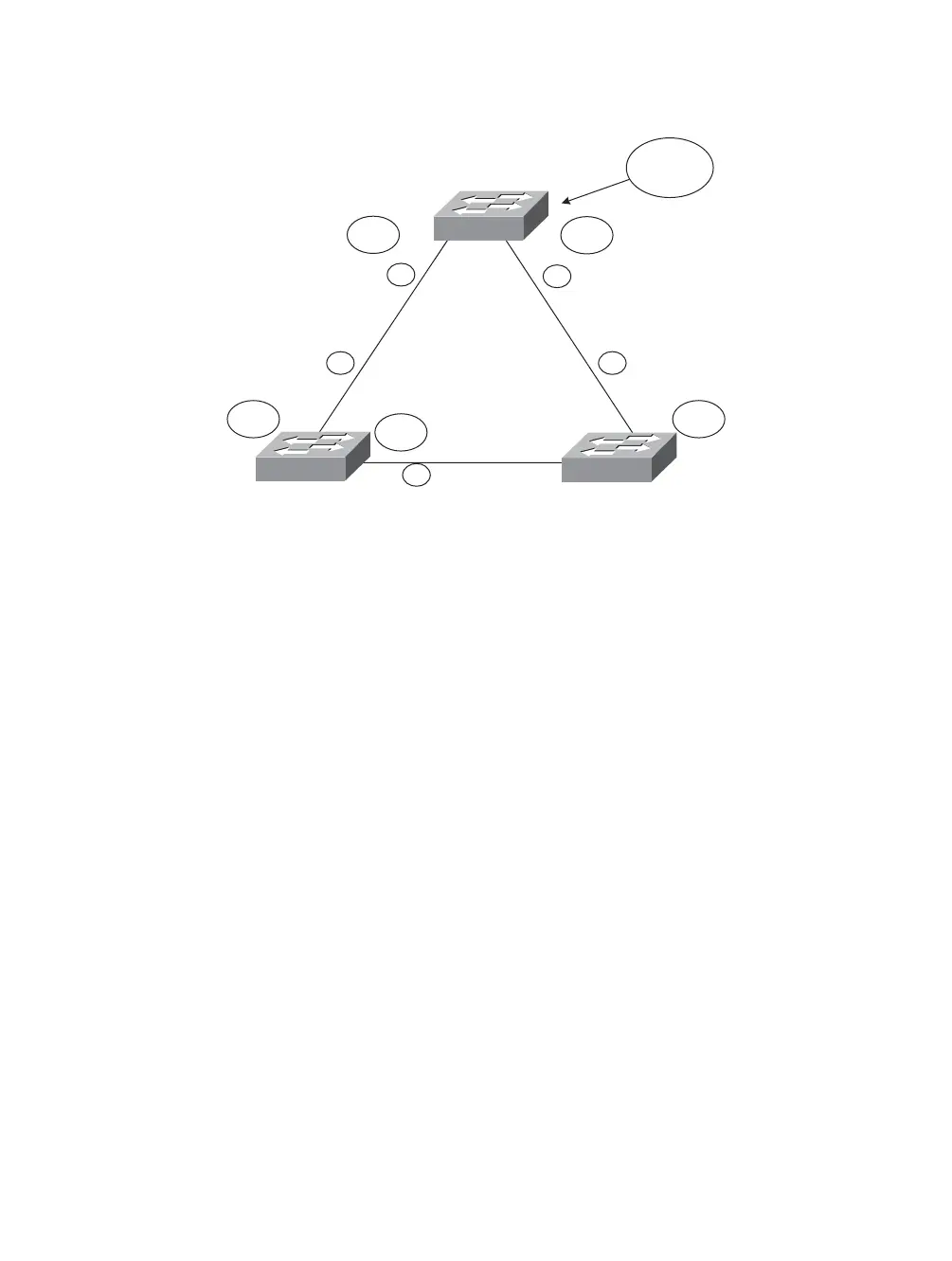
Catalyst A
Catalyst B Catalyst C
Root Path Cost = 0+19
19
19
19
1/2
32768:00-00-00-00-00-0a
32768:00-00-00-00-00-0b 32768:00-00-00-00-00-0c
1/1
1/2
1/1
1/2
Root
Bridge
DP
DP
Root Path Cost = 0+19
RP RP
Root Path Cost =
0+19+19
Root Path Cost =
0+19+19
DP
X
F
F
F
F
F
Figure 7-1 Network Diagram for the STP Operation Example
3. The designated ports are chosen: By definition, all ports on the root bridge become
designated ports for their segments. Therefore, ports 1/1 and 1/2 on Catalyst A are
designated. Catalyst B port 1/2 and Catalyst C port 1/2 share a segment, requiring
that one of them become designated. The root path cost for each of these ports is
0+19+19 or 38, resulting in a tie. The lowest-sending BID breaks the tie, so Catalyst
B (having the lowest MAC address of the two) port 1/2 becomes the designated
port.
4. All ports that are neither root nor designated ports are put in the blocking state:
The only remaining port that is neither root nor designated is Catalyst C port 1/2.
This port is moved to the blocking state (as shown by the X in the figure).
7-2: STP Configuration
1. (Optional) Enable or disable STP:
(global) [no] spanning-tree [vlan vlan]
STP is enabled by default on VLAN 1 and any newly created VLANs. Without a
specified VLAN, STP is enabled or disabled on all VLANs. Be aware that if STP is
disabled, bridging loops are not detected and prevented. You should always enable
STP.
2. (Optional) Set the STP mode for the switch:
spanning-tree mode {pvst | mst | rapid-pvst}
 Loading...
Loading...











