Chapter 7 Motion Control ASDA-A2
Revision February, 2017 7-13
7.6 The Position Unit of PR Mode
The position data of PR mode is represented by PUU (Pulse of User Unit). It is also the proportion
between the controller position unit and the internal position unit of the servo drive, which is the so-
called electronic gear ratio of the servo drive.
1. The position unit of the servo drive (pulse): Encoder unit: 1280000 (pulse/rev), which will
not change.
2. User unit (PUU): The unit of the controller.
P pulse per revolution (PUU/rev), the gear ratio should set as:
GEAR_NUM (P1-44) / GEAR_DEN (P1-45) = 1280000 / P
7.7 Description of Register in PR Mode
1. Position register of PR mode: All is represented in PUU (Pulse of User Unit).
2. Command register (monitoring variable 064): Command termination register Cmd_E. It
represents the absolute terminal coordinate of position command.
3. Command output register (monitoring variable001): Cmd_O; it represents the absolute
coordinate from the current output command.
4. Feedback register (monitoring variable 000): Fb_PUU; it shows the absolute feedback
position of the motor.
5. Deviation register (monitoring variable 002): Err_PUU; it is the deviation between the register
from command output and feedback register.
6. In PR mode, either in operation or stop status, it satisfies the condition of Err_PUU = Cmd_O -
Fb_PUU.
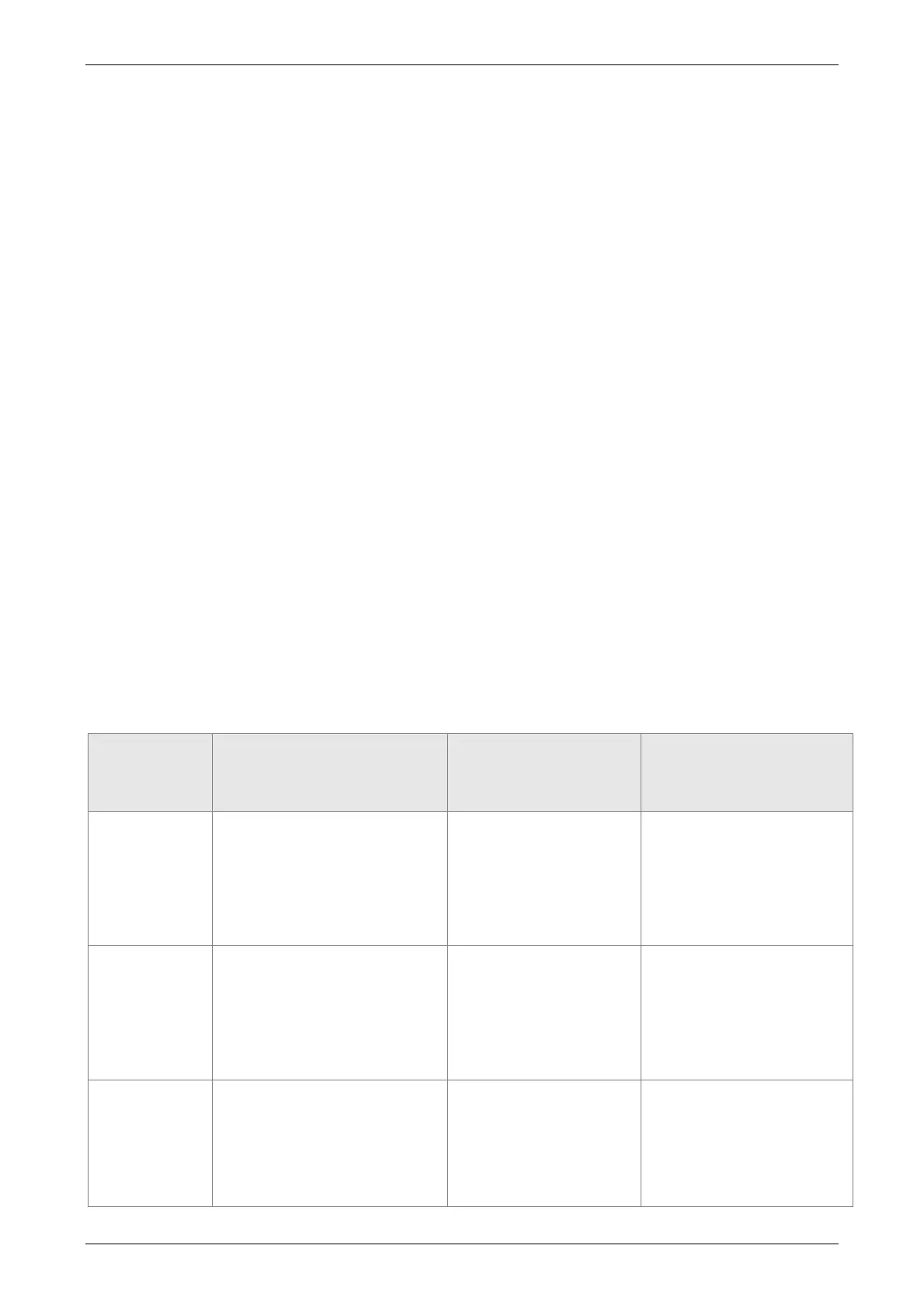
Influence brought by position command:
Type of
Command
When issuing the command
=>
=>When command is
executing=>
=> Command is
completed
Absolute
Positioning
Command
Cmd_E = command data
(absolute)
Cmd_O does not change.
DO.CMD_OK is OFF
Cmd_E does not
change.
Cmd_O continuously
output
...
Cmd_E does not change.
Cmd_O = Cmd_E
DO.CMD_OK is ON
Incremental
Positioning
Command
Cmd_E+= command data
(incremental)
Cmd_O does not change.
DO.CMD_OK is OFF
Cmd_E does not
change.
Cmd_O continuously
output
...
Cmd_E does not change.
Cmd_O = Cmd_E
DO.CMD_OK is ON
Issue the
command of
DI:STP to
stop the
command
Cmd_E does not change.
Cmd_O continuously output
DO.CMD_OK is
unchangeable
Cmd_E does not
change.
Cmd_O stops
according to the
deceleration curve
Cmd_E does not change.
Cmd_O = position after
stop
DO.CMD_OK is ON

 Loading...
Loading...











