Chapter 4 WiringMS300
23
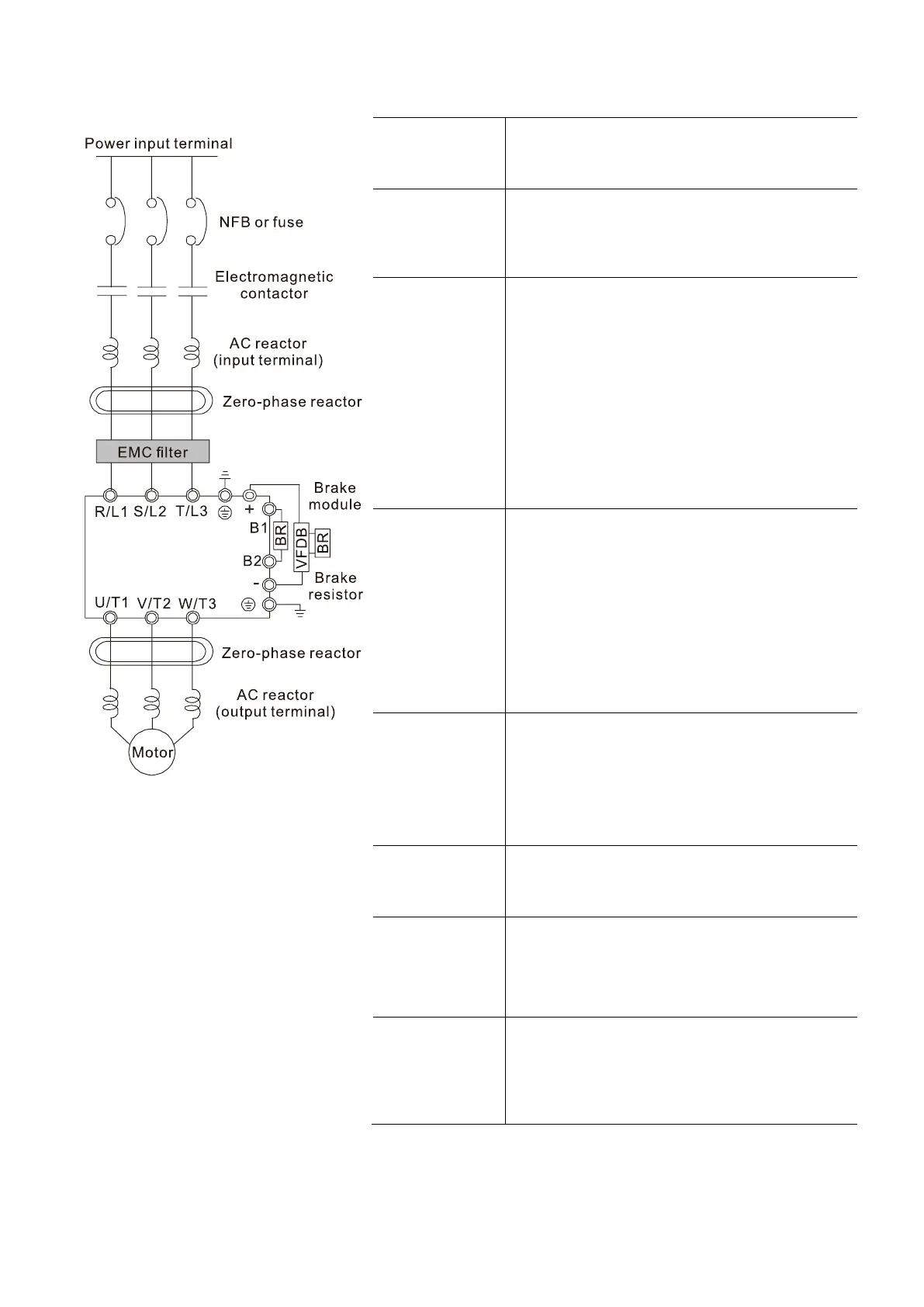
4-1 System Wiring Diagram
Supply power according to the rated power
specifications indicated in the manual (refer to
Chapter 9 Specification).
There may be a large inrush current during
power on. Refer to Section 7-2 NFB to select a
suitable NFB or Section 7-3 Fuse Specification
Chart.
Electromagnetic
contactor
Switching the power ON/OFF on the primary
side of the electromagnetic contactor can turn
the drive ON/OFF, but frequent switching can
cause machine failure. Do not switch ON/OFF
more than once an hour.
Do not use the electromagnetic contactor as the
power switch for the drive; doing so shortens the
life of the drive.
Refer to Section 7-2 Magnetic Contactor / Air
Circuit Breaker to select the electromagnetic
contactor that meets your requirement.
AC reactor
(input terminal)
When the main power supply capacity is greater
than 500 kVA, or when it switches into the phase
capacitor, the instantaneous peak voltage and
current generated may destroy the internal
circuit of the drive.
It is recommended that you install an input side
AC reactor in the drive. This also improves the
power factor and reduces power harmonics. The
wiring distance should be within 10 m. Refer to
Section 7-4 AC/DC Reactor for details.
Used to reduce radiated interference, especially
in environments with audio devices, and reduce
input and output side interference.
The effective range is AM band to 10 MHz.
Refer to Section 7-5 Zero Phase Reactors for
details.
Can be used to reduce electromagnetic
interference. Refer to Section 7-6 EMC Filter for
details.
Brake module
&
Brake resistor
(BR)
Used to shorten the deceleration time of the
motor. Refer to Section 7-1 Brake Resistors and
Brake Units Used in AC Motor Drives for details.
AC reactor
(output terminal)
The motor cable length affects the size of the
reflected wave on the motor end. It is
recommended that you install an AC output
reactor when the motor wiring length exceeds
the value listed in Section 7-4.
 Loading...
Loading...











